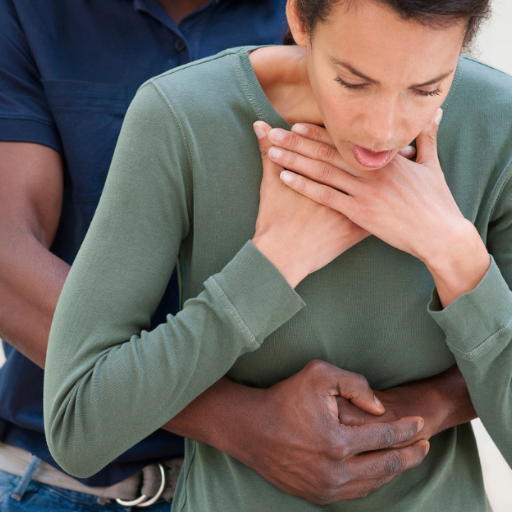

Pregnant women are particularly susceptible to choking emergencies, which pose serious health risks. These situations require immediate action, which is informed so that the mother and the unborn child are kept safe. This guide details how to administer CPR to pregnant people. Understanding pregnancy anatomy and required first aid modifications will help the readers learn how to assist safely in choking cases. This article addresses the most critical procedural modifications, tips of utmost importance, and precise measures developed to resolve these issues without fear or hesitation.
What are the emergency steps for choking in pregnant women?
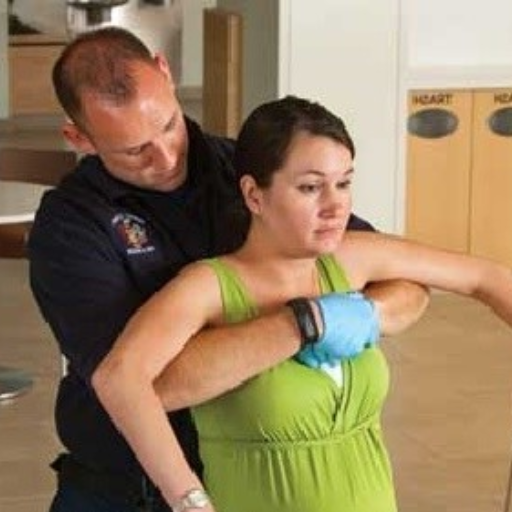
- Evaluate the Choking Incident: First, quick body scans should be done to check if the person can speak, breathe, or show any form of choking sign, such as covering their throat.
- Get Emergency Assistance: Make an emergency call to seek medical help immediately. This step should be done at once.
- Perform Your Chest Thrusts:
- Stand Behind The Person, Making Sure To Wrap Your Arms Around The Person’s Chest Rather Than Abdomen To Prevent Any Possible Injury To Them.
- Form A Fist And Put It Over The Center Of The Sternum.
- Using The Other Hand To Grab The Fist And Then Apply Force Inwards And Upwards Simultaneously.
- Repeat The Fist Thrust Until The Airway Is Clear Or The Person Becomes Unconscious.
- If The Person Becomes Unconscious, Make Sure To Place Them On The Ground Realistically. If You’re Educated In CPR, Begin The Procedure And Perform Chest Compressions While The Paramedics Are Out To Act.
How do you recognize a choking pregnant woman?
Choking while pregnant inflicts excellent pain on the woman, and for someone who is incapacitated, be it in range of abilities such as speaking or moving, needs to be observed. Below are some key indicators to keep an eye on:
- Ineffective Coughing: The woman in distress is not likely to be coughing at all and would rather be completely absent at the point in time, suggesting that her respiratory tract is more or less fully obstructed.
- Silent Distress: Speaks or produces sound not at all because the obstruction hints towards choking.
- Universal Distress Signal: For a person possessing even an iota of common sense, grabbing one’s neck with one or both hands should ring a bell.
- Cyanosis: Evidence of a woman’s lips, skin, or fingernails not being particularly striking means that tissues are deprived of adequate oxygen.
- Panic Or Agitation: The unresponsive person devoid of any conscious behavior is likely to be frightened or distressed for an extended point of time due to the inability to breathe, which might be shocking, to say the least.
Making an early attempt to recognize these signs potentially helps provide prompt aid, drastically increasing chances for afflicted women.
Why should you avoid abdominal thrusts?
In certain situations, abdominal thrusts, or the Heimlich maneuver, are best avoided as they can potentially cause harm. Pregnant women, for instance, should not be given abdominal thrusts as they can harm the fetus. In this scenario, a thrust to the chest is suggested. Obese persons may also have difficulty with thrusts, considering the extra thick layers of tissue; therefore, a thrust to the chest may be more effective in relieving airway obstruction.
Moreover, someone may have an increased risk with the above procedures if they have a pre-existing medical condition, such as a history of abdominal surgery, aneurysms, or osteoporotic changes. Abdominal thrusts can cause blunt trauma to internal organs, fractured ribs, and other injuries. Also, scientific choking intervention studies propose different means of back blows or chest thrusts might be as efficient and safer for patients depending on the circumstances, hence why it is increasingly essential for those in the medical field to focus on analyzing the situation more to adapt the procedures to mitigate injuries.
What are the correct chest thrust techniques?
Based on my investigations, correct execution of chest thrust skills necessitates great precision, focusing on safety and maneuverability. The first step is to place yourself directly behind the person who is choking, then encircle them with your arms at chest level. Now, standing behind the choking individual, make one of your hands into a fist and position it on the midline of your chest, targeting the sternum area. With the first securing the position, place your other hand on top of your fist and grip firmly. You are required to control backward thrusts that are angled slightly inwards and upwards. Each thrust should be forceful but controlled to generate enough pressure to dislodge the obstruction. It is essential not to push the area beneath the chest bone since this will significantly increase the possibility of internal injury. Change this skill if the person’s size or body condition demands it, but always ensure that emergency services are called when the obstruction can’t be removed. Achieving confidence in performing this procedure will take proper training, but it will allow you to save someone’s life.
How does the American Red Cross recommend handling a choking pregnant woman?
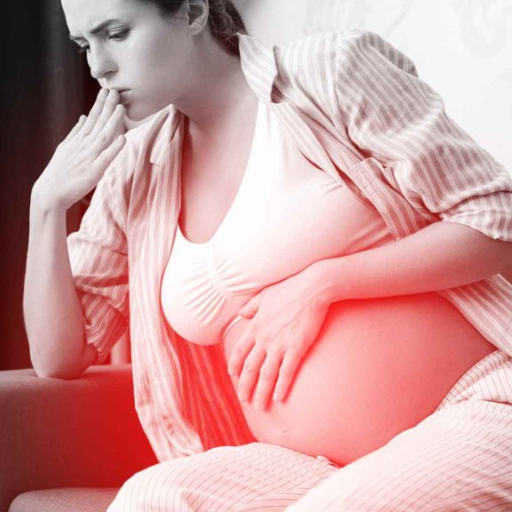

To lessen the chance of injuring the fetus in a pregnant woman who is choking, the American Red Cross recommends using chest thrusts instead of abdominal thrusts. Place your arms under the patient’s armpits while standing behind them. Position your fist at the midpoint of their sternum. Place your other hand over your fist, then make rapid, firm, inward, and upward thrusts. Continue performing verbal until the blockage is removed or the person loses consciousness. If the person is unresponsive, start CPR right after calling emergency services. Like with any medical procedure, this technique has to be taught to do it correctly.
What does American Red Cross training include?
The American Red Cross training offers a variety of taught skills and procedures that apply to different scenarios, such as CPR (Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation), AED (Automated External Defibrillator) usage, and first aid. These also include choking emergency response for adults, children, and infants. The regimens make sure to make situational adaptations, too, like chest thrusts for pregnant women and other methods for people of different sizes or conditions.
Technical parameters include performing CPR at a rate of 100-120 compressions per minute and a depth of 2 inches for adults. An automatic resuscitator must maintain the uninterrupted sequence of 30 chest compressions followed by two rescue breaths. During AED use training, they must learn the appropriate position of pads in the upper right and lower left sides of the chest and understand when the device is talking to them. Children of different ages and sizes get special guidelines for choking emergencies, ensuring all-round safety.
These courses have video illustrations, practical demonstrations, and written exams to ensure students can handle actual medical situations. Certification is frequently issued for two years, and during that period, it is recommended to use ‘refresher’ tools to retain valuable skills for as long as possible.
How to use back blows for a pregnant woman?
I place the pregnant woman in a position so that she is slightly bent forward at the waist so that her airways can quickly clear, using gravity to her advantage. I then hit the area between her shoulder blades with the heel of my hand, firmly and with force, while ensuring that each blow was decisive but not excessive. If the obstruction still is not clear, I implement pregnancy-specific chest thrusts that will not harm the fetus but, rather, aid in dislodging the obstruction.
What to do if the choking victim becomes unresponsive?
If a choking victim becomes unresponsive, act immediately by following these steps:
- Call for Emergency Services – Dial emergency medical assistance (e.g., 911) immediately for professional help. Do not delay this step.
- Perform CPR:
-
-
- Check for Breathing – Look, listen, and feel for normal breathing for no longer than 10 seconds. If the victim is not breathing, begin CPR.
- Chest Compressions – Perform 30 chest compressions at a rate of 100-120 compressions per minute and a depth of at least 2 inches (5 cm) for adults. Allow the chest to recoil between compressions fully.
- Open the Airway – After compressions, open the airway by tilting the head backward and lifting the chin.
- Attempt Rescue Breaths – Provide two rescue breaths. If the chest does not rise, reposition the airway and try again. If the airway remains blocked, continue CPR.
-
- Check the Airway Between Compressions – Before delivering breaths, look into the victim's mouth for any visible obstruction. If an object is seen, use a finger sweep to remove it carefully, ensuring not to push it further down.
- Continue Until Help Arrives – Persist with the CPR cycle (30 compressions, two breaths) until emergency responders take over or the victim shows signs of recovery, such as breathing or movement.
These instructions are aligned with current guidelines provided by leading health and emergency organizations, ensuring effective action during a life-threatening scenario.
How can first aid help save lives in choking emergencies?

Choking situations are critical because there is little to no oxygen flow to the body. First Aid is important because it serves the dual purpose of providing urgent medical assistance and preserving the person’s life before they can receive professional medical attention. Specific methods that remove blockages from the airways, such as back blows, chest thrusts, and CPR, could mean the difference between life and death. When done correctly, these procedures will almost always guarantee that oxygen reaches every critical body region, including the brain. The use of these methods dramatically increases the chances of life after injury.
Why is it essential to clear the airway?
Ensuring one clears an airway is critical to ensure oxygen can reach the lungs, brain, and other vital organs. When a person does not have a clear airway, it can lead to oxygen deprivation within the body. This can cause severe brain injury or death in mere minutes. By addressing these blocks promptly, I can ameliorate severe damage and ensure that the person’s condition is stabilized until professional medical help is provided.
When to perform CPR and AED?
When a person is unresponsive and not breathing or only gasping for air, CPR and AED should be used right away. To begin with, I start with performing CPR to maintain blood circulation, and as soon as an AED becomes available, I use it to give the necessary shock if recommended. This is a race against the clock, whereby every second without taking action drastically decreases the chances of the patient surviving.
What role does essential life support (BLS) play?
Essential life support (BLS) is pivotal in sustaining life since it provides life-saving care. BLS focuses on ensuring that the airway is clear, effective breaths are given, and blood is supplied to the body through quality chest compressions. It aims to maintain the patient's health status while help is on the way so that the probability of survival increases and long-term damage is limited. With my skills, I can perform BLS effectively, pumping oxygenated blood into the brain and vital organs until aid arrives.
How to provide general care to a choking pregnant woman?

To assist a pregnant woman who is choking, it is imperative to modify the basic abdominal thrusts for her condition. Instead of disrupting the pregnant woman’s abdomen by performing abdominal thrusts, do chest thrusts. Stand behind the patient so that your arms are under her armpits with your hands clasped on her chest at the center of the sternum. Perform strong thrusts inwards and upwards until the obstruction is removed or the choking victim loses consciousness. In case the pregnant woman passes out, chest compressions for BLS should be initiated without any delay. Always remember to contact emergency help as soon as possible.
Why should you place one hand on the person's back?
When performing first-aid for choking, stabilization support is provided by placing one hand on the person’s back. This aids in beating balance and anchors the person when performing closed fist-back blows so they do not tip over. For example, when performing five blows to the back above the mid scapula correctly, keeping a hand on the back prevents the person from losing balance and helps give force where it needs to be to remove the obstruction from their throat. It also decreases the chances of harm to the person choking during this maneuver. Your supporting hand should always be placed so that it helps you to steer at all times.
How do you wrap your arms around the person correctly?
To wrap your arms around the person correctly during a choking relief procedure, follow these steps:
- Positioning: Stand directly behind the person to ensure complete control. Maintain a stable stance to support both yourself and the choking individual.
- Placement of Arms: Wrap your arms securely around the person's waist. Ensure your hands are positioned in the midline of your abdomen for the practical application of force.
- First Position:
-
-
- Form a fist with one hand, placing the thumb against the person's abdomen.
- The fist should be positioned just above the navel and well below the sternum to target the diaphragm effectively.
-
- Hand Alignment: Grasp your fist with the other hand to create a firm grip, allowing maximum control and strength application.
- Application of Force:
-
-
- Perform quick, upward thrusts using controlled force directed inward and upward (Heimlich maneuver).
- Each thrust should be deliberate and forceful enough to generate pressure to dislodge the airway obstruction.
-
These parameters should be adhered to carefully to ensure safety and efficacy. Avoid applying excessive force, as this could lead to internal injuries, especially if the person is frail or a child. Continuously monitor their reaction throughout the procedure and seek emergency assistance if necessary.
What should you do if the foreign object is visible?
If the foreign object causing the obstruction is visible in the person's mouth, do not attempt blind sweeps or actions that may push the object further into the airway. Instead, follow these steps:
- Positioning:
-
-
- Ensure the person is sitting or standing upright to keep their airway accessible.
- If the individual is responsive and cooperative, instruct them to remain calm and avoid unnecessary movement.
-
- Visual Inspection:
-
-
- Open the person’s mouth carefully and ensure proper lighting to locate the object.
- Only proceed if you can clearly see the object and safely remove it without risk.
-
- Removal:
-
-
- Use your index finger and thumb to grasp and remove the visible object gently. Unless you are appropriately trained, avoid using force or unnecessary tools.
- If tweezers or similar implements are required, ensure hygienic and careful use to avoid injury.
-
- Caution:
-
-
- If the object is tightly lodged or cannot be reached safely, cease attempts and focus on maintaining airflow by seeking professional medical assistance immediately.
- Monitor for signs of worsening obstruction, such as the inability to breathe, speak, or cough effectively.
-
Always prioritize professional intervention if the situation escalates or removal attempts are unsuccessful. This procedure reduces the risk of complications and ensures the safety of the individual.
Why is it critical to stay informed about emergency choking procedures?

It is essential to constantly make yourself knowledgeable on emergency choking procedures to assess how to tackle dangerous situations effectively. Airflow obstruction can lead to oxygen deprivation, which, if not attended to promptly, may be fatal. Knowing the correct procedures for delivering back blows or abdominal thrusts and how to seek medical attention can address and avert dire situations. In emergencies, learning how to counter situations with back thrusts helps minimize stress levels, which is essential when every second matters.
How can staying up to date with training help?
Regular training guarantees that individuals maintain and improve their proficiency in managing choking emergencies. Practicing keeps muscle memory in place and reinforces correct applications of the technique, such as the proper abdominal and back thrusts, force, and position. Also, recent training utilizes best practices and guidelines to make responses relevant to contemporary medicine. For example:
- Application of Force in Abdominal Thrusts: The obstruction is effectively expelled using about ten to 20 pounds of force under the rib cage and above the navel.
- Have Knowledge Updated: It is suggested that CPR and first-aid skills, including choking techniques, be refreshed not more than once every two years or as guidelines change.
- Improvement of Basic Technique: Training is revised to adapt to people's needs, such as children or pregnant women/effective and safe intervention.
The remainder of this paragraph will focus on confidently assisting responders with multi-phased scenarios. The updated knowledge helps them to lower the probability of risks while improving results in critical emergencies.
What impact does understanding emergency steps have on outcomes?
Knowing the measure of emergency steps to be taken directly impacts how effectively responses to crises can be given, thus minimizing harm and saving lives. Understanding procedures dramatically increases the chance of performing lifesaving interventions like CPR, bleeding control, and hazardous area evacuation, increasing the survival rate. Best-known emergency protocols recommend that response time is of the essence; for example, it is said that CPR given within 3-5 minutes of cardiac arrest will triple one’s chances of survival. The same is said for the Automated External Defibrillator (AED), which can increase the chances of recovery by almost 75% if used within 3-4 minutes. Organizations and individuals can carefully alleviate risks and improve preparedness for unforeseen circumstances by properly familiarizing themselves with emergency equipment, such as understanding the chain of survival protocols and conducting regular emergency drills.
References
- Choking Treatment for a Pregnant Lady - 1FirstAid1
- Choking: First Aid - Mayo Clinic
- First Aid Basic Tips For A Choking Pregnant Woman - The First Aid Nest
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What should I do first if a pregnant woman is choking?
A: If a pregnant woman is choking, you should encourage her to cough if she can speak or make sounds. If the obstruction persists, you may need to perform back blows and chest thrusts instead of abdominal thrusts.Q: How do I perform back blows on a pregnant woman who is choking?
A: To perform back blows, stand behind the person and place one arm across the person's chest for support. Use the heel of your other hand to give five firm back blows between the person's shoulder blades.Q: How do I give chest thrusts to a choking pregnant woman?
A: Move behind the person and place your hands under the person's arms. Make a fist with your other hand and put it on the lower half of the sternum (breastbone), then give five quick thrusts. This is an alternative to abdominal thrusts for pregnant women.Q: What should I do if the choking person becomes unresponsive?
A: If the person becomes unresponsive, call for emergency help immediately and begin CPR. You may need to kneel behind the person if they are lying down. Use chest compressions and rescue breaths as needed.Q: How can I perform CPR on a pregnant woman?
A: To perform CPR on a pregnant woman, kneel beside her and place the heel of your hand on the center of her chest. Place your other hand on top and begin chest compressions at 100-120 per minute and about 2 inches deep. Use two fingers to give gentle breaths if you are trained.Q: What should I do if the person is choking and alone?
A: If the person is choking and alone, they can try to give themselves abdominal thrusts by thrusting their upper abdomen over the back of a chair or using their hands. They should call for emergency assistance if possible.Q: Why are abdominal thrusts not recommended for pregnant women?
A: Abdominal thrusts are not recommended for pregnant women because they can put pressure on the uterus and potentially harm the baby. Instead, chest thrusts are advised to avoid injury.Q: Can a minor child perform first aid on a choking pregnant woman?
A: It is generally not recommended for a small child to perform first aid on a choking pregnant woman due to their size and strength. However, children can be taught to call for help and alert an adult or trained professional.Q: How can I prepare for a choking emergency involving a pregnant woman?
A: Consider taking CPR and first aid training services to prepare for a choking emergency. Preparing and signing up for these courses can give you the skills needed in an emergency.Q: What should I do if an object becomes lodged and the person becomes unconscious?
A: If an object becomes lodged and the person becomes unconscious, call for emergency services immediately and start CPR. Check for the object in their mouth before breathing, and continue chest compressions until help arrives.







 Login with Google
Login with Google Login with Facebook
Login with Facebook