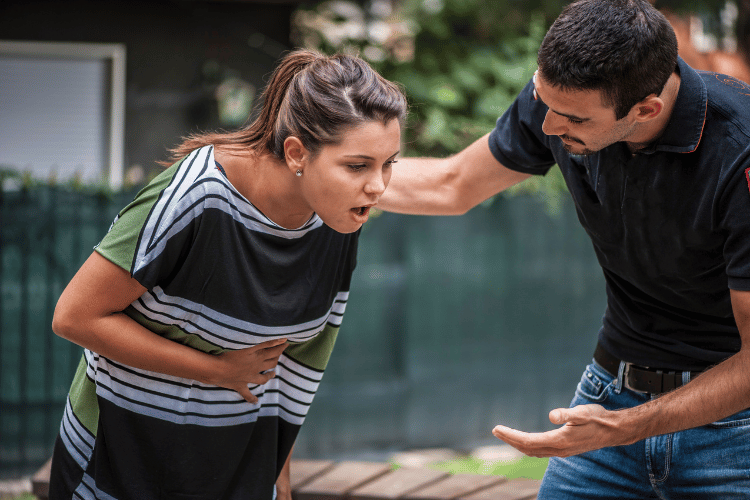

Choking is a critical medical emergency that requires immediate attention. It occurs when an object, often food or a small item, obstructs the airway, preventing airflow into the lungs. If not addressed promptly, this condition can lead to life-threatening complications. For parents, caregivers, and anyone, understanding choking symptoms and knowing how to respond can mean the difference between life and death. This guide provides vital information about identifying choking symptoms, responding effectively, and preventing such incidents.
Key Indicators of Choking
Recognizing the signs of choking is crucial, especially when every second counts. While general symptoms apply to individuals of all ages, children may exhibit unique signals that demand special attention.
General Symptoms of Choking
- Inability to Speak or Cry: A blocked airway prevents sound production.
- Coughing or Wheezing: The body attempts to expel the obstruction.
- Change in Skin Color: Look for redness, paleness, or a blue tint, especially around the lips or face.
- Clutching the Throat: Often referred to as the universal choking sign.
- High-Pitched or Noisy Breathing: Stridor or wheezing may signal a partially blocked airway.
- Loss of Consciousness: Prolonged choking can lead to oxygen deprivation and fainting.
Specific Signs in Children
- Weak or completely absent coughing.
- Cyanosis (turning blue), particularly around the lips, face, or nails.
- Wide eyes or expressions of panic.
- Silent episodes where the child grasps at their throat or struggles to breathe.
- High-pitched breathing sounds (stridor).
Being aware of these signs is vital to responding quickly and appropriately.
Different Levels of Choking Symptoms
Choking symptoms vary based on the severity of the blockage. Here's how they are typically categorized:
-
Mild Choking
- The person can still breathe and cough forcefully, indicating a partial obstruction.
- They may be able to speak or cry, although with some difficulty.
-
Moderate Choking
- Breathing becomes labored, with wheezing or weak sounds.
- The person may appear visibly distressed, clutching at their throat.
-
Severe Choking
- The person cannot breathe, speak, or cough at all.
- Their skin may turn blue due to oxygen deprivation.
- They may eventually lose consciousness if the airway remains obstructed.
Understanding these levels helps determine the urgency and method of intervention.
First Aid Techniques for Choking
Timely first aid can save a life during a choking emergency. Different techniques apply based on the person’s age and the severity of the situation.
Steps for Back Blows and Abdominal Thrusts
For Children Over One-Year-Old
-
Back Blows
- Stand or kneel behind the child.
- Bend them slightly forward at the waist.
- Use the heel of your hand to deliver five firm back blows between the shoulder blades.
-
Abdominal Thrusts (Heimlich Maneuver)
- Stand behind the child and wrap your arms around their waist.
- Make a fist and place it just above their navel but below the ribcage.
- Grasp the fist with your other hand, then perform quick, upward thrusts up to five times.
- Alternate between back blows and abdominal thrusts until the object is dislodged.
For Infants Under One Year
- Place the baby face on your forearm, supporting the head and neck.
- Deliver five firm back blows between the shoulder blades.
- If this does not work, turn the infant face up and deliver five chest thrusts using two fingers on the breastbone.
When the Child Becomes Unresponsive
If the choking persists and the child becomes unresponsive, proceed to CPR immediately (see details below).
Preventing Choking Incidents
Prevention is always better than cure. The following tips can help minimize the risk of choking, particularly in children.
Safe Food Practices
- Cut food into small, manageable pieces.
- Avoid offering hard, sticky, or round foods such as whole grapes, nuts, popcorn, and hard candies to young children.
- Have children sit upright while eating and encourage slow, deliberate chewing.
Remove Small Objects from Reach
- Regularly inspect and childproof your home.
- Keep small items, such as buttons, coins, and batteries, out of sight and reach.
- Use gates or childproof locks to restrict access to hazardous areas.
Educate All Caregivers
- Train babysitters, family members, and childcare professionals on choking hazards and first aid measures.
- Encourage participation in first aid courses to build confidence in handling emergencies.
By implementing these practices, you significantly lower the likelihood of choking incidents.
What to Do if a Child Becomes Unresponsive?
Recognizing Unresponsiveness
If a child stops moving, breathing, or responding, they may have become unconscious due to choking.
Begin CPR Immediately
-
For Children Over One-Year-Old:
- Place the child on their back on a firm surface.
- Perform 30 chest compressions (about one-third the depth of their chest) at 100–120 compressions per minute.
- Open the airway by tilting the head back and lifting the chin.
- Deliver 2 rescue breaths and check for airway obstruction before resuming compressions.
-
For Infants Under One Year Old:
- Use two fingers to perform chest compressions instead of your entire hand.
- Keep the head in a neutral position and provide gentle breaths.
Continue cycles of compressions and rescue breaths until help arrives or the child regains consciousness.
Call for Emergency Help
- If alone, perform CPR for two minutes before calling emergency services.
- If someone else is present, have them call 911 while you perform CPR.
Swift action and persistence in CPR can make all the difference.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the signs of choking?
Choking symptoms include difficulty breathing, high-pitched sounds, inability to speak, and turning blue.
How do I perform abdominal thrusts on a child?
Stand behind the child, wrap your arms around their waist, and make a fist above the navel. Perform quick upward thrusts to expel the blockage.
Can choking happen even with partial obstruction?
Yes, partial obstructions can still cause difficulty breathing, which may escalate if left untreated.
How can I prevent choking in infants?
Avoid giving infants solid or hard foods, supervise during meals, and keep small objects out of their reach.
What should I do if I’m alone and choking?
Attempt to cough forcefully. If that fails, use a firm surface or your hand to perform abdominal thrusts on yourself.
What should I do after clearing the obstruction?
Seek medical attention to ensure no complications or injuries to the throat or airway.
Conclusion
Awareness, preparation, and quick action are critical regarding choking. This knowledge can empower anyone to handle emergencies effectively, from recognizing symptoms to administering life-saving first aid and preventing choking hazards. Consider attending CPR and first aid classes to further build your confidence and skills. Remember, your vigilance and readiness can save lives.
Understanding choking symptoms and mastering response techniques, we can all contribute to creating safer environments for ourselves and our loved ones.
Source:-
Adult & Child Choking: Symptoms and First Aid - American Red Cross This page offers detailed guidance on recognizing choking symptoms and performing first aid techniques like back blows and abdominal thrusts.
-
First Aid for Someone Unresponsive & Breathing - American Red Cross This resource explains how to handle situations where a person becomes unresponsive, including CPR steps.
-
Respiratory Distress (Trouble Breathing) - American Red Cross This page discusses respiratory distress, which can include symptoms related to choking, and provides first aid recommendations.






 Login with Google
Login with Google Login with Facebook
Login with Facebook