Choking is an emergency that needs immediate treatment in order to escape potentially tragic outcomes such as suffocation, where a person could lose consciousness and even die. This informative piece, In its most basic form, centers on preparing people with the basic information that is required to manage the anatomical as well as the child and adult choking response. The article examines a number of different aspects of the physiological processes involved in choking and gives a detailed description of the procedures that are necessary for administering first aid. With simple and easily followed instructions, readers will be ready to use the techniques of the Heimlich maneuver and back blows, appropriate to other aged males and females. Both preventive measures and post-treatment have been explained to better manage choking emergencies.
 Choking can be identified with respect to a totally apnoeic state with a disordered voice and cough where palpitations of the person also occur alongside the person holding their neck with both hands with a notion of universality called ‘the choking sign.’ Moreover, wheezing or squeaky sounds, reddening or darkening face, as well as cyanosis, otherwise known as hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy( bẹx, ad), is also caused due to severe shortage of airflow. If the airway is kept blocked for long, a person might lose the conscious self-control of the body. Therefore, it is imperative to identify these signs at the right time in order to initiate timely resuscitative measures and manage such situations.
Choking can be identified with respect to a totally apnoeic state with a disordered voice and cough where palpitations of the person also occur alongside the person holding their neck with both hands with a notion of universality called ‘the choking sign.’ Moreover, wheezing or squeaky sounds, reddening or darkening face, as well as cyanosis, otherwise known as hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy( bẹx, ad), is also caused due to severe shortage of airflow. If the airway is kept blocked for long, a person might lose the conscious self-control of the body. Therefore, it is imperative to identify these signs at the right time in order to initiate timely resuscitative measures and manage such situations.
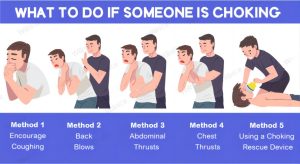
 In these scenarios, I understand the proper sequence of actions to take. There is only one condition I need you to clarify. Can you speak, cough, or breathe? If the answer is negative, it is time to provide them first aid. For anyone older than 12 months, call for assistance and start giving back blows and abdominal thrusts, up to 5 of the first and also 5 of the latter. Similarly, chest thrust for those aged less than one, giving up to 5 such thrusts. If you see that neither call for aid nor another attempt is successful, then wait for professional help to relieve you. The key task that will define the success rate of this entire undertaking is staying calm.
In these scenarios, I understand the proper sequence of actions to take. There is only one condition I need you to clarify. Can you speak, cough, or breathe? If the answer is negative, it is time to provide them first aid. For anyone older than 12 months, call for assistance and start giving back blows and abdominal thrusts, up to 5 of the first and also 5 of the latter. Similarly, chest thrust for those aged less than one, giving up to 5 such thrusts. If you see that neither call for aid nor another attempt is successful, then wait for professional help to relieve you. The key task that will define the success rate of this entire undertaking is staying calm.
 I am in a position to tell you in broad terms the immediate measures to be taken when someone is choking. First and foremost, make a quick assessment of whether the person is actually choking. The reason is that if consensus is reached on this aspect, then it encompasses intervention. So, it must be noted that if the person can neither cough nor talk or breathe, it is likely that the airway is blocked. Therefore, do not hesitate to call for an ambulance, as doing so may save someone's life. To the point that you do not wait for the direction and start with the movement of administering back blows and abdominal thrusts, as previously mentioned. As for children below the age of two, replace these with gentle back and chest thrusts. Repeatedly alternate between these measures until the resources required to get the airway clear, come. Always remember that being composed and slow in the execution of these measures is critical when it comes to the success of operations in case of choking.
I am in a position to tell you in broad terms the immediate measures to be taken when someone is choking. First and foremost, make a quick assessment of whether the person is actually choking. The reason is that if consensus is reached on this aspect, then it encompasses intervention. So, it must be noted that if the person can neither cough nor talk or breathe, it is likely that the airway is blocked. Therefore, do not hesitate to call for an ambulance, as doing so may save someone's life. To the point that you do not wait for the direction and start with the movement of administering back blows and abdominal thrusts, as previously mentioned. As for children below the age of two, replace these with gentle back and chest thrusts. Repeatedly alternate between these measures until the resources required to get the airway clear, come. Always remember that being composed and slow in the execution of these measures is critical when it comes to the success of operations in case of choking.
 It is critical for the respective audiences of the Red Cross and First Aid App to appreciate how these applications work in crises or emergencies. Remember that these tools have features that improve the way you handle such emergencies. Here’s a breakdown of how they can assist:
It is critical for the respective audiences of the Red Cross and First Aid App to appreciate how these applications work in crises or emergencies. Remember that these tools have features that improve the way you handle such emergencies. Here’s a breakdown of how they can assist:
 I can confirm the numerous benefits that come with taking a first aid course. To begin with, it provides you with the critical tools necessary to act quickly and correctly during a medical crisis, which can lead to saving someone’s life. It also gives you the assurance that you will be able to deal with any unexpected situations accurately and calmly. Moreover, having a grasp of what first aid entails allows one to encourage and facilitate safer conditions by recognizing risky situations and taking appropriate steps to avert them. Finally, a first aid course is not only about learning new pieces of information but also about attaining an advocacy level where you will be actively engaging in improving the safety of people around you.
I can confirm the numerous benefits that come with taking a first aid course. To begin with, it provides you with the critical tools necessary to act quickly and correctly during a medical crisis, which can lead to saving someone’s life. It also gives you the assurance that you will be able to deal with any unexpected situations accurately and calmly. Moreover, having a grasp of what first aid entails allows one to encourage and facilitate safer conditions by recognizing risky situations and taking appropriate steps to avert them. Finally, a first aid course is not only about learning new pieces of information but also about attaining an advocacy level where you will be actively engaging in improving the safety of people around you.
What Are the Signs and Symptoms of Choking?
 Choking can be identified with respect to a totally apnoeic state with a disordered voice and cough where palpitations of the person also occur alongside the person holding their neck with both hands with a notion of universality called ‘the choking sign.’ Moreover, wheezing or squeaky sounds, reddening or darkening face, as well as cyanosis, otherwise known as hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy( bẹx, ad), is also caused due to severe shortage of airflow. If the airway is kept blocked for long, a person might lose the conscious self-control of the body. Therefore, it is imperative to identify these signs at the right time in order to initiate timely resuscitative measures and manage such situations.
Choking can be identified with respect to a totally apnoeic state with a disordered voice and cough where palpitations of the person also occur alongside the person holding their neck with both hands with a notion of universality called ‘the choking sign.’ Moreover, wheezing or squeaky sounds, reddening or darkening face, as well as cyanosis, otherwise known as hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy( bẹx, ad), is also caused due to severe shortage of airflow. If the airway is kept blocked for long, a person might lose the conscious self-control of the body. Therefore, it is imperative to identify these signs at the right time in order to initiate timely resuscitative measures and manage such situations.
Recognizing When a Person Who is Choking Needs Help
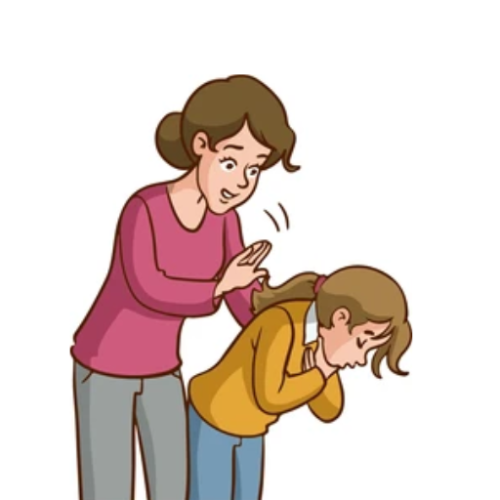
There is a situation in which the lack of awareness can be deadly, and to recollect that moment, have been through that feeling before. Therefore, I would like to emphasize that when someone is in the position of being choked, the first thing that should come to mind is understanding signs of that person in distress- as such, losing the ability to speak or covetingly attempting to cough or inhale. In such a case, especially if the person who is choking tries to grab their throat, which is pretty universal in the indications for choking, then it is time to be aggressive in your response. The person might also start turning blue around the lips or fingertips, which is also a major sign of oxygen deprivation, and such a case needs to be an emergency. So, knowing the requirements of these signs would have given the response more ability to respond. Rapid comprehension and application of the fundamental principles of first aid are tools available to all of us; the desire to apply them is the decisive factor. What this approach can do is decrease the probability of life-threatening situations caused by choking.Understanding Airway Obstruction
I am able to assert that knowledge of airway obstruction is a great asset when handling any choking incident. If I may elaborate on this issue further by breaking it down into several sub-topics so that you will be able to address such situations more effectively:- Types of Airway Obstruction: Any obstruction of the airway - be it internal or external can be referred to as an airway blockage. In a complete blockage, the affected person will neither breathe, talk, or cough. When a person suffers from partial airway blockage, they would be able to cough and breathe, though the performance would be feeble and ineffective. Modalities to correct the situation must follow this assessment as this provides an understanding of the level of the blockage.
- Causes of Obstruction: In most cases, choking is caused when a faster swallowing speed is beyond the capacity of the mouth or when food or small objects sit somewhere between the mouth and throat. Adults are most likely to opt out of chewing their food or start talking in the midst of eating, which results in the choking phenomenon. As for kids, small toys and things around the house fit the bill. Knowing the cause comes in handy when attempting to administer first aid.
- Evaluating the Severity: Other indications encompass a prominent fear-stricken face accompanied by instances of the throat being held and a cumulative inability to cough vigorously or even produce any noise. These instances alone, or if combined with a change in skin tone to a bluish color due to low amounts of oxygen, make this situation a bit more dangerous.
- First-aid Techniques: If a person is chocking The Heimlich Maneuver (back blows and abdominal thrusts) is the best way to corrrect the situation if applied in a correct manner. When and how these Maneuvers are executed are extremely important and different methods are required for children and adults so it is best to stay aware and be alert.
- Stay Calm and Call for Help: Fighting panic in emergencies is the best way to think rationally and perform impactful actions. When giving first aid it is also useful to make a call to professionals to get paramedic assistance in due course.
Common Risk for Choking Situations
I can state that curbing chest asphyxiation is a hundred percent reliant on assessing certain situations that are high risk. Most of the risks tied to choking tend to occur during mandatory meal breaks. It is especially the case when such a person attempts to communicate or share a joke, which leaves them at potential risk of not chewing their food properly as it should be the case. There are lots of people in the world who are at risk for choking due to other factors, such as disliking chewing beef, hotdogs, nuts, and even grapes as they search for ease over safety. Children are also at risk as they are children, and at an age where curiosity is at its peak, they are more prone to taking small toys or even coins that contain tiny parts and swallowing them. Identifying all of these risks will help alongside having strict supervision, especially of children, as it is key to success when aiming to reduce the intake of choking emergencies. If practiced widely, such provisions can greatly reduce the likelihood of any life-threatening scenarios.How to Perform First Aid for Choking?
 In these scenarios, I understand the proper sequence of actions to take. There is only one condition I need you to clarify. Can you speak, cough, or breathe? If the answer is negative, it is time to provide them first aid. For anyone older than 12 months, call for assistance and start giving back blows and abdominal thrusts, up to 5 of the first and also 5 of the latter. Similarly, chest thrust for those aged less than one, giving up to 5 such thrusts. If you see that neither call for aid nor another attempt is successful, then wait for professional help to relieve you. The key task that will define the success rate of this entire undertaking is staying calm.
In these scenarios, I understand the proper sequence of actions to take. There is only one condition I need you to clarify. Can you speak, cough, or breathe? If the answer is negative, it is time to provide them first aid. For anyone older than 12 months, call for assistance and start giving back blows and abdominal thrusts, up to 5 of the first and also 5 of the latter. Similarly, chest thrust for those aged less than one, giving up to 5 such thrusts. If you see that neither call for aid nor another attempt is successful, then wait for professional help to relieve you. The key task that will define the success rate of this entire undertaking is staying calm.
Steps to Dislodge the Object in a Choking Victim
Thanks to my vast experience in handling choking emergencies, I understand the procedure for performing dislodgement on a choking victim. It is essential to execute these steps quickly:- Assess the Situation: In the beginning, determine whether this person is, in fact, choking by asking if they can speak or cough. If they can do neither, it signifies a full blockage.
- Call for Help:Regardless of the scenario, hold on to your end of the bargain, and, given the circumstances, someone is still required to contact the relevant emergency service. Such assistance is important since medical personnel may have to rely on more sophisticated assistance in order to be effective.
- Administer Back Blows: For children above the age of one and adults, use the heel of your hand to deliver varying degrees of force, from controlled to slight. Provide up to five highly forceful back blows between the person’s scapulae and the back. In all the situations, practice extreme caution.
- Perform Abdominal Thrusts (Heimlich Maneuver): Grasp them firmly about the waist from behind. Then, make a fist and position it in the call or area just above that person's navel. Now, place your other hand on top of that fist and do quick upward thrusts.
- Repeat as Necessary: If the item does not come out in all of the processes, apply back blows that are followed by abdominal thrusts and last until medical assistance comes in. Keep awake and observe how the person has changed.
- Special Considerations for Infants: An infant is permanently prone to choking hazards such as food, liquids, powders, and others such as plastic objects, toys or and small parts of an object that can get lodged into their throat, hence following this up when it comes to babies without teeth, under the age of one, it is instructed to use five gentle chest thrusts and five back blows and any of the two parts of a pacifier if needed. A pillow could also be used to assist the back blows being needed to ensure babies safety when he/she is under age of one.
How to Use the Heimlich Maneuver (or Heimlich Manoeuvre)
The Heimlich Maneuver is something I would be able to explain readily. As an officer who specializes in first aid procedures, I would note that the Heimlich Maneuver was meant for a situation where breath cannot be obtained due to an obstruction such as a foreign object. Accordingly, here’s how it can be performed:- Check for Blockage: In order to understand if obstruction is present, the initial step would be to see if the patient is able to breathe or talk. If the individual manages to cough or talk, it is safe to assume there is no need to begin any measures to clear the airway.’’
- Call for Emergency Help: As many emergency responders are trained professionals, they should be consulted immediately a by someone whether it be over a phone or another means.
- Stand Behind the Person: Stand behind the person experiencing choking of the airway and place both your hands around their belly roughly one inch above the navel of their body.
- Position Your Hands:The first step would be to make a fist which will assist in the pressure. The fist need also be slightly tilted sideways and placed a bit above the belly button of the person who is choking.
- Perform Quick Thrusts: Now, with one of the hands, grab the other hand as a fist and begin to thrust towards the upward and inward direction, slowly trying to create enough pressure to remove any obstruction in the airway.
- Repeat if Needed: In case the obstruction is not removed via that method, you can try the first method again until the person regains consciousness; at that point, they should be able to do all three: breathe, talk, and swallow normally.
- Special Considerations for Infants: For infants, hold them face down on your forearm and deliver five gentle back blows between the shoulder blades, followed by five chest thrusts using two fingers.
Executing Back Blows and Abdominal Thrusts
In the case of throat-choking situations, the priority is always back blown and abdominal thrusts to remove the obstruction. When performing back blows, approach the patient from the side slightly behind. Use the heel of your hand to deliver five strong blows between the shoulder blades of the patient. These targeted hits help expel obstructions from the airway, which might compromise the patient. Reverse abdominal into thrusts (more popularly referred to as a Heimlich Maneuver) whenever these blows are deemed to be too weak. In this movement, the other fisted hand moves into the abdomen (just above the patient’s navel) and is pulled rapidly toward the patient. This further force is aimed at increasing the pressure sufficient enough to completely push the object out of the airway. Keep changing between these two movements until the professional reaches there, or you remove the obstruction without panicking or losing focus.What Are the Emergency Steps When Choking Occurs?
 I am in a position to tell you in broad terms the immediate measures to be taken when someone is choking. First and foremost, make a quick assessment of whether the person is actually choking. The reason is that if consensus is reached on this aspect, then it encompasses intervention. So, it must be noted that if the person can neither cough nor talk or breathe, it is likely that the airway is blocked. Therefore, do not hesitate to call for an ambulance, as doing so may save someone's life. To the point that you do not wait for the direction and start with the movement of administering back blows and abdominal thrusts, as previously mentioned. As for children below the age of two, replace these with gentle back and chest thrusts. Repeatedly alternate between these measures until the resources required to get the airway clear, come. Always remember that being composed and slow in the execution of these measures is critical when it comes to the success of operations in case of choking.
I am in a position to tell you in broad terms the immediate measures to be taken when someone is choking. First and foremost, make a quick assessment of whether the person is actually choking. The reason is that if consensus is reached on this aspect, then it encompasses intervention. So, it must be noted that if the person can neither cough nor talk or breathe, it is likely that the airway is blocked. Therefore, do not hesitate to call for an ambulance, as doing so may save someone's life. To the point that you do not wait for the direction and start with the movement of administering back blows and abdominal thrusts, as previously mentioned. As for children below the age of two, replace these with gentle back and chest thrusts. Repeatedly alternate between these measures until the resources required to get the airway clear, come. Always remember that being composed and slow in the execution of these measures is critical when it comes to the success of operations in case of choking.
Immediate Actions to Help Save Lives
allow us to clarify the specific steps that can be taken to save someone`s life in case of choking. You start by determining whether the airway is indeed compromised and whether the patient is engaged with their ability to cough, speak, or breathe. In cases where there is no such engagement, it is time to take action.- Call for Help: If there is someone within your range who can assist you, have that person call for emergency assistance; if not, and you are the only one around, make a call after you have finished providing assistance, but do it as quickly as you can.
- Administer Back Blows: Stand back and to the side of the choking person. Using the heel of your hand, firmly strike between the person's shoulder blades in an upward motion between one and five times. The aim is to provide enough force in an effort to remove the object lodged.
- Perform Abdominal Thrusts: If back blowing does not help, grab the patient from behind the waist and pull them closer to you after taking care of this aim. The motion of this will be facing towards the caul as you instruct them gently to do so. If this action still doesn't work, go for the navel; place your fist above it and then repeat that motion using that one hand again, but this time sharper. Do all of the motions exactly as stated above.
- Repeat if Necessary: Continue to alternate between administering five back blows with five abdominal thrust motions until the airway obstruction is dislodged completely. Proceed with that until a medical professional or physician arrives, then stop moving altogether.
When to Begin Chest Compressions or CPR
I have an easy tip on how to commence chest compressions or CPR and when not to in the case of a choking patient. Thus, chest compressions or CPR should be started whenever the choking patient turns unconscious and is not breathing. In this case, the person is not only unconscious, but also the airway is fully blocked so that lung expansion can never take place. It is, therefore, imperative that CPR is immediately started with the aim of minimizing the time A& E personnel have to wait to assist with restoring pulmonary perfusion during their resuscitation efforts.- Lack of Consciousness: If the individual has collapsed so much that he or she is unresponsive, the lack of oxygen reaching his or her vital organs is serious, and CPR should be commenced without wasting time.
- No Breathing or Gasping: One should examine whether the individual is breathing or only gasping. If the person has lost consciousness and cannot breathe normally, CPR should be started.
- No Pulse: For those who are taught this procedure, it should take no longer than 10 seconds to check the pulse. Otherwise, or if uncertain that a pulse is felt, lay deep, descent chest compressions without delay; about 30 compressions each sequence.
- Effective CPR Technique: With the heel of one palm, locate the centre of breast bone of the victim and place it between the nipples, place the other hand on top of this one and clasp the fingers. Push the compressions hard to a minimum of 2-inch depths at a speed rate of 100 to 120 CPM.
- Continue Until Help Arrives: Continue to press the chest and practice how to give oxygen until someone arrives or the patient gets more alive, breathing or moving their body.
Dealing with a Person Who Becomes Unresponsive
the unresponsiveness of an individual in an emergency is a situation that is very much business-related and needs to be handled properly. In such a case, here are comprehensive measures you can take:- Check Responsiveness: Try speaking to the person as you pat on them. If there seems to be no response, follow the steps that follow.
- Call for Help: Contact emergency medical services immediately. Alternatively, you can instruct a person that is near you to initiate the call. In either case, the information exchange with specialists during the transfer is essential.
- Assess Breathing: Ask questions or use your hand or breathe against them while looking for mouth movement to see if there are signs of normal breathing. Also note any abnormal or gasping type breaths taken.
- Prepare for CPR: If he isn’t breathing, roll the person onto his or her back, which is located on a firm landing surface like the floor.
How Can the Red Cross and First Aid App Assist?
 It is critical for the respective audiences of the Red Cross and First Aid App to appreciate how these applications work in crises or emergencies. Remember that these tools have features that improve the way you handle such emergencies. Here’s a breakdown of how they can assist:
It is critical for the respective audiences of the Red Cross and First Aid App to appreciate how these applications work in crises or emergencies. Remember that these tools have features that improve the way you handle such emergencies. Here’s a breakdown of how they can assist:
- Emergency Instructions:The First Aid App explains through a clear and simple graphical interface all the steps in rational order of various emergencies making it easy for everybody to use even in stress situations.
- Video Demonstrations: It contains videos and recordings of different first rescue tasks, allowing the user to view an explanation of how to do each action.
- Offline Accessibility: The app's contents can be stored in tablet PCs so that crucial information can even be obtained in the absence of internet connection during the time of crisis.
- CPR and AED Guidance: Outlines the process of carrying out CPR and using an Automated External Defibrillator,r which is essential when there are cardiac cases and one suffers from choking.
- Prevention Tips: Explains how to avert instances and emergencies from occurring and inform in advance on certain events resulting in enhancing safety provisions for the user and the surroundings.
- Regular Updates: The point content gets periodically updated so that the material incorporates the most recent health safety guidelines and procedures hence can be trusted for first aid.
- Localized Help: Components that would make it possible for you to contact other local health facilities to obtain emergency treatment in your place.
Benefits of American Red Cross Training
To state that the American Red Cross training was helpful when dealing with emergencies would be an understatement. Here’s how the training has equipped me:- Comprehensive Emergency Skills: The training gave me the abilities to walk through multiple scenarios that required differing emergency procedures, for instance, performing CPR or treating a cut or a burn. Such knowledge now places me at a position where I can act efficiently and with conviction whenever there is an emergency.
- Hands-On Practice: Practical lessons are part of the course where students get to practice some of the techniques. This practice is supervised by instructors who have gone through the necessary certification processes. This first-hand experience is of great importance in making sure that I am ready to implement what I have learned in the real world.
- Certification and Credibility: From my participation in the Red Cross training, I have been able to obtain a certificate which is widely recognized. This makes me have self-confidence and enhances other people's confidence in my potential to use first aid whenever I am called to do so.
- Continued Learning Opportunities: The training does not end with the earning of the certificate. The Red Cross has interventions that are aimed at ongoing learning and skills refreshment which help ensure that I remain at the forefront of new changes in the organization and its ways of doing things.
- Risk Assessment Skills: I think the most important thing that I learnt during my training was how to appraise a scenario in a matter of seconds regardless of its complexity. The ability to know the right time and the right way to do something has significantly improved my ability to make decisions in critical moments.
- Preparedness and Prevention: The focus is not on merely reacting to situations that are deemed emergencies but rather on understanding how to avert such scenarios altogether. This has allowed me to take precautionary steps that curtail the possibility of there being chances of accidents to begin with.
Using the First Aid App for Quick Guidance
let me simplify what it offers and how each of them can assist you during emergencies: The app offers simple, easy-to-follow, step-by-step instructions on how to respond to common emergencies such as cuts and sprains, which enables those who have no previous first aid knowledge to help out. This feature is handy for those in need, making it possible for everyone to learn first aid without any prior complications. For better comprehension of the techniques and bone-setting procedure, the App features videos which explain the procedure. It also aims to clear off any difficulties when performing the procedure, therefore, the risk of errors is minimized. Even in instances where the connection is unstable, users have no need to worry since the application has all the resources one might require. It has to be one of the most useful applications, especially for people who spend a large amount of their time at such places. Just like that, all of this information is provided to you in the most beneficial circumstances. In a time where a person doesn't have a heartbeat or is suffering from one, the app serves as a lifesaver by utilizing CPR methods and AEDs. In an alternate scenario, all of these methods hold great importance in maintaining a person’s life. As it is essential that one stays fit, the app not only focuses on emergency responses but also provides guidance on how minor accidents and injuries can be avoided. With the aid of the app, you are able to reach nearby local health authorities, as a result, all the required assistance is targeted around you. With an emphasis on these features, the First Aid App equips you with the confidence to be able to help in times of crisis, to do so in the best manner.Exploring Free First Aid Resources
it's safe to assume that free information sources may significantly enhance formal one's training. So, here’s how you would go about finding and using such resources:- Online Courses and Tutorials: Several organizations provide free online classes on the rudimentary techniques of first aid. Such courses are often offered in a systematic manner and can be done at your own pace. Courses with video lessons should be the target as they provide a better explanation.
- Informative Websites: Websites containing information from health organizations usually have lots of informative material on various first aid aspects. Such materials are kept in check and can serve as useful tips to those looking for updates on new information pertaining to means and measures.
- Mobile Applications: Downloading free first aid applications can guarantee you that you will have vital tips at any given point. Usually they are quite useful because they allow browsing offline and contain videos on how to perform certain important tasks when internet connection is unavailable.
- Community Workshops: Another good way of practicing is through attending workshops organized by local authorities or community groups. These workshop sessions not only give the practical part of the training but also allow one to ask questions and receive hands on assistance.
- Public Libraries: A good number of public libraries stock first aid devices and books for free use. Such materials can be helpful as well in terms of borrowing from a public library since it will increase your knowledge and give you a good overall strategy of tackling emergencies.
Why Should You Take a First Aid Course?
 I can confirm the numerous benefits that come with taking a first aid course. To begin with, it provides you with the critical tools necessary to act quickly and correctly during a medical crisis, which can lead to saving someone’s life. It also gives you the assurance that you will be able to deal with any unexpected situations accurately and calmly. Moreover, having a grasp of what first aid entails allows one to encourage and facilitate safer conditions by recognizing risky situations and taking appropriate steps to avert them. Finally, a first aid course is not only about learning new pieces of information but also about attaining an advocacy level where you will be actively engaging in improving the safety of people around you.
I can confirm the numerous benefits that come with taking a first aid course. To begin with, it provides you with the critical tools necessary to act quickly and correctly during a medical crisis, which can lead to saving someone’s life. It also gives you the assurance that you will be able to deal with any unexpected situations accurately and calmly. Moreover, having a grasp of what first aid entails allows one to encourage and facilitate safer conditions by recognizing risky situations and taking appropriate steps to avert them. Finally, a first aid course is not only about learning new pieces of information but also about attaining an advocacy level where you will be actively engaging in improving the safety of people around you.
Learning Basic Life Support Techniques
Being active in the domain of first aid, I feel that understanding Basic Life Support (BLS) techniques is really useful and important for a number of reasons. Allow me to reason kindly out these elucidations for you:- Your knowledge in basic life support techniques can help out in emergencies. The BLS techniques include but are not limited to, chest compressions and mouth to mouth resuscitation. Statistically, 64% of people having out of hospital cardiac arrests have to wait around 11 minutes for first responders and paramedics. It is crucial to bear in mind that life saving BLS techniques can indeed, help wait till professional help arrives. As BLS professional training entails, the BLS professional learns effective CPR techniques; they also learn how to properly- correct the position of the head and neck, fully inflate the lungs, and teach oneself the rhythm and the pace of the beating of the heart. BLS training can assist in relaying vital information in the case of someone going into cardiac arrest. A reported 11 million children, toddlers,s and infants go to the ER each year due to various mishaps resulting in asphyxiation. By properly applying those learned techniques first, the correct pace and depth,h, and timing of the compressions, we see an overall increase in cardiac patients' survival rates.Unless we talk about Automated External Defibrillator (AED) devices for certain patients in need of these AEDs, around 100,000 patients die each year due to cases where AEDs are not available. Patients suffering from heart failure should be subjected within 5 minutes to AED devices. AED devices can and do save lives. Proper BLS training can teach you how to save a life under an immense amount of pressure while relaxed.Over the years, BLS training has evolved and expanded, incorporating smart devices such as AEDs. An estimated 67% of people die from suffocation and choking. Chokes account for an endless possibility of emergencies, and it is essential to keep in mind that there is always a solution to those problems. Protection gloves and mouth-chewing devices are always great helpers in avoiding choking or suffocating.BLS techniques enable you to potentially change a life or impact someone's day. Sudden emergency situations require quick strategic aiming of the hand to reply to the existent problem and can prevent disease from progressing. Such life saving responses can in turn save a life, BLS can help and endorse faster strategic thinking when aiming to reply to medical emergencies.Team Coordination, simply being trained enables the person to deal with extreme as well as dangerous situations in collaboration with their fellow trainees, enabling effectiveness in working in of a group in an emergency setting. For example, a person trained with BLS can comprehend what priorities need to be held at the top and what roles to play in order to successfully complete an objective.
Preparing for Choking First Aid Situations
The tension of choking first aid situations can be eased by preparation and the knowledge of how to react to accidents. There is no pretending that being ready to provide assistance in such times is easy. I’ve come to appreciate this as an industry expert. With that said, let’s go through these crucial steps one by one:- Recognize Signs of Choking: The very first thing you will have to do is note the presence of choking in the casualty. This can be indicated by the inability to speak, nonproductive coughing, or a person holding their throat, which is considered a standard signal of distress.
- Back Blows: However, if a person is truly in distress and is conscious but can’t breathe, then stand behind them and strike their back. Aiming with your palm heel to the center of your back, apply firm blows between the shoulder blades. You may need to do this a few times – five times at most.
- Abdominal Thrusts (Heimlich Maneuver): If the previous one does not give the desired results then back blows can be replaced with abdominal thrusts. Position yourself behind the person, make a fist and place it a little above the navel, then place your other hand over the fist. Upward quick thrust motions should be used to try and clear the obstruction. This may be required for up to five movements.
- Repeat the Cycle: Redo the cycle of striking five times to the back and applying up to five abdominal thrusts until the obstruction is dislodged or the patient goes limp.
- Calling for Help: If the patient loses consciousness, proceed to directly call other personnel for help. They may need forceful techniques, and CPR will be required if the victim goes into coma and is not breathing.
- Prevention Tips: When eating a meal, encourage the individual to chew every piece of food before swallowing it since it minimizes the risk of choking. Additionally, ensure that small items are out of reach of children and explain that playing with such items is dangerous as they can get lodged in children’s throats.
How a First Aid Course Can Help Save Lives
I accept that first aid training can be the difference between success and failure in some serious situations. Those courses place emphasis on practical, hands-on lessons that enable someone to act during an emergency. Knowing how to do basic care allows you to take charge of the victim and give him or her the greatest chance of survival. Each and every one of these skills is critical, whether it is administering CPR, using an AED, or taking care of someone who is choking. Finally, becoming efficient in these procedures also helps one to stay calm, reassuring them of their ability to instruct and command the situation in an orderly one. That is why taking part in a first-aid course is really beneficial. It enriches you not only with skills but also with the ability to make tough, lifesaving choices under pressure.Reference
- Mayo Clinic: Choking First Aid - Provides detailed steps on how to assist someone who is choking.
- American Red Cross: Adult & Child Choking - Offers guidance on recognizing choking symptoms and administering first aid.
- St John Ambulance: Adult Choking - Provides advice on first aid techniques for choking adults.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What should I do if a choking child is still conscious?
A: If a choking child is still conscious, you should encourage them to cough. If they cannot cough, speak, or breathe, you can perform the Heimlich maneuver or give back blows to help dislodge the object.Q: How do I perform the Heimlich maneuver on an adult who is choking?
A: To perform the Heimlich maneuver on an adult who is choking, stand behind them and place your arms around their waist. Make a fist with one hand and place it just above the navel. Grasp the fist with your other hand and thrust inward and upward until the object is expelled or the person can breathe again.Q: What should I do if a baby is choking?
A: If a baby is choking, you should turn the infant face down along your forearm, supporting their head and neck. Give five back blows between the shoulder blades with the heel of your hand. If the object does not come out, turn the infant face up and perform five chest thrusts using two fingers in the center of the chest.Q: When should I call 999 for a choking child?
A: You should call 999 for a choking child if they become unconscious if the method you are using to help them is not working, or if they are still unable to breathe after several attempts to help dislodge the object.Q: What are the signs that a toddler may be choking?
A: Signs that a toddler may be choking include the inability to breathe, coughing, wheezing, or making a high-pitched sound. They may also hold their throat or show signs of distress. If these symptoms are present, immediate first-aid advice should be followed.Q: How can I help a choking baby under 1 year old?
A: For babies under 1 year old, you should first assess if the baby is choking. If they are, turn the baby face down along your forearm and give 5 back blows. If that does not work, turn the baby face up and perform five chest thrusts with two fingers in the center of the chest.Q: Why is it important to support a baby's head and neck during first aid for choking?
A: It is important to support a baby's head and neck during first aid for choking to ensure stability and prevent injury. Babies have weaker neck muscles, and proper support helps keep the airway clear while you are performing back blows or chest thrusts.Q: What should I do if the method doesn’t work to help a choking adult?
A: If the method doesn’t work and the adult is still choking, you should continue to encourage coughing, call 999 or have someone call 911, and be prepared to perform CPR if they become unconscious.Q: What can cause choking in children and adults?
A: Common causes of choking include food, small toys, or other objects that obstruct the throat or windpipe. It is essential to monitor young children while eating and playing to avoid choking hazards.1782













 Login with Google
Login with Google Login with Facebook
Login with Facebook