
Choking is a life-threatening scenario that needs a response in a span of seconds. Choking can happen without any notice, and hence, knowledge about how to prevent choking incidents from happening or how to react in the case of choking is very crucial, whether in private or public places. The purpose of this blog is to present the necessary procedures for when one is beset by the life-threatening complication of the inability to breathe due to the constricted airway, including the identification of the choking indicators, quick and simple first aid procedures, and the applicable techniques that could potentially decrease the chances of choking from happening. These skills can be lifesaving and make a crucial difference when dealing with emergencies, whether in a dining environment, home, or other public spaces.
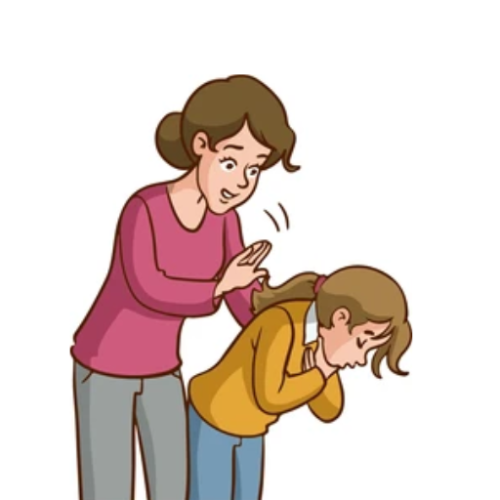
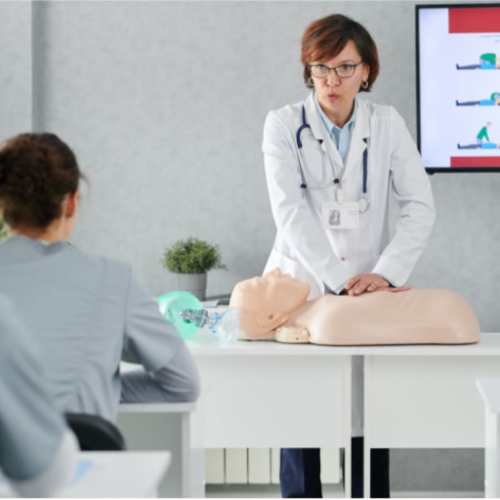
 When one has the problem of choking, the initial step is to stay calm and act right – ask if the person choking is able to speak and talk – if yes, then it is recommended to cough vigorously in order to clear the blockage. In the case that speech and coughing are not options, the chin lift of the Heimlich maneuver is to be done. Stand behind the choking person and wrap your arms around his waist; place one of your hands in a fist just above the person's navel. The other hand should be placed around the fist, and sharp thrusting motions will be done to the directed area until the object is pushed out. If the person loses consciousness, call the emergency room and start CPR until the CPR is back.
When one has the problem of choking, the initial step is to stay calm and act right – ask if the person choking is able to speak and talk – if yes, then it is recommended to cough vigorously in order to clear the blockage. In the case that speech and coughing are not options, the chin lift of the Heimlich maneuver is to be done. Stand behind the choking person and wrap your arms around his waist; place one of your hands in a fist just above the person's navel. The other hand should be placed around the fist, and sharp thrusting motions will be done to the directed area until the object is pushed out. If the person loses consciousness, call the emergency room and start CPR until the CPR is back.
 Choking in adults, usually due to food, can be avoided through awareness and management of one’s surroundings and food intake. Suggest that chewing all mouthfuls completely and trying not to speak or laugh during meals, which creates the danger of aspiration, be modified. Intoxication during eating should also be avoided due to compromised natural reflexes. Also, hard-to-chew foods like steak or raw vegetables can be made less hazardous by cutting them into small bites before eating them. Making an effort to create an eating environment that is calm and focused by eliminating distractions may also help. Finally, it would be prudent to provide education to adults regarding the Heimlich maneuver and basic first aid for choking incidents in order to be ready in advance and act fast during such emergencies.
Choking in adults, usually due to food, can be avoided through awareness and management of one’s surroundings and food intake. Suggest that chewing all mouthfuls completely and trying not to speak or laugh during meals, which creates the danger of aspiration, be modified. Intoxication during eating should also be avoided due to compromised natural reflexes. Also, hard-to-chew foods like steak or raw vegetables can be made less hazardous by cutting them into small bites before eating them. Making an effort to create an eating environment that is calm and focused by eliminating distractions may also help. Finally, it would be prudent to provide education to adults regarding the Heimlich maneuver and basic first aid for choking incidents in order to be ready in advance and act fast during such emergencies.
 The absence of it could lead to a loss of life. The inability to quickly recognize that a person is choking may cost the victim’s life. The most critical fact in this situation is getting the piece of food that has been stuck in the throat out. Techniques such as back blows and abdominal thrusts, commonly known as the Heimlich maneuver, are often employed. The basic aim of these procedures is to facilitate coughing, which will dislodge the foreign object. Where these don’t work, knowing when to seek assistance and how best to apply CPR if there is a need becomes paramount. First aid helps when one has to provide immediate medical assistance to the victim before the medical team arrives.
The absence of it could lead to a loss of life. The inability to quickly recognize that a person is choking may cost the victim’s life. The most critical fact in this situation is getting the piece of food that has been stuck in the throat out. Techniques such as back blows and abdominal thrusts, commonly known as the Heimlich maneuver, are often employed. The basic aim of these procedures is to facilitate coughing, which will dislodge the foreign object. Where these don’t work, knowing when to seek assistance and how best to apply CPR if there is a need becomes paramount. First aid helps when one has to provide immediate medical assistance to the victim before the medical team arrives.

What Should You Do if Someone is Choking?
 When one has the problem of choking, the initial step is to stay calm and act right – ask if the person choking is able to speak and talk – if yes, then it is recommended to cough vigorously in order to clear the blockage. In the case that speech and coughing are not options, the chin lift of the Heimlich maneuver is to be done. Stand behind the choking person and wrap your arms around his waist; place one of your hands in a fist just above the person's navel. The other hand should be placed around the fist, and sharp thrusting motions will be done to the directed area until the object is pushed out. If the person loses consciousness, call the emergency room and start CPR until the CPR is back.
When one has the problem of choking, the initial step is to stay calm and act right – ask if the person choking is able to speak and talk – if yes, then it is recommended to cough vigorously in order to clear the blockage. In the case that speech and coughing are not options, the chin lift of the Heimlich maneuver is to be done. Stand behind the choking person and wrap your arms around his waist; place one of your hands in a fist just above the person's navel. The other hand should be placed around the fist, and sharp thrusting motions will be done to the directed area until the object is pushed out. If the person loses consciousness, call the emergency room and start CPR until the CPR is back.
How to Perform the Heimlich Maneuver Effectively
I am able to speak with authority about the importance of learning and properly performing the technique of abdominal thrusts. This procedure can be lifesaving when someone is choking and becomes unable to breathe. One thing that is clear is confidence is key when performing abdominal thrusts. First, place yourself behind the person who is choking and, while standing in an aggressive style, encircle their waist with your arms. Place your fist above the person’s navel, and place your other hand over your fist. Use caution but also maintain purpose as you perform quick, upward thrusts. Apply the correct amount of force depending on the individual in order to be effective but ensure that they aren’t placed in potential risk of harm. Being confident and acting quickly have a better likelihood of a desirable outcome, which ensures the victim is now able to breathe. Undoubtedly, one of the most important and useful skills to learn for such moments is how to perform abdominal thrusts.Steps for Back Blows and Abdominal Thrusts
I would like to show you how to do back blows and abdominal thrusts. These are techniques that can straightforwardly save a life should a person be choking.- Assess the Situation: Choking can be serious; so before getting involved, ensure that the individual is not just panicking but is in a choke situation where they have difficulty talking breathing or coughs with difficulty. In these circumstances, color of their skin may also change to bluish.
- Ask for Consent: Take permission from adult patients if they are fully conscious before you undertake the procedure. This is crucial for ensuring their willingness towards what you are about to do.
- Perform Back Blows:
- Position yourself slightly sideways and behind the individual that is choking.
- While reinforcing their chest with one hand, make the person bend over so that the item obstructing their airway comes out of the person’s mouth rather than off the person’s head.
- Using the palm of your hand, give them five hard strokes between the shoulder blades.
- Check the Situation Again:When back blows have been finished, check if the obstruction has been removed. If not, go on with abdominal thrusts.
- Perform Abdominal Thrusts (Heimlich Maneuver):
- Now, wrap your arms around the person’s waist from behind.
- Make a fist and place it just above their abdomen, then cover it with the other hand.
- With your hands, make five inward upward pulls towards the center, which should be quick thrusting motions.
- Re-Assess: Following these steps, check again if the patient’s airway is clear. Continue with the sequence of five back blows and five abdominal thrusts until the patient is able to breathe, cough, or speak or until professional assistance arrives.
When to Call 911 or Your Local Emergency Services
Understanding when a choking incident can be classed as an emergency where professional help is required is quite critical. These are the key considerations:- Loss of Consciousness: In case a person becomes unconscious, 911 has to be called without delay. This means that the person requires urgent medical care.
- Inability to Cough, Breathe, or Speak:Where a patient is unable to vocalize or even take deep breaths or exert a productive cough after performing basic measures such as back slaps and abdominal thrusts, that is the time to request emergency services.
- Weak or Ineffective Coughing: If the patient is coughing and the cough becomes increasingly less forceful or yields no readily apparent benefit at all, choking is at a critical stage, and assistance should be sought.
- Development of Blue-Tinted Skin (Cyanosis): The yellowness of the skin, particularly the whole or parts of lips or fingers, demonstrates that oxygen is not getting to the important tissues, and factors are in place that suggest the need for emergency services as soon as possible.
- Emergency Help is Not Arriving:Where there is a scenario where the patient’s airway can not be cleared well and no response has been noted, or a circumstance where more skilled medical aid would take time to arrive, it is prudent to call 911 when there is no imminent danger.
How Can You Prevent Choking in Adults?
 Choking in adults, usually due to food, can be avoided through awareness and management of one’s surroundings and food intake. Suggest that chewing all mouthfuls completely and trying not to speak or laugh during meals, which creates the danger of aspiration, be modified. Intoxication during eating should also be avoided due to compromised natural reflexes. Also, hard-to-chew foods like steak or raw vegetables can be made less hazardous by cutting them into small bites before eating them. Making an effort to create an eating environment that is calm and focused by eliminating distractions may also help. Finally, it would be prudent to provide education to adults regarding the Heimlich maneuver and basic first aid for choking incidents in order to be ready in advance and act fast during such emergencies.
Choking in adults, usually due to food, can be avoided through awareness and management of one’s surroundings and food intake. Suggest that chewing all mouthfuls completely and trying not to speak or laugh during meals, which creates the danger of aspiration, be modified. Intoxication during eating should also be avoided due to compromised natural reflexes. Also, hard-to-chew foods like steak or raw vegetables can be made less hazardous by cutting them into small bites before eating them. Making an effort to create an eating environment that is calm and focused by eliminating distractions may also help. Finally, it would be prudent to provide education to adults regarding the Heimlich maneuver and basic first aid for choking incidents in order to be ready in advance and act fast during such emergencies.
Understanding Common Choking Hazards
I would also find it pertinent to identify and deal with possible choking hazards present in everyday environments. Most people may not understand how rampant these threats really are, especially in regard to food. Certain foods such as nuts, popcorn, and hard candies, for instance, tend to baffle people in terms of their propensity to cause choking. Even play objects that comprise small-sized parts and coins that are not food can be a serious hazard as well, especially in homes with children. Once these dangers are known, appropriate measures can be taken to ensure that persons such as young children, elders, or other vulnerable persons are not put in jeopardy through such measures as supervision during meals or the washing of the hands of young children prior to mealtimes, and so forth. More preventive measures with better education will reduce the rate at which choking cases occur, making it much safer in different contexts.Tips to Help Prevent Choking at Home
I maintain that the focus should always be on being alert and taking basic preventive measures in order to reduce the chance of choking risk within the home. These are some of the practical issues that I suggest concerning safety:- Supervise Meal Times: Avoid leaving children or upholding the seating of motionless adults whilst drinking or eating as this reduces risk factors significantly but more importantly allows for defence action to be taken in case something goes wrong.
- Educate on Safe Eating Practices: Make it known to everyone chewing food well and covering their mouths while eating should be a norm and it’s also of utmost importance to sit straight while eating.
- Modify Food Texture: If young children or elderly adults find it hard to chew food, modification of food texture is necessary such as chopping the food into smaller portions or soft cooking.
- Keep Hazardous Items Out of Reach: Remember to keep Non-edible object like coins, buttons or mini toy parts where kids cannot reach such places include shelves, drawers or cabinets.
- Create a Distraction-Free Eating Environment: During meal time encourage turning off televisions or staying away from using devices such as mobile phones which helps children focus on food.
- Know Emergency Procedures: In a patients choking situation having a basic knowledge of procedures such as the Heimlich maneuver can prove for a major difference and that is one of the reasons why you should be on the same wavelength at your family.
Importance of Cutting Food Into Small Pieces
Chopping food into small size bites is very important for many reasons especially the issue of choking prevention. For instance small pieces are swallowed much easier, which is important for youngsters, aged people, and people with swallowing problems. This basic act reduces chances of food being stuck in the neck.- Ease of Chewing and Swallowing: Smaller portions lessen the force and effort required to crush and chew, thus making them safe for swallowing.
- Reduced Risk of Choking: The chances of suffering from choking are reduced by slicing food into smaller portions so that an un chewed large chunk of food does not block the wind pipe.
- Promotes Thorough Chewing: Cutting food into pieces and taking smaller bites causes one to eat slowly, chew properly, and this is very favorable for the digestive system.
- Customized Texture: Smaller or finely chopped portions provide the texture suited for people having problems with dental or chewing because they are easier to manage.
- Improved Portion Control: Small portions facilitate a more gradual pace of eating enabling one to enjoy food and preventing over indulgence.
What is the Role of First Aid in Choking Situations?
 The absence of it could lead to a loss of life. The inability to quickly recognize that a person is choking may cost the victim’s life. The most critical fact in this situation is getting the piece of food that has been stuck in the throat out. Techniques such as back blows and abdominal thrusts, commonly known as the Heimlich maneuver, are often employed. The basic aim of these procedures is to facilitate coughing, which will dislodge the foreign object. Where these don’t work, knowing when to seek assistance and how best to apply CPR if there is a need becomes paramount. First aid helps when one has to provide immediate medical assistance to the victim before the medical team arrives.
The absence of it could lead to a loss of life. The inability to quickly recognize that a person is choking may cost the victim’s life. The most critical fact in this situation is getting the piece of food that has been stuck in the throat out. Techniques such as back blows and abdominal thrusts, commonly known as the Heimlich maneuver, are often employed. The basic aim of these procedures is to facilitate coughing, which will dislodge the foreign object. Where these don’t work, knowing when to seek assistance and how best to apply CPR if there is a need becomes paramount. First aid helps when one has to provide immediate medical assistance to the victim before the medical team arrives.
Importance of Immediate First Aid for Choking
I want to simplify the notion of how important it is to perform first aid for choking. Yes, choking is one incident that is required to be managed swiftly as it may worsen with the slightest delay. One of the important points to note is that it is essential to keep one’s cool and go into action. The following parameters will try to emphasize the importance of immediate first aid:- Time Sensitivity: One of the most dangerous aspects of choking is that it cuts off the oxygen supply to the body. Once the airflow is blocked, brain damage can develop in as little as four minutes. Hence, the requirement for immediate response is great in order to avoid grievous injury.
- Recognition of Symptoms: Health practitioners should be very alert to the potential complications that arise when chronic choking is present, such as reproductive organ damage (females & males) as well as brain damage if airflow disruption occurs for more than a couple of minutes. There is also a risk of comatose assuming broad yes to society on the majority of occasions. People who get chronic choking usually suffer unless interventions like administering lazy mouth are applied. Chronic coughing or notable throat strangled are barriers to being successful in first-responding scenarios where immediate help is required.
- Effective Techniques: Performing back blows and abdominal thrusts are effective methods for dislodging an obstruction with ease. These methods are intended to aid in the clearance of the airway, and every person should be taught such lifesaving techniques.
- Preventing Panic: Giving calm and rational first aid to a patient also contributes to the prevention of panic in the person as well as the people's shoes around. This feeling of panic can assist in promoting the appropriate degree of focus, ensuring that tactics are utilized correctly.
- Emergency Response Knowledge: It is very important to be in the know about when to alert other emergency departments and staff when it is evident that the first aid received at the center isn’t adequate to maintain adequate patient status.
How to Dislodge the Object from the Airway
In the position of an operating practitioner, the most conceiving manner in alleviating the occlusion is by the use of back blows in conjunction with abdominal thrusts. First, place yourself behind the person who is choking. Using the heel of the palm, give five back blows between the s’ shoulder blades. If h this does not dislodge the obstruction, perform abdominal thrusts (known as the Heimlich maneuver). Standing behind the individual, make a fist with one hand and place it just above the individual’s navel, making sure that the other hand grasps it. Perform five inward and upward movements in quick succession. Continue alternating back blows and abdominal thrusts until the object is expelled. If the victim is unconscious, give him or her artificial respiration and call for medical assistance. These techniques are important, easy, and worth the trouble because they save lives when accurately executed.When Should You Begin CPR?
The golden rule that should always be borne in mind when starting CPR is time. CPR will always be appropriate in my case, already the presence of unconsciousness and unusual breathing is a signal for me to start breathing. No normal respiration, no pulse, these clearly show the need to do CPR. The faster CPR is started, the greater the chances of survival and the lower the risk of irreversible damage. Do remember to call ambulance services at the earliest - prolonged CPR and early professional intervention constitute the basis of successful emergency treatment. Every moment is important, and quick executive decisions are paramount!What are the Guidelines from the American Red Cross for Choking?
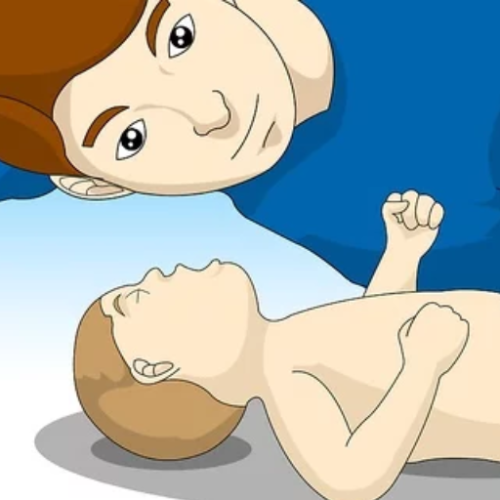
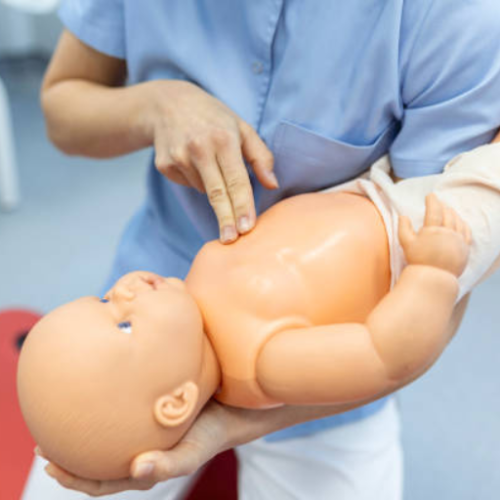
Let me summarize first what has been prepared by the American Red Cross with regard to choking; the procedure for any conscious adult or child has been to perform back slaps and abdominal thrusts, one after the other, similar to what has been described earlier. The protocol for the infants is a bit different, in which the recurrent event involves five gentle slaps on the back and five on the chest. The American Red Cross states that if the choking problem is not managed within a short period of time or the patient loses consciousness, emergency medical services must be called. Until emergency services arrive, continuous evaluation and modification of the interventions performed serve the greatest importance. As always, the focus would be on the safety and clearing of the airway of the incapacitated person.Understanding the American Red Cross Recommendations
The American Red Cross recommendations outline the steps that need to be taken in emergencies. The two essential things for CPR are starting chest compression and rescue breaths when the person is Pulseless and not breathing normally, and calling Emergency Medical Help as necessary. It is important to note that duration matters in terms of the chances of survival. Chest compression and rescue breaths are given in a specific ratio i.e 30:2 in case of adults, in case of emergencies where assistance has not yet arrived. When it comes to the American Red Cross and choking emergencies, it is important to note that different choking episodes require different approaches and the kind of person affected. If an adult or child is conscious, encourage them to perform himself. If an infant is choked on something, five back strokes followed by five gentle thrusts to the chest are to be performed. One should always review their immersion to make sure they have not changed for a while. If the person becomes unresponsive or unconscious and doesn't revive within a few minutes, please contact 911. A complete response to these emergencies, which also protects the person’s health and safety, is outlined by these steps.How to Address Choking Incidents in the Elderly
With the ever-increasing number of aged populations, the threats of choking incidents have shown to increase, and therefore, careful attention should be given when handling choking episodes in aged people. There is a substantial demographic gap in regard to age and increased chances of illness or trauma, which further complicates the physical responsiveness of elderly people. In case of a choking incident, before commencing any procedure, the first step is to confirm that the person's airway is clear. Once the airway has been confirmed, I apply a series of back slaps and thrusts to the abdomen according to the person’s strength. It is important to be gentle and yet deliver the force needed to avoid secondary injuries. During the intervention, I asked myself and continually checked the condition of the injured person. The need to call the emergency department is warranted if my primary approaches fail to relieve the obstruction or when the person is rendered unconscious. In times like these, one can hinder the effectiveness of the practice by remaining calm and showing confidence until medical assistance reaches the site. These steps help me to render my care safely while enhancing the welfare and safety of the elderly person who is involved in the incident.What are the Steps for First Aid if a Person is Choking?

- Assess the Situation: Open your eyes and check if the person is having a cough, speaking, or breathing; if they are not able to do so, it means the airway is completely blocked, and action is needed immediately.
- Call for Help: If you are tending to a person who is choking, engage someone who’s a bystander to call 911. If nobody is in sight, place the call yourself, and, if need be, put it on speakerphone.
- Apply Back Blows: This active rescue maneuver requires the first bystander to step back from the victim and place him in front of them. The asisted person is about to extend their upper body slowly forward, and upto five quick blows are administered inwards between their shoulder blades.
- Perform Abdominal Thrusts (Heimlich Maneuver): In case the earlier attempts have failed, first place another person to bear down on the victim's chest and the other will go behind the victim, putting their arms around the waist. Then make a fist with one hand above the navel and grasp with the opposing hand. Strike with the blade of your hand upwards in three quick motions.
- Repeat if Necessary: If nothing in this last round assessment works, then simply return each time to view the obstruction. Then, the last round still had back blows with five more under-placing thrusts. Alternatively, any throttling severs or strangulating bottoms to interfere with fainting did not ventilate.
- Seek Medical Assistance: However, attempt to push out the obstruction until it has been taken out or a physician has gotten in contact. Continuity in taking care of the patients who faint and have no pulse should be almost instantly CPR started.
How to Stand Behind the Person and Assist
The major lesson I have learned with regard to assisting someone who is choking is the importance of positioning myself relative to the patient. Whoever is assisting the person should place him or herself to one side at the back of the person she is trying to help. This will enable a stable and advantageous position during the procedure. Maintain a steady stance with one foot advanced to provide balance. When administering back blows, support the choking person's weight by leaning them forward with one hand while striking them with the other hand. In performing abdominal thrusts, it is important to place your hands where the maximum force is generated and still does not cause any harm. Above all, try to remain composed and instruct the choking person as well as other people who may be assisting.Using Back Blows and Abdominal Thrusts Safely
With respect to industry know-how, performing back blows and abdominal thrusts has its safeties, especially when the grasp of the technique and the need to execute comes into play. Start with ensuring the person is positioned appropriately, and their body is slightly leaned forward so that the position helps remove the blockage. Give back blows with hands over the settled area between the shoulder blades in a steady and controlled manner. For the abdominal thrusts, the pant-clenched fist should be positioned just above the navel and held with an opposing hand, followed by rapid, upward thrusts. Be sure to evaluate the situation on an individual basis and avoid abuse of force that could result in damage. It goes without saying that any case may take numerous tries, and time is of the essence, so stay relaxed and patient on the task.Ensuring the Airway is Clear
It is critical to quickly evaluate whether each intervention carried out was effective in clearing the airway. After back blows or abdominal thrusts, assessing whether the piece of material causing the obstruction has been removed is essential. People, in this case, should be encouraged to cough forcefully, as it may assist in the removal of the obstruction. Coupled with my experience in the industry, this practicing method works, as I always advocate for improvement indicators like the return of speech or normal breathing patterns. If the obstructor is not removed in a couple of tries, emergency services should be called immediately while still providing care to the patient. On all occasions, encourage the person and maintain your composure to mitigate anxiety as you are likely to be the one in tension.Reference
- Johns Hopkins Medicine: Choking First Aid
- Mayo Clinic: Choking First Aid
- American Red Cross: Adult & Child Choking First Aid
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are the primary causes of choking?
A: Choking occurs when a foreign object, such as a piece of food or small objects, becomes lodged in the throat or windpipe, blocking the flow of oxygen to the brain. This is one of the leading causes of choking, particularly in children younger than four, who often choke on small objects.Q: How can I help someone who is choking?
A: If the person is coughing forcefully, encourage them to keep coughing to try to dislodge the object. If they cannot speak, cough, or breathe, you should lean the person forward and deliver back blows with the heel of your hand between the person's shoulder blades. If necessary, use abdominal thrusts by standing or kneeling behind the person and wrapping your arms around their abdomen, making a fist with one hand, and placing it above the navel.Q: What should I do if a choking person becomes unconscious?
A: If the person is unconscious, you should immediately call emergency services and begin cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR). Use chest compressions to try to dislodge the object and provide life support until professional help arrives.Q: How do I prevent choking in children?
A: To prevent choking in children, keep small objects out of reach and avoid giving them hard or sticky foods that could block the windpipe. Supervise children while they eat, and teach them to chew food thoroughly. It's also important to stay up to date with first aid training, such as American Red Cross training, to know how to respond when choking occurs.Q: When should I call for emergency help during a choking incident?
A: Call for emergency help if the choking person cannot breathe, speak, or cough, if they become unconscious, or if the object cannot be dislodged and the person shows signs of severe distress. Immediate professional medical intervention is crucial in these situations.Q: Why is it important to act quickly when someone is choking?
A: Acting quickly is essential because choking can cut off oxygen to the brain, leading to brain damage or death within minutes. Prompt action can help dislodge the foreign object and restore airflow, increasing the chances of survival and preventing serious injury.Q: What role does positioning play in helping a choking person?
A: Proper positioning is vital in helping a choking person. Lean the person forward slightly and support the person's chest with one arm across it. This position allows gravity and the back blow to work effectively in dislodging the object. For infants, support the back of the infant's head and keep their body angled downward.Q: Are there any risk factors that increase the risk of choking?
A: Yes, certain risk factors can increase the risk of choking, such as eating too quickly, talking or laughing while eating, consuming alcohol, which might impair swallowing, and medical conditions affecting swallowing. Being aware of these factors can help you take precautions to prevent choking.Q: Why is it important to kneel down behind a choking child or small adult?
A: Kneeling down behind a choking child or small adult is important to ensure that you have the proper leverage and control when performing abdominal thrusts. This position allows you to apply the necessary force effectively to dislodge the object.790





 Login with Google
Login with Google Login with Facebook
Login with Facebook