It is common for people to choke on water from time to time. Knowing what to do in such a situation can greatly increase the victim's chances of surviving. Choking can lead to severe blood loss to the brain or even damage other body organs depending on the time taken to respond. In this guide, I will talk about the indications that a person is choking on water and how to pull somebody out of that situation. Let’s get started:
What are the Symptoms of ‘Choking’ on Water?
Choking on water is dangerous and requires assistance immediately. So, how would you know if someone is choking on water? The signs could be as subtle as an abnormal breathing pattern or the obvious signs of choking water. Such symptoms indicate that the person being choked requires immediate support. Here are some of the primary signs that can be observed:
- Coughing or Wheezing: Choking on water often triggers coughing or wheezing as the body tries to clear the obstruction from the airway.
- Difficulty Breathing: The person may exhibit difficulty breathing with labored or shallow breaths.
- Gagging or Gasping: Gagging or gasping for air can indicate that the person cannot adequately breathe.
- Clutching the Throat: The person may instinctively reach for their throat, a universal sign of choking.
How to Tell if Someone is Struggling to Breathe?
If a person is having difficulty locating a way to breathe due to water choking, panic actions might accompany such a challenging situation. Pay attention to these signs that may indicate that a person is unable to breathe properly:
- Panic or Fearful Expression: The person may display a panicked or fearful expression, indicating their breathing struggle.
- Turning Blue or Red: An individual unable to breathe properly may show bluish or reddish discoloration around their lips, face, or fingertips.
- Inability to Speak: If the person cannot speak or make any sounds, it may indicate that their airway is partially or completely blocked.
Common Reflex Responses When Something Goes Down the Wrong Pipe
Water forcefully going down the wrong pipe triggers the reflex responses of the body even while trying to bring the foreign object out of their passageways. An example of these reflex actions is:
- Coughing: Coughing helps bring out water or any other foreign object inserted in the body as it is the natural way amongst bodies to protect the airspace and its zones.
- Gagging or Retching: Klimers defines Gagging or Retching as another reflex action that the body utilizes to get rid of foreign bodies in the airways.
- Watery Eyes or Runny Nose: To set the irritation caused by water entering the wrong pipe, the body could react with excessive tear production or a runny nose, these excessive reactions are also reflex movements to clear the airways.
It is worth mentioning these reflex actions are useful to clear the airspace, but if the gagging/choking stubbornly persists, it is high time action is taken to help and, if deemed right, get emergency assistance.
What Should You Do if Someone Chokes on Water?
In a choking incident, it is crucial to act quickly and appropriately to help dislodge the obstruction and restore normal breathing. The Heimlich maneuver, also known as abdominal thrusts, is a widely recognized technique for clearing a blocked airway. Here are the steps to perform the Heimlich maneuver effectively:
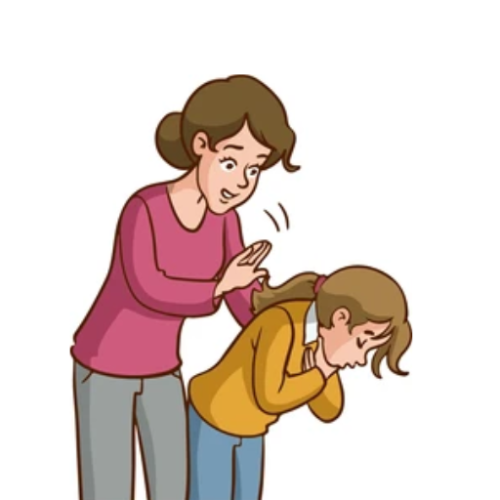
- Stand behind the person who is choking and slightly to the side.
- Place your arms around their waist and lean them forward.
- Make a fist with one hand and place the thumb against the person's abdomen, just above the navel.
- Grasp your fist with your other hand and give quick, upward thrusts into the abdomen, using your body weight to provide force. Each thrust should be firm and inward but not too forceful.
- Continue with these thrusts until the object blocking the airway is dislodged or until the person can breathe or cough forcefully.
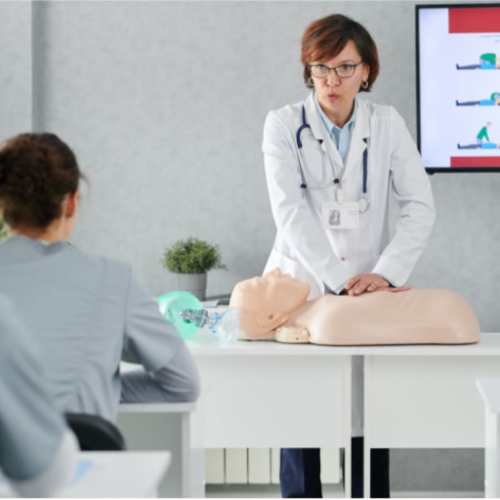
It is important to note that the Heimlich maneuver should only be performed on conscious individuals who cannot breathe, speak, or cough due to a severe obstruction in the airway. If the person becomes unconscious, immediately start CPR and call emergency services. It is always recommended to seek medical help after any choking incident, even if the object has been cleared.
Remember, quick and effective action can significantly improve the situation for someone who is choking. Stay calm, act promptly, and seek professional medical assistance.
How Can You Encourage Coughing to Clear the Airway?
The cough reflex is a body mechanism that removes an obstruction to the respiratory passage. It is an important mechanism that assists in getting rid of foreign bodies or secretions in the throat to avoid choking. In the event of an obstruction, the body begins an involuntary set of actions designed to clear the obstruction by forceful exhalation. The resultant sound is a cough.
Ways To Assist An Individual To Start Coughing Include:
- Promote Calm Breathing: If the individual has an airway blockage, it is crucial to stay composed and urge them to breathe slowly and deeply. This will allow the airway muscles to relax to some extent, which may help remove the blockage.
- Back Blows And Abdominal Thrusts: When patients have not succeeded in doing wonders about why they cough or breathe, back blows and abdominal thrusts can effectively remove airway modernization. Standing back to the person, apply deep back blows to the heel of your palm between the shoulder blades. If these back blows do not yield any result, then complete abdominal thrusts by placing your hands above the celiac's navel at his back and pulling thrusts.
- Modified Heimlich Maneuver: A modified Heimlich maneuver can be applied, especially to obese or pregnant individuals. Stand behind the person. Clasp your arms around the upper side of their chest. Then, place the palm of your hands roughly where the belly button is. Push in and up, which should help pull the object free.
When Coughing Doesn't Work: Next Steps
If they still cannot breathe or cough, try to go to the apps section and call emergency services while performing CPR for those who go unconscious. Do not ignore medical assistance even if the object is removed, as there can also be choking complications.
Acting quickly and professionally can make all the difference for a choking person. Try to work quickly, and if you are unsure, seek physician assistance.
What is Dry Drowning, and How Can You Prevent It?
Water aspiration is when one inhales water or other substances, which leads to respiratory tract complications. A dry drowning incident is somewhat related to breathing underwater and inhaling a spasm that leads to the lungs. Preventive measures on water safety and shedding light on the risks involved are essential to reduce the chances of a choking event. Here are some ways to avoid water choking and recognizing aspiration pneumonia after a water-related accident when possible:
- Supervision and Vigilance: A drowning incident can happen to children and inexperienced swimmers while they are in or around water, so it is best to supervise them as well while they are in the water to prevent over-exhaustion.
- Teach Proper Water Entry: Children and adults should not snorkel or hold their breath while entering the water, so it is important to correct this habit before it becomes a concern.
- Swimming Lessons: While swim lessons teach children and adults floating, breath control, and swim strokes are essential, children and adults should also be encouraged to keep practicing and sharpen their skills.
- Limit Diversions: Do not aim to play games or be involved in rough and tumble games while in the water, as they can be a diversion and increase the accidental inhalation of water.
- Do Not Go Beyond Skill and Comfort Levels: Swimmers or individuals using water for recreational activities should be encouraged to go within their sphere of comfort and skills. Water inhalation chances increase greatly when people go beyond what they are used to.
- Get Trained in CPR: Brushing up some skills in cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) or getting officially certified is essential. The sooner CPR is administered, the higher the chances of survival and the lower the complications in a choking incident.
- Make an Aspiration Pneumonia Diagnosis: You should be able to diagnose aspiration pneumonia after a water incident or near drowning. This might have followed a about of choking, with cough, shortness of breath, chest pain, fever, and fatigue as symptoms. In such cases, seek medical attention immediately.
Water safety measures always involve taking preemptive actions. You can minimize the chances of harming yourself or people around you while they’re in or around water by being cautious, trained, and dealing with any near-drowning or choking events swiftly. Be ready and careful, and always remember to prioritize safety around water.
How to Stay Calm During a Choking Incident?
It's crucial to remain composed while choking, as it will allow you to assist better the person who's choking. When aiding someone who is choking, you may follow these measures until the right kind of help arrives:
- Determining the Severity of the Situation: First, assess whether the person has a complete or partially obstructed airway, and if a person has a complete blockage, encourage them to cough, as it can help. However, you must take instant measures if they start talking or coughing.
- Using Back Blows and Abdomen Thrusts: While someone is choking, you should stand behind them and, using the palm of your hand, slam the midsection between the shoulder blades; these are called back blows, in case they don’t budge the object then switch to back thrusts which are also called the Heimlich maneuver. Make sure to implant your arms around the person's stomach and use one of your fists close to their stomach and above their navel; using your other hand, make repetitive thrusts upwards to aid in the removal of the object.
- Prompt the Choking Individual to Cough: Instruct the individual to inhale forcefully to dislodge the object from their throat. Tell them to maintain an open airway and refrain from doing anything that will cause the foreign object to go in more deeply.
- Notify the Emergency Services: If you cannot call for help, breathe, or cough, contact emergency services immediately! Don’t hang up; do as directed by the phone person.
- Continue Providing Assistance: If this person becomes unconscious, let the person down on the ground and start CPR if you have the relevant skills. Continue guiding the individual until the emergency response team comes.
Never forget that being composed helps you assist a person who is choking. These employable medical procedures will help you assert that you should go to another hospital for more help.
What are the risks of choking, and how can they be Mitigated?
Water can be classified as one of the most nourishing elements available, but choking on water also chills the body. Hence, one has to be careful while gulping on it. Water, if consumed incorrectly, could risk one’s health, which is why there are a few cardinal principles to follow regarding drinking. The following comprises the most vital tips to keep in mind:
Risk Factors for Choking on Water:
- Drinking Too Quickly: If someone swallows a large amount of water too quickly, the risk of choking on water increases significantly. So, refrain from excessively gulping or large amounts of water as such actions would deprive your throat of the time it needs to ensure smooth water circulation through the body.
- Talking Or Laughing While Drinking Water: People engage in conversation while drinking water, not realizing that a small amount of water can seep into their windpipe instead of the esophagus, resulting in choking. Drinking water and Odishu laughing should never be practiced together – so dont do that!
- Physical Conditions: Water, or any other liquid for that matter, if drunk, in an asymmetrically awkward position, can risk turning the water into a choking hazard as a structural abnormality, weakness in any of the throat muscles, and neurological disorder can increase the threshold for the water turning into a choking hazard. So when drinking something, always try to sit comfortably so you can avoid making the chances of water turning into a choking hazard negligible, and feel free to use more protective measures if need be.
Proper Swallowing Techniques:
Practicing proper swallowing techniques is essential to minimize the risk of choking on water. Follow these tips:
- Avoid Enlarging the Gulp: To make swallowing easier, taking small, controlled sips rather than “guzzle” the water is more prudent.
- Don’t Rush: There’s more freedom to pause for a moment after a sip of water and take the next one. This would prevent the water from flooding your mouth and remove it.
- Don’t Gulp First: Take care that every gulp or sip you take should have neglected the previous sip; otherwise, it results in all of them being intertwined and having a peppery taste.
Tips for Safe Drinking Habits:
To further reduce the risk of choking on water, consider these additional tips:
- Maintain an upright stance: Always sit up while drinking water. This way, the water flows easily down the throat with the aid of gravity.
- Avoid unnecessary distractions: Avoid activities such as watching television while drinking water, as they can be distracting. Instead, concentrate on the drink to ensure a safer consumption.
- Use suitable drinking tools: Containers that are easier to hold and have the right spout size should be used. This will limit the flow of water and, hence, potential spills or excessive intake.
Taking into consideration safe drinking habits lets one understand the risk factors that come from choking on water, which lets one reduce accidents and ensure one's well-being. When drinking water, always remember to be mindful; take small sips, and after every small sip, pause to allow the swallowing to take place. After all, it's important to keep hydrated but in a safe manner.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What are the signs that someone is choking on water?
A: Besides exhibiting panic and a worried face, water ingestion is indicated by a lack of breath, coughing, or speech inability. While attempting to remove the liquid from their mouth, one can also see them holding their throat and experiencing a round of coughing.
Q: How can I help someone who is choking on water?
A: Begin by helping the person in question by asking them to cough out loud, as the cough may help clear the airway. If they cannot cough, administer a few deep thrusts in their abdomen or some strong slaps between the shoulder blades.
Q: What should I do if someone tries to ingest water and cannot cough?
A: For instance, if someone shows the exact signs of water choking but cannot cough, one would use their arms to encircle their waist while gently but firmly pushing out the water from their stomach by pats or thrusts.
Q: Can coughing help clear water from the airway?
A: Yes, a cough can extract some water from the airway. Hence, it is better to advise a person to cough if he can, as this may help expel the fluid.
Q: What are the dangers associated with swallowing water?
A: Swallowing of water may cause significant lung damage and even death in extreme cases because such water would eventually cause drowning. Other medical conditions may also arise if water is inhaled, such as a shortage of air that doctors will likely treat.
Q: When should I seek medical assistance if a patient inhales water and is still breathless?
A: A medical professional should be called if a person is straining to breathe badly, is in a coma, or if later, if the conditions dont change after administering back blows/thrust to the abdomen, cyanotic CPR is needed.
Q: How can I ensure people do not choke on water when drinking it?
A: To prevent choking, one should avoid drinking water too quickly and instead sip it by taking small amounts. This is to avoid drinking too much water at once, which may lead to a loss of breath and thus cause choking.
Q: How important is CPR for the victim in situations involving water?
A: CPR, short for cardiopulmonary resuscitation, is helpful during water activities if a victim becomes unresponsive and cannot breathe. It can help keep the required oxygen in the body until medical assistance is received.
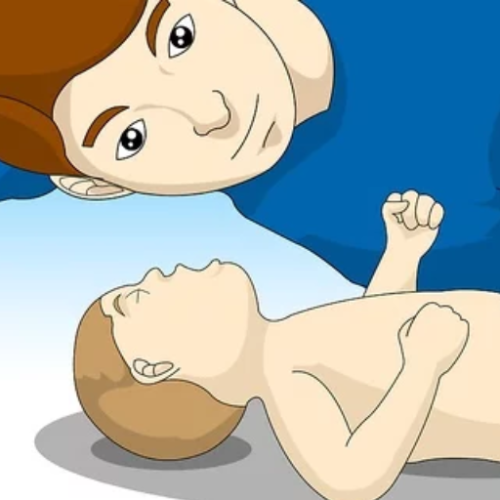
Q: What precautions should be taken for infants and small children who might have inhaled water?
A: First, check their level of consciousness and breathing capability. If inhalational water is being given, try to see if the children are coughing. Then, encourage them to cough. If they are struggling, do back blows and abdominal thrusts as appropriate, and contact a physician in case the condition worsens.
References
-
Choking on Water: Signs and What to Do After an Incident - This article discusses effective methods like coughing forcefully and using back blows to clear water from the airway.
-
What To Do If Someone Is Choking on Water - This source advises gently coughing to clear the airway and dislodge excess saliva.
-
Choking in Water: Immediate First Aid and Life-Saving Tips - This page provides tips on coughing softly to clear the airway and prevent further choking.














 Login with Google
Login with Google Login with Facebook
Login with Facebook