An avulsion wound is a serious injury where a portion of skin or tissue is forcibly torn away, often caused by accidents or trauma. These wounds require immediate attention to prevent infection and promote proper healing. In this blog, we’ll explain what an avulsion wound is, how it differs from other types of injuries, and the essential steps for treatment and recovery.
Understanding Avulsion Injuries
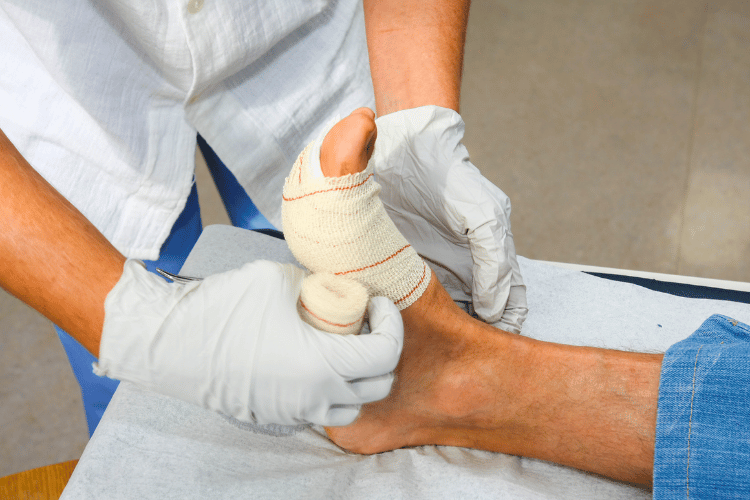
Avulsion injuries are a specific type of trauma that occurs when a body structure, such as skin, tissue, or even bone, is forcibly detached from its normal position. These injuries can range from minor to severe, depending on the extent of the detachment and the area affected. Understanding the nature and types of avulsion injuries is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment.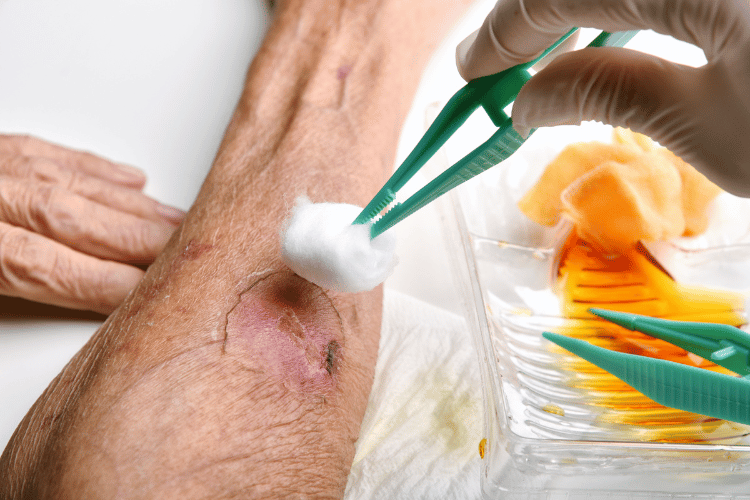
Avulsion Injuries
Definition of Avulsion
An avulsion refers to the tearing away of a structure from its point of attachment, often caused by sudden force or trauma. This can involve soft tissues like skin and muscles or even harder structures like bones and tendons. Avulsions are typically associated with high-impact incidents, such as sports injuries, accidents, or falls, where the force exerted on the body exceeds the strength of the tissue or attachment point. The severity of an avulsion can vary, with some cases requiring minimal intervention and others necessitating surgical repair.Types of Avulsion Injuries
Avulsion injuries can be categorized based on the type of tissue affected and the mechanism of injury. Below are the most common types:- Skin Avulsions: These occur when a section of skin is torn away from the underlying tissue. Skin avulsions are often seen in accidents involving sharp objects or machinery and may require skin grafts for repair.
- Tendon Avulsions: In this type, a tendon is pulled away from the bone, often taking a small fragment of bone with it. Tendon avulsions are common in athletes and can occur in areas like the fingers, shoulders, or ankles.
- Bone Avulsions: This injury involves a piece of bone being torn away from the main structure, usually at the site of a ligament or tendon attachment. Bone avulsions are frequently seen in high-impact sports or accidents.
- Muscle Avulsions: These occur when a muscle is forcibly detached from its attachment point, often resulting in significant pain and loss of function. Muscle avulsions are less common but can be severe when they occur.
Common Avulsion Injuries
Certain areas of the body are more prone to avulsion injuries due to their anatomical structure and exposure to stress or trauma. Below are some of the most frequently encountered avulsion injuries:- Fingertip Avulsions: Often caused by accidents involving doors, tools, or machinery, these injuries can range from minor skin tears to the complete loss of a fingertip. Treatment may involve wound care, splinting, or surgical repair.
- Ankle Avulsions: Common in sports like basketball or soccer, ankle avulsions occur when a ligament or tendon pulls away a piece of bone. Symptoms include swelling, pain, and difficulty bearing weight.
- Pelvic Avulsions: Seen in young athletes, particularly those involved in running or jumping sports, pelvic avulsions occur when a tendon or muscle pulls away from the pelvic bone. These injuries often require rest and physical therapy for recovery.
- Shoulder Avulsions: These injuries typically involve the rotator cuff or biceps tendon and are common in activities that involve repetitive overhead motions, such as swimming or baseball. Treatment may include physical therapy or surgery, depending on the severity.
Skin Avulsion: Causes and Symptoms
Skin avulsion is a severe type of injury that involves the tearing away of skin and sometimes underlying tissue from the body. This type of trauma can result from various accidents or high-impact incidents and often requires immediate medical attention to prevent complications such as infection or excessive blood loss.
Skin Avulsion
What is a Skin Avulsion?
A skin avulsion is a traumatic injury where a section of skin is forcibly detached from the underlying tissue. Unlike cuts or lacerations, which may leave the skin partially attached, an avulsion often involves the complete separation of the skin, leaving an open wound. Depending on the severity, the injury may expose muscles, tendons, or even bone. Skin avulsions are considered medical emergencies and often require advanced wound care, including sutures, skin grafts, or reconstructive surgery, to restore the affected area.Symptoms of Skin Avulsion
The symptoms of a skin avulsion can vary depending on the extent and location of the injury. However, some common signs include:- Severe Pain: The exposed nerves and tissue make avulsions extremely painful, especially if the wound is large or deep.
- Bleeding: Skin avulsions often result in significant bleeding, as the injury typically involves damage to blood vessels.
- Exposed Tissue: In more severe cases, the underlying tissue, muscles, or even bone may be visible.
- Swelling and Redness: The area around the wound may become swollen and inflamed due to the trauma.
- Risk of Infection: Open wounds from avulsions are highly susceptible to bacterial infections, which can cause additional redness, pus, or fever if not treated promptly.
Common Causes of Skin Avulsion
Skin avulsions are typically caused by high-impact or forceful incidents that exert significant pressure on the skin. Below are some of the most common causes:- Accidents with Machinery: Industrial or construction equipment, such as saws or conveyor belts, can easily catch and tear skin, leading to avulsion injuries.
- Motor Vehicle Accidents: High-speed collisions often result in severe trauma, including avulsions caused by friction or impact with sharp objects.
- Sports Injuries: Contact sports or activities involving falls, such as cycling or skateboarding, can lead to avulsions when the skin scrapes against rough surfaces.
- Animal Bites: Severe bites from dogs or other animals can tear away sections of skin, especially if the bite involves pulling or shaking.
- Falls or Slips: Falling onto sharp or jagged surfaces, such as rocks or broken glass, can result in skin avulsions, particularly on the hands, knees, or face.
Types of Avulsion Wounds
Avulsion wounds are injuries where tissue is forcibly detached from its original position, often exposing underlying structures such as bone, muscle, or tendons. These injuries can occur in various parts of the body, each presenting unique challenges and requiring specific treatment approaches. Below are some common types of avulsion wounds.Periosteal Avulsion
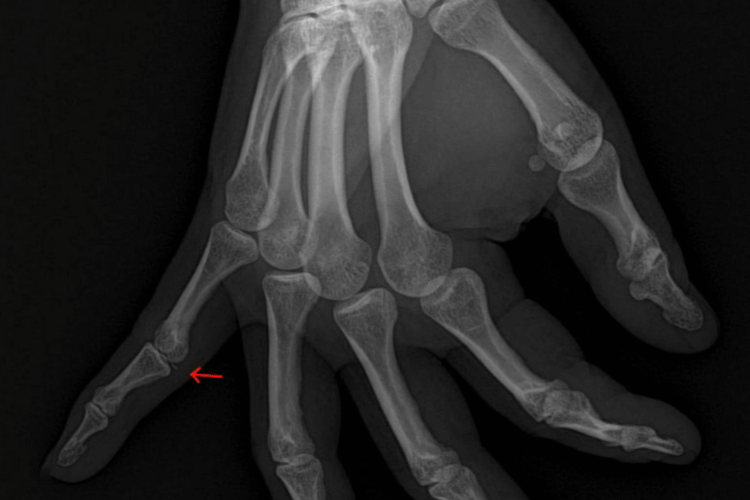 A periosteal avulsion occurs when the periosteum, a thin layer of connective tissue that covers bones, is torn away due to trauma or excessive force. This type of injury is often associated with high-impact accidents, such as falls or sports injuries, where ligaments or tendons pull on the periosteum with enough force to detach it from the bone.
Symptoms of periosteal avulsion include localized pain, swelling, and difficulty moving the affected area. In severe cases, the injury may expose the bone, increasing the risk of infection. Treatment typically involves immobilizing the area to allow healing, but surgical intervention may be necessary if the detachment is extensive or if there are complications like fractures.
A periosteal avulsion occurs when the periosteum, a thin layer of connective tissue that covers bones, is torn away due to trauma or excessive force. This type of injury is often associated with high-impact accidents, such as falls or sports injuries, where ligaments or tendons pull on the periosteum with enough force to detach it from the bone.
Symptoms of periosteal avulsion include localized pain, swelling, and difficulty moving the affected area. In severe cases, the injury may expose the bone, increasing the risk of infection. Treatment typically involves immobilizing the area to allow healing, but surgical intervention may be necessary if the detachment is extensive or if there are complications like fractures.
Nail Avulsion
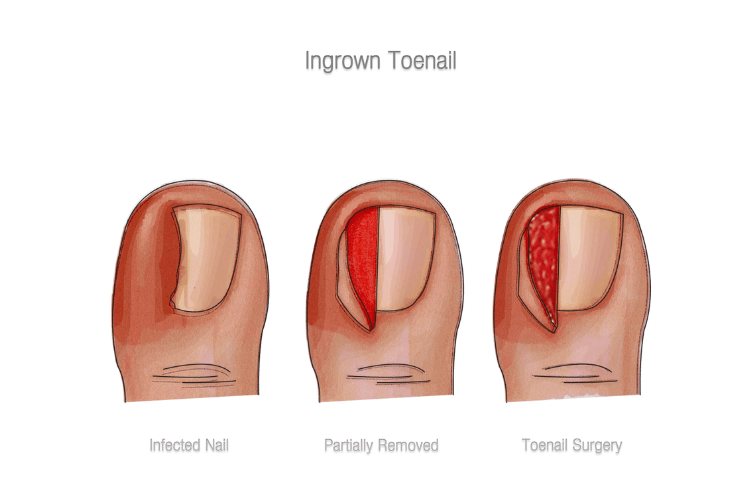 Nail avulsion refers to the partial or complete detachment of a fingernail or toenail from its nail bed. This type of injury is commonly caused by blunt trauma, such as stubbing a toe, or by crushing injuries involving heavy objects. Nail avulsions can also occur due to repetitive stress, fungal infections, or medical procedures like ingrown toenail removal.
Symptoms include intense pain, bleeding, and swelling around the nail bed. In some cases, the exposed nail bed may be highly sensitive to touch or pressure. Treatment depends on the severity of the injury. Minor cases may only require cleaning and bandaging, while more severe avulsions might necessitate surgical removal of the nail and antibiotics to prevent infection. Regrowth of the nail can take several months, depending on the extent of the damage.
Nail avulsion refers to the partial or complete detachment of a fingernail or toenail from its nail bed. This type of injury is commonly caused by blunt trauma, such as stubbing a toe, or by crushing injuries involving heavy objects. Nail avulsions can also occur due to repetitive stress, fungal infections, or medical procedures like ingrown toenail removal.
Symptoms include intense pain, bleeding, and swelling around the nail bed. In some cases, the exposed nail bed may be highly sensitive to touch or pressure. Treatment depends on the severity of the injury. Minor cases may only require cleaning and bandaging, while more severe avulsions might necessitate surgical removal of the nail and antibiotics to prevent infection. Regrowth of the nail can take several months, depending on the extent of the damage.
Eyelid Avulsion
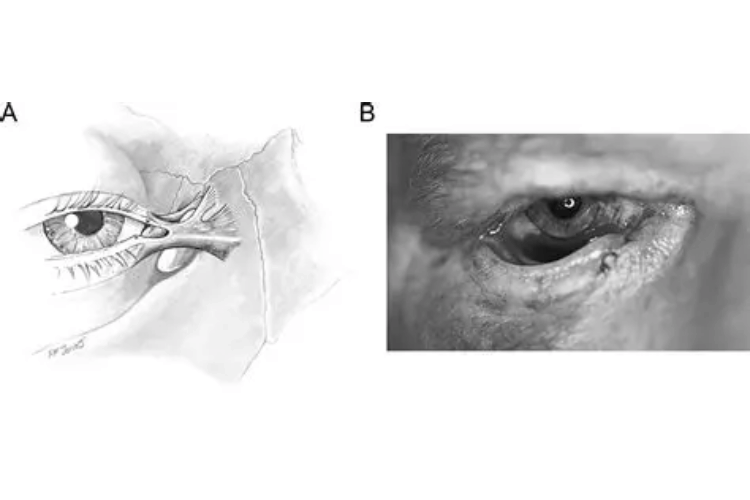 Eyelid avulsion is a rare but serious injury where part or all of the eyelid is torn away from its attachment to the surrounding tissue. This type of avulsion is often caused by sharp objects, animal bites, or high-impact trauma, such as car accidents. Eyelid avulsions are particularly concerning because they can affect the eye's ability to function properly and may lead to complications like corneal damage or vision loss.
Symptoms include severe pain, bleeding, and visible detachment of the eyelid. The injury may also expose underlying structures, such as the conjunctiva or orbital muscles. Immediate medical attention is crucial for eyelid avulsions, as surgical repair is often required to restore both the appearance and functionality of the eyelid. Post-surgical care may include antibiotics, pain management, and follow-up procedures to address any complications.
Understanding these types of avulsion wounds highlights the importance of prompt medical evaluation and tailored treatment to minimize complications and promote recovery. Each type of avulsion presents unique challenges, making early intervention critical for optimal outcomes.
Eyelid avulsion is a rare but serious injury where part or all of the eyelid is torn away from its attachment to the surrounding tissue. This type of avulsion is often caused by sharp objects, animal bites, or high-impact trauma, such as car accidents. Eyelid avulsions are particularly concerning because they can affect the eye's ability to function properly and may lead to complications like corneal damage or vision loss.
Symptoms include severe pain, bleeding, and visible detachment of the eyelid. The injury may also expose underlying structures, such as the conjunctiva or orbital muscles. Immediate medical attention is crucial for eyelid avulsions, as surgical repair is often required to restore both the appearance and functionality of the eyelid. Post-surgical care may include antibiotics, pain management, and follow-up procedures to address any complications.
Understanding these types of avulsion wounds highlights the importance of prompt medical evaluation and tailored treatment to minimize complications and promote recovery. Each type of avulsion presents unique challenges, making early intervention critical for optimal outcomes.
Treatment Options for Avulsion Wounds
Avulsion wounds require prompt and appropriate care to minimize complications such as infection, excessive bleeding, or delayed healing. The treatment process typically involves immediate first aid, ongoing wound care, and advanced medical interventions when necessary. Below is a detailed guide to the treatment options for avulsion injuries.Initial Care for Avulsion Injuries
The first step in managing an avulsion wound is to provide immediate first aid to stabilize the injury and prevent further damage. Start by applying direct pressure to the wound using a clean cloth or sterile gauze to control bleeding. Elevating the injured area above heart level can also help reduce blood loss. If the avulsed tissue is still attached, gently reposition it without forcing it back into place. For completely detached tissue, carefully wrap it in a clean, damp cloth and place it in a sealed plastic bag. Keep the bag on ice to preserve the tissue for potential reattachment. Avoid placing the tissue directly on ice, as this can cause further damage. Once the bleeding is under control, cover the wound with a sterile dressing and seek immediate medical attention.Wound Care Techniques
Proper wound care is essential for preventing infection and promoting healing. After initial treatment, the wound should be cleaned thoroughly to remove debris and reduce the risk of bacterial contamination. This is typically done using saline solution or an antiseptic wash. Avoid using harsh chemicals like hydrogen peroxide, as they can damage healthy tissue. Once the wound is clean, apply an antibiotic ointment to reduce the risk of infection and cover it with a sterile, non-stick dressing. Dressings should be changed daily or as directed by a healthcare provider, ensuring the wound remains clean and dry. Monitoring for signs of infection, such as increased redness, swelling, or discharge, is crucial during the healing process. In cases where the avulsion involves exposed bone, tendons, or other deep structures, more advanced wound care techniques may be required. This can include the use of specialized dressings, such as hydrocolloid or foam dressings, to maintain a moist healing environment and promote tissue regeneration.Treatment Methods for Healing
The specific treatment methods for avulsion wounds depend on the severity and location of the injury. Below are some common approaches:- Suturing or Stapling: For minor avulsions where the tissue is still viable, sutures or staples may be used to reattach the skin and close the wound. This helps reduce scarring and speeds up the healing process.
- Skin Grafts: In cases where a significant amount of tissue is lost, skin grafts may be necessary. This involves taking healthy skin from another part of the body and transplanting it to the injured area to cover the wound.
- Surgical Debridement: For wounds with extensive contamination or dead tissue, surgical debridement may be required to remove damaged tissue and create a clean environment for healing.
- Vacuum-Assisted Closure (VAC) Therapy: This advanced technique uses a vacuum device to create negative pressure around the wound, promoting blood flow and accelerating tissue repair.
- Antibiotics and Pain Management: Depending on the risk of infection, oral or intravenous antibiotics may be prescribed. Pain management is also an important aspect of treatment, often involving over-the-counter or prescription medications.
Wound Healing and Recovery
The healing and recovery process for wounds, particularly avulsion injuries, can vary significantly depending on the severity of the injury and the care provided. Understanding the factors that influence healing, the stages of recovery, and when to seek medical attention is essential for ensuring optimal outcomes.Factors Affecting Wound Healing
Several factors can impact the speed and effectiveness of wound healing. These include both internal and external influences that either promote or hinder the body’s natural recovery process:- Severity of the Injury: The depth and size of the wound play a significant role in determining how quickly it heals. Larger or deeper avulsion wounds often require more time and advanced medical interventions.
- Age and Overall Health: Younger individuals and those in good health typically heal faster due to better circulation and immune function. Chronic conditions like diabetes or vascular diseases can slow the healing process.
- Infection Risk: Wounds that are not properly cleaned or cared for are more susceptible to infection, which can delay healing and lead to complications.
- Nutrition: A diet rich in vitamins, minerals, and proteins supports tissue repair and regeneration. Nutritional deficiencies can impair the body’s ability to heal.
- Smoking and Alcohol Use: Smoking reduces oxygen flow to tissues, while excessive alcohol consumption can weaken the immune system, both of which negatively affect wound healing.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as corticosteroids or chemotherapy drugs, can interfere with the body’s ability to repair damaged tissue.
Avulsion Wound Healing Process
The healing process for avulsion wounds typically occurs in three distinct stages, each playing a critical role in recovery:- Inflammatory Phase: This initial stage begins immediately after the injury and lasts for a few days. During this phase, the body works to stop bleeding through clot formation and initiates an immune response to prevent infection. Swelling, redness, and warmth around the wound are common during this time.
- Proliferative Phase: In this stage, which can last several weeks, new tissue begins to form as the body produces collagen and other proteins to repair the damaged area. Blood vessels regenerate, and the wound starts to close as granulation tissue develops.
- Maturation Phase: The final stage of healing can take several months, depending on the severity of the wound. During this phase, the newly formed tissue strengthens and remodels, and the scar becomes less prominent over time.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While many wounds can be managed at home with basic first aid, certain situations require prompt medical evaluation. Seek professional care if you experience any of the following:- Excessive Bleeding: If the wound continues to bleed heavily despite applying pressure, medical intervention is necessary.
- Signs of Infection: Redness, swelling, warmth, pus, or a foul odor from the wound may indicate an infection that requires antibiotics.
- Exposed Structures: If the wound reveals underlying tissues such as bone, tendons, or muscles, immediate medical attention is critical.
- Delayed Healing: If the wound shows no signs of improvement after several days or appears to worsen, consult a healthcare provider.
- Severe Pain or Fever: Persistent pain or a fever may signal complications that need to be addressed by a medical professional.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is an avulsion wound?
A: An avulsion wound is a severe injury where a portion of skin and, in some cases, underlying tissue is forcibly torn away from the body. This type of injury often results from accidents involving machinery, falls, or sharp objects. The severity can range from minor skin loss to extensive tissue damage, depending on the force and area affected.
Q: What are the signs of infection in an avulsion wound?
A: Signs of infection in an avulsion wound include increased redness, swelling, warmth around the wound, pus or fluid discharge, and fever. If you notice any of these symptoms, it is essential to seek immediate medical attention to prevent complications such as delayed healing or systemic infection.
Q: How should I clean an avulsion wound?
A: To clean an avulsion wound, gently rinse it with clean, lukewarm water to remove dirt and debris. Avoid using harsh substances like alcohol or hydrogen peroxide, as they can damage healthy tissue and delay healing. After cleaning, apply an antibiotic ointment and cover the wound with a sterile bandage to protect it from infection.
Q: What types of treatment options are available for avulsion wounds?
A: Treatment for avulsion wounds depends on the severity of the injury. Minor wounds may only require cleaning, dressing, and regular monitoring. More severe injuries might need sutures, skin grafts, or surgical procedures to reattach torn tissue or repair underlying structures like tendons or muscles.
Q: What is the healing time for an avulsion wound?
A: The healing time for an avulsion wound varies based on the extent of the injury and the treatment provided. Small wounds may heal within a few weeks, while more severe injuries can take several months. In some cases, additional treatments like physical therapy or follow-up surgeries may be required to ensure full recovery.
Q: Can avulsion wounds lead to amputation?
A: In extreme cases, where a large portion of a limb or body part is avulsed, there is a risk of amputation. This typically occurs if the blood supply cannot be restored or if the tissue is too damaged to heal. Immediate medical care is critical to assess the injury and explore options to save the affected area.
Q: What is a skin graft and when is it used?
A: A skin graft is a surgical procedure where healthy skin is transplanted to cover an area with significant skin loss, such as from an avulsion wound. Skin grafts are commonly used for large or deep wounds that cannot heal naturally, helping to promote recovery, reduce scarring, and restore functionality to the affected area.
Q: How can I prevent infection in an avulsion wound?
A: To prevent infection in an avulsion wound, keep the wound clean and dry, and cover it with a sterile dressing. Change the bandage regularly and apply an antibiotic ointment as directed. Additionally, monitor for signs of infection, such as redness or swelling, and seek medical care promptly if symptoms develop.
Q: What is a brachial plexus avulsion?
A: A brachial plexus avulsion is a specific type of nerve injury where the nerves controlling the arm and hand are torn away from the spinal cord. This can result from trauma, such as a high-impact accident, and may lead to loss of movement or sensation in the affected limb. Immediate medical evaluation is necessary to determine the extent of the injury and explore treatment options, which may include surgery or physical therapy.
Conclusion
Avulsion wounds are severe injuries that demand prompt and proper care to minimize complications and ensure effective healing. By understanding the nature of these wounds and following the appropriate treatment steps, you can reduce the risk of infection and promote a faster recovery. Always seek medical attention for avulsion wounds to ensure the best possible outcome.













 Login with Google
Login with Google Login with Facebook
Login with Facebook