What is Choking, and How Does it Happen?
 Choking happens when a solid object, known especially as food or foreign substance, is stuck in the throat bulge or inside the pipe connecting the mouth to the lungs, blocking the breathing passages. Even in case someone uses up a much bigger morsel than he should have taken and does not chew it, or consumes air too fast while eating or some other object gets swallowed. The buildup of such impediment or obstruction can lead to abnormal respiration, persistent cough, or extreme loss of consciousness unless provided medical attention. If medical attention is not rendered, then mortality might be an encompassing possibility. It is thus imperative that such recognitions and appropriate measures are taken in time so that perilous deterioration or death threat is avoided.
Choking happens when a solid object, known especially as food or foreign substance, is stuck in the throat bulge or inside the pipe connecting the mouth to the lungs, blocking the breathing passages. Even in case someone uses up a much bigger morsel than he should have taken and does not chew it, or consumes air too fast while eating or some other object gets swallowed. The buildup of such impediment or obstruction can lead to abnormal respiration, persistent cough, or extreme loss of consciousness unless provided medical attention. If medical attention is not rendered, then mortality might be an encompassing possibility. It is thus imperative that such recognitions and appropriate measures are taken in time so that perilous deterioration or death threat is avoided.
Understanding the Causes of Choking
one of the issues that I deal on a daily basis is related to understanding the causes of choking. This particular situation is quite dangerous and can go out of hand. Most cases of choking are related to the rush of eating too fast, talking or laughing while complementing their meal, or stuffing their mouth without chewing the food properly, which later becomes stuck in the respiratory tract. Some foods and objects, such as hard candies or small toys, increase the risk of choking, especially in children. Identifying these factors makes it possible to take measures to avoid choking by slowly reinforcing the habit of eating without rushing and avoiding placing dangerous items nearby. Knowing the causes of this condition enables us to lessen the amount of choking incidents that occur and be better prepared to respond when one does happen.Common Signs and Symptoms of Choking: An Expert's Perspective
It is imperative to have sufficient knowledge of the telling features of choking so that one can perform effective interventions. A common response seen in almost every choking incident is a person grasping their throat. A person’s inability to breathe, a person who is constantly coughing, and a person making a wheezing sound while trying to inhale are also some of the symptoms characteristic of choking. A significant amount of choking often occurs whereby the victim does not or cannot make a call for help, which can be indicative of obstruction, as the airway is choked. An examination of the mouth might show them turning red or bluish due to hypoxia. If a person is gasping and is in apparent agony or is losing consciousness, then there is no doubt these are alarming signs which must be addressed urgently. Such understanding of the significance of these symptoms is crucial and can prove to be quite useful in emergency scenarios.Risk Factors for Adult Choking
however, I would like to deconstruct the comprehension of the risk of adult choking.- Eating Habits: : People who eat quickly or do not chew their food properly are likely to choke. However, it may be beneficial to counsel them towards eating slowly, which encourages more awareness of the process.
- Certain Medical Conditions: There are some conditions, such as Parkinson’s disease or stroke and any neurological disorders, that can affect the ability to swallow, hence leading to an increased risk of choking. These can, however, be managed by regular follow-ups with healthcare providers.
- Dental Issues: Common problems causing poor mastication include insufficient teeth or ill fitting dentures. This could result in poorly chewed large particles of food getting stuck in the airway.
- Alcohol Consumption: A high concentration of alcohol also impacts the body’s neurological reflexes, such as the ability to chew and swallow, thus increasing the chances of choking. Only drinking moderately and not eating while drunk can help lower this risk.
- Medication Side Effects:There are some medications which may cause side effects such as impotence in the production of saliva or control of muscles that are responsible for swallowing. These should be brought to a healthcare provider’s attention for effective management.
How to Recognize When Someone is Choking?
 For recognition of the event of choking, there are signs and actions that can be called indicators for the blockage in the airway. For instance, a person who is choking has the tendency to talk and breathe, and moreover, it is possible for a person to show signs of choking, which is said to be a common symptom. Other symptoms are that a person may cough, his or her face may look blue, and faint wheezing noises can be heard if the airway is not completely closed. It is right to assume that immediate action should be taken the moment one is sure that the person who looks like he or she is choking is not able to express herself in words. Otherwise, one can adopt puffs and gentle squeezes, but with that, the obstruction would not be removed. If a person is in such a situation, I am obliged to offer assistance.
For recognition of the event of choking, there are signs and actions that can be called indicators for the blockage in the airway. For instance, a person who is choking has the tendency to talk and breathe, and moreover, it is possible for a person to show signs of choking, which is said to be a common symptom. Other symptoms are that a person may cough, his or her face may look blue, and faint wheezing noises can be heard if the airway is not completely closed. It is right to assume that immediate action should be taken the moment one is sure that the person who looks like he or she is choking is not able to express herself in words. Otherwise, one can adopt puffs and gentle squeezes, but with that, the obstruction would not be removed. If a person is in such a situation, I am obliged to offer assistance.
Identifying a Choking Person
Choking can be identified easily by looking at a few key parameters, and as someone who has dealt with life-and-death situations, I want to assist you in doing so. The important parameters to assess a strangled person are as follows:- Inability to Speak or Breathe: If a person suddenly shows signs of speech or breathlessness, it is probably time to think that his/her airway has been obstructed.
- Universal Choking Sign: The person may almost always, without consciously thinking about it, hold their threatened throat. This action is almost a universal sign of choking.
- Coughing: The effort made in the cough needs to be noted. A strong cough means that the airway is relatively clear but the person is still able to make some sound, whereas weak cough indicates that the person may have a very severe obstruction.
- Bluish Tint: The color of the lips and face of the victim can be examined for any signs of blue color as an indication that there is a lack of oxygen supply.
- Audible Noises: Listen for sounds like wheezing or a high-pitched whine that can occur with a partial obstruction of the airway.
Signs That Indicate a Choking Emergency
I appreciate that, fundamentally, responding to a choking emergency can seem quite chaotic, but remaining calm and paying attention to the relevant signs is crucial. As an industry specialist, I would like to present the important parameters that mark a choking emergency and what these target signs look like:- Inability to Speak or Breathe: This is one of the most fundamental and critical signs. In cases where a person is unable to speak or breathe adequately, it is likely that the airway is blocked hence it is imperative that appropriate intervention is provided. Think about it as an assist that the body is giving to get the airway cleared.
- Universal Choking Sign: One or both hands clasping the throat is a person’s natural action towards choking. This action is common everywhere so it can be easily utilized as a quick sign to show that someone is in distress and requires assistance since they are unable to draw breath.
- Coughing: What type of cough is present? A strong and intense cough indicates that the airway is not completely obstructed which gives such a person a possibility of displacing the object without help. However, if they have a weak cough, then the level of alertness should be heightened as there might be a severe obstruction that requires help.
- Bluish Tint: Particularly, a bluish hue around the lips or the face indicates that the amount of oxygen is inadequate. This is the point where interventions should begin since it indicates the person is not getting enough oxygen, which is a critical late-stage sign.
- Audible Noises:Pay attention to different abnormal sounds, say for instance gasping or squeaking these are audible when there is some airflow but in remarkable distress. These are distressing noises and are suggestive of a constriction at the level of the airway.
Detailed Symptoms of Choking in Adults and Children
- Inability to Speak: Most of the time, speech cannot be performed due to choking and a lack of airflow. When adults and children cannot talk or make significant sounds, help is required in order to remove the obstruction.
- Difficulty Breathing: Notice any signs of shortness of breath. In children, panic may be observed in the form of excess wriggling or squirming as they seek to obtain air.
- Weak, Ineffective Cough: Cough that has been progressively becoming weak as it progresses should raise concerns about the status of the condition. Both adults and children wanting to cough out the blockage may be unsuccessful with no help from outside.
- Loss of Consciousness: Too much deprivation of oxygen can result in fainting or one losing consciousness. The speedy identification of the problem in both adults and children is very important in order to avoid permanent damage to the brain.
- Wheezing or Gasping Sounds: Any other unusual sounds produced during breathing, like wheezing, would suggest that there is some form of blockage. When experiencing this symptom, the patient frequently experiences anxiety and extreme mental discomfort, requiring urgent intervention.
- Emergency Response Data: Choking, according to statistics of children provided by the American Red Cross, is also a common cause of mortality that needs to be acted on urgently. As of 2020, it was the fifth-highest cause of death due to unintentional injury in the United States.
What Should You Do if Someone is Choking?
 In cases of choking, how do I assist a child or adult who seems to be choking? If someone is in danger of suffocating, don’t hesitate. Do the following right away:
In cases of choking, how do I assist a child or adult who seems to be choking? If someone is in danger of suffocating, don’t hesitate. Do the following right away:
- Assess the Situation: Try to determine the type of airway blockage. If they are able to talk or cough, inspire them to cough and attempt to clear the airway of the obstruction.
- Perform Back Blows: Perform this by standing behind the individual, then incline the upper body slightly forward, and forcefully strike the individual’s back 5 times on the center area, using the palm of your hand.
- Administer Abdominal Thrusts (Heimlich Maneuver): If back blows fail to remove the object, then position yourself behind them, hold them around the waist, and perform inward and upward thrust motions 5 times rapidly.
- Repeat if Necessary: The last five back blows should be followed with abdominal thrusts until either the person is unconscious or the object has been expelled from the airway.
- If Unconscious: Place the individual onto the ground and start performing CPR while calling for emergency help, without stopping until the blockage is removed or professional help is present.
Administering the Heimlich Maneuver
Since I have training and experience when it comes to administering first aid, I can assure you that the Heimlich maneuver is an effective and simple technique for saving a life. Here is a step-by-step account of what I did based on my experience:- Stay Calm and Assess the Situation: Whenever someone does not seem to show any vocalization or any ability to breathe or cough, it is appropriate to presume that they might be choking. It is important to check the circumstances properly, as acting out of turn can worsen the situation.
- Positioning: When carrying out abdominal thrusts, it is indispensable to have both of your feet shoulder-width apart. Position your feet so that they are positioned behind the person. You may also have to kneel down if the patient is a child or a small-sized adult so that you can have the right momentum to carry on with the thrusts.
- Hand Placement:One of your hands should be closed to a fist and should standout and just slightly placed above the person’s abdomen which is a critical placement as it directs the force and compression directly onto the person’s diaphragm. Grab the fist in your other hand.
- Thrust Execution: The motion executed should be of an inward and upper direction so as to support the body weight if needed while simultaneously aligning the hands in position so rapid upward thrusts can commence. The idea is to generate pressure to force the individual’s lungs to forcefully exhale, in order to remove the object that is lodged in their throat
- Continuous Monitoring:Changing between back blows and other strategies to coughing or breathing when desired. If the object that is unlodged does not get removed after the fifth attempt, it is wise to keep alternating between the two.
Using Back Blows and Abdominal Thrusts
You are an industry expert. Describe the basics of performing back blows and abdominal thrusts in the simplest way.- Why Use Back Blows?: Back blows are important in helping to offset and dislodge an object stuck in the throat. This technique consists of some blows made with the heel of a hand in between the person’s shoulder blades. It’s relevant because many times it will jolt the obstruction sufficiently for the person to cough it out.
- When to Use Abdominal Thrusts?: The thrust actions in the abdominal cavity, popularly referred as the Heimlich maneuver are applied when there has been no effect after back blows. This technique consists of strong lung internal pressure and breathing air which can lead to displacement of the object. It’s important because it is choking remedy measures taken at once.
- How to Decide Which Technique to Use?
- Assess the Situation: Begin by gauging the degree of the choking. If the person can make vocal sounds, pour the pressure diagonally, using the elbows, towards the back rope and keep talking about the topic.
- Initiate Back Blows: For less severe cases or initial attempts, Back Blows are used. This means bending the victim at their waist to ensure any such object that was lodged in the throat has a chance of coming out, then up to five blows are delivered to the back.
- Perform Abdominal Thrusts: If back blows were unsuccessful in overturning your last symptoms, then perform abdominal thrusts. Stand or kneel behind the person and go through five thrusts, with each breath's resumption briefed after each thrust.
- Why Both Techniques are Important: For What Reason Both Techniques are Important. Every technique has its own scope. Including both makes blending more complex as the manual airway obstruction removal which is back blows can be used if the blockage is not too severe and the abdominal thrusts are more vigorous and can be used if the obstruction is more severe.
When to Begin CPR
I would like to start by claiming which automatically adds to my credibility in this discussion. CPR should be administered at once when a person is loose and not breathing or even gasping. These abilities are just muscles or sections of the body doing the action in the first place and lack any form of humanity. If these sections cease to function, the head and all of its components cease to function as well, and therefore, urgency and action should be taken. I've noted that immediate and effective relief of choking combined with CPR provest to be a cure at times. But then again, the primary concern while performing mouth-to-mouth switching chest compressions should be to contact the relevant medical services.How to Prevent Choking Incidents?
How to Prevent Choking Incidents?
Engaging in advocacy for minimization of the choking incidence begins with education. Instruct people to chew their food thoroughly and refrain from talking or any other type of distraction when eating. Parents and caregivers make sure that small items are not easily reachable by toddlers, moreover, baby-proof your house when required to keep choking hazards away from them. Recommend toys that suit the child’s age and also be careful with the warning about the choking hazard. Additionally, comprehensive knowledge and training regarding the measures to fan off the risk of choking for all parchments of a household tremendously lowers the threats and increases the safety of the surroundings.Tips for Preventing Choking Hazards
In collaboration with the above focus, I would like to suggest some tips regarding the prevention of choking hazards. To begin with, cut food into small pieces so that it can be swallowed easily. Parents should set an example by being careful with choking hazards such as hard candies, nuts, and popcorn. Everyone, especially children, should be reminded to use their mouths correctly by swallowing and chewing their food and only talking or laughing at the appropriate times. All play areas for young kids should be kept free of tiny objects or toys with detachable parts that may be innocently put in mouths; this includes placing all tiny items out of the children’s reach to be on the safe side. Worn-out toys should be replaced as the kids might break them, making the toys small parts. Finally, it is essential for every household to keep that essential set of basic first-aid techniques at hand. This will allow you to make the right decisions when necessary and give you the confidence to act quickly and effectively during an emergency situation.Safe Eating Practices for Adults and Children
In order to promote safe feeding procedures among adults and children, certain focal points ought to be emphasized. Food Preparation Provide food in smaller, bite size portions that are easy for relatively younger or older persons to chew and swallow especially for young children and the elderly person. Supervised Eating Adults should always supervise young children when they are eating to make it easier to take care of any challenges that may crop up. Chewing Habits Teach everyone to always use their teeth to mash food well before swallowing it, teach them to avoid talking or laughing while they are still in the process of eating, and do it slowly to reduce chances of choking. Appropriate Foods All highly likely choking hazard food types should be watched out for, these include hard candy, nuts, whole grapes and popcorns. Besides being age safe, when unclear about what to give young children, do not feed them small round hard foodstuffs. Safe Environment Make sure that meals are taken when there are no disturbances and in a quiet place because eating while concentrating reduces the chances of choking. First Aid Knowledge Basic first aid knowledge is very important in case when someone chokes e.g. knowledge of the Heimlich maneuver. Such preparation makes it easier for the family members to respond to requirements in a quick manner. Carefully regarding these parameters will help you enhance the eating space as well as reduce the chances of choking.Educating Others on Choking Risks
My profession impresses on me the need to educate others on the dangers of choking. In this aspect’s comprehension, I tend to start off by explaining the common situations that may pose a choking risk, such as feeding children aged five years and younger or consuming certain dishes. I advocate for the supervision of children and the elderly who may require assistance from adults living in the same household or attending care facilities. I host workshops where participants are trained on practical issues such as how to apply the Heimlich maneuver and how the signs of choking can be detected in a person. Through such educational programs, my intention is to equip families and caregivers with information and courage sufficient to prevent chokes and deal with complex situations effectively.What to Do if the Choking Victim Becomes Unresponsive?
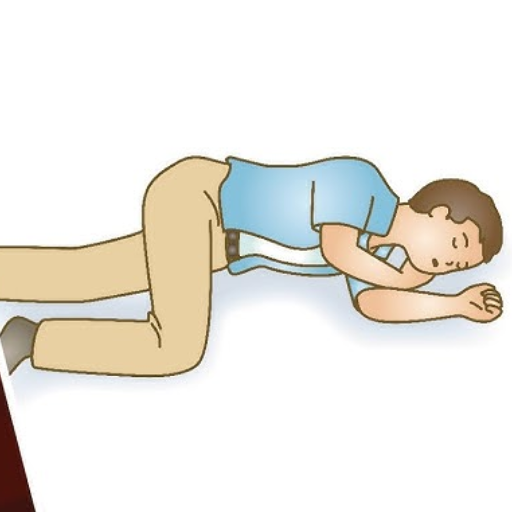 The first thing you must do, even before calling for help, is to check if the victim is responding. If the choking victim is unresponsive, we need to move fast and complete these resinous sign steps. So the first thing that you should do is. Place a hand around the victim’s back and the other one supporting her head. Call for ambulance assistance while gently easing the person down flat on her back. Assuming her legs and feet are in proper alignment with her torso and still supporting her head with a hand. The same methods as CPR will ensure chest compressions. Place the heel of one hand across the center of the person’s chest and use the other hand on top of it. The effective force will be applied, and around a hundred to one hundred and twenty contractions will occur in a minute. The person will now assist you in rolling the body on her side, providing a backstroke with one hand. Every so often, they will also check inside the mouth for anything that appears as an obstruction and will try to perform easy removal if possible. Until the coming for help, such movements would continue, and little assistance would be given from the side until the victim started normal and independent breathing. If you follow this technique, then the odds of turning into a more positive side will increase for sure.
The first thing you must do, even before calling for help, is to check if the victim is responding. If the choking victim is unresponsive, we need to move fast and complete these resinous sign steps. So the first thing that you should do is. Place a hand around the victim’s back and the other one supporting her head. Call for ambulance assistance while gently easing the person down flat on her back. Assuming her legs and feet are in proper alignment with her torso and still supporting her head with a hand. The same methods as CPR will ensure chest compressions. Place the heel of one hand across the center of the person’s chest and use the other hand on top of it. The effective force will be applied, and around a hundred to one hundred and twenty contractions will occur in a minute. The person will now assist you in rolling the body on her side, providing a backstroke with one hand. Every so often, they will also check inside the mouth for anything that appears as an obstruction and will try to perform easy removal if possible. Until the coming for help, such movements would continue, and little assistance would be given from the side until the victim started normal and independent breathing. If you follow this technique, then the odds of turning into a more positive side will increase for sure.
Steps to Take When a Person Becomes Unresponsive
- Call for Help: Quickly call emergency services so that help can arrive fast, but the victim should be your priority.
- Ensure Safety: If the person is unresponsive, hold onto them firmly and lay them down properly so that they are on a level surface and able to receive CPR.
- Administer CPR: For most people, the speed aim for your chest compressions is 100-120 in a minute. Place the heel of one hand on the middle of the chest, then cover that with your other hand and press hard and fast.
- Check Airways: Check their mouth and throat for blockage after performing a round of compressions. Take out any objects that can be seen, but do not push them in further.
- Continue Until Help Arrives: Continue the cycle of compressions, but add breath checks for the victim in between until the doctors get to you or the patient breathes on their own.
Performing CPR on a Choking Victim
so let me take you through the procedure of cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) for someone who is choking. Choking and eventually losing consciousness makes it necessary for a person to combine CPR with attempts to maintain an air passage. This can be done in the following manner:- Call for Emergency Services:No matter how good you are in terms of providing CPR, the first thing you need to do is call for help.
- Assess the Situation: Make sure that the person is indeed unconscious and isn’t breathing properly. Allow them to drop gently to the floor if they are standing or sitting.
- Begin Chest Compressions: The first step is to shove the heel of one hand directly in the center of the134891976 person’ s chest followed by the other hand which should be placed in a perpendicular direction on it. Concentrate all your strength on pushing down forcefully and fast on the chest and make sure it isn’t below a hundred per minute and isn’t above 120. This aids in the flow of blood across the body.
- Airway Checks: After about thirty compressions, move the person’s head back slightly to the back and see if there are any visible obstructions to the airway. If something of the sort exists, and you can remove it without forcing it further down the throat, then proceed to remove the obstruction carefully.
- Rescue Breaths if Appropriate: If the person sees that the airway has been relieved, they should give 2 rescue breaths if trained and ready to go. Pinch the person’s nose closed, place your mouth over the mouth of the victim, and give one soft blow until you see the chest go up. It is important that a paused second passes after every breath.
- Repeat: It is necessary to repeat the process of compressions and checks until the patient’s airway opens; they start breathing autonomously, or the emergency personnel intervene.
Remember, staying calm and performing these actions methodically can make a significant difference and potentially save a life.
When to Call Emergency Services
Always bear in mind that remaining composed and implementing the said measures in a deliberate manner can yield favorable results and may, in fact, save a life.Where to Learn More About Choking First Aid?
 While calling emergency services should always be the first step during an emergency, many still overlook how critical it is whose priority during that phase. In situations where people are unconscious or not breathing, the priority of concern should be the assistance of contacting the professionals regardless of how delayed that would set other actions in the action chain. This way, the professionals will receive a prior call and may initiate their actions, so they do not have to lose precious time. Therefore, the principle of priority during salvaging respiratory functions should always be to get assistance first, be it speaking to any other professional. In the case of a cardiac arrest, I cannot stress enough how much calling professionals for help can even be the only thing that helps with the principle of CPR.
While calling emergency services should always be the first step during an emergency, many still overlook how critical it is whose priority during that phase. In situations where people are unconscious or not breathing, the priority of concern should be the assistance of contacting the professionals regardless of how delayed that would set other actions in the action chain. This way, the professionals will receive a prior call and may initiate their actions, so they do not have to lose precious time. Therefore, the principle of priority during salvaging respiratory functions should always be to get assistance first, be it speaking to any other professional. In the case of a cardiac arrest, I cannot stress enough how much calling professionals for help can even be the only thing that helps with the principle of CPR.
Resources from the American Red Cross
The resources provided by the American Red Cross appear to be of great help to any person who wants to advance their first aid and CPR skills. They provide a variety of courses, including off-campus classes, web-based courses, and hybrid courses, which combine both. Each of the courses has easily understandable materials and well-outlined provisions for instructions, enabling such learners, whatever their background, to understand and be able to put the skills to use. A key highlight is the emphasis on practical elements where skills and competency are cultivated in real-life situations. The Red Cross also incorporates the most recent training requirements into further development of training so that information is reliable and always up to date. Besides, there are a number of certification types that are offered, which means that you will be prepared and qualified to deal with emergencies. Such organized and detailed materials clearly put the American Red Cross among the best-suited institutes for taking first aid and CPR training syllabi.First Aid Courses for Adults and Infants
I can confidently say that there are no two more important first aid courses than those offered to adults and infants. These courses prepare people for a huge range of possible emergencies, from a simple cut to a life-threatening scenario. For adults, the sessions emphasize training them for situations more common in workplace or household settings, such as heart attacks or heavy blood loss. For infants, however, first aid covers a basic understanding of potential infant health emergencies like choking or baby not responding, which call for soft yet firm methods. In my opinion, these practical sessions are the most useful part of the courses as they allow the student to put the theoretical knowledge into practice and, through that, gain confidence and preparedness.Online Tutorials and Training for Choking Emergencies
Understanding how to deal with emergencies and in particular chocking emergencies effectively can come in handy at a later stage and is a skill every person must possess. Such online choking emergency techniques tutorials and training may help individuals or the audience to deal with choking emergencies effectively.- Understanding the Signs of Choking: Recognizing the signs of choking is paramount. A person may look frightened, be unable to verbalize anything, or maybe seen holding their throat. Recognizing them on time can be lifesaving.
- Knowledge of Basic Techniques: Basic knowledge of even one technique which is the Heimlich maneuver where the windpipe obstructing object is dislodged by applying pressure on the abdomen, is critical. It is crucial for everyone to safely acquire and perfect this particular method through practice in a controlled environment.
- Adaptability to Different Age Groups: The techniques can vary for different choking persons of different ages. Like children, a gentle back slap and chest thrust technique instead of the more aggressive Heimlich maneuver is applied to infants. These differences are well taught during training, including the rationale behind each one.
- Calm and Composed Response: Online rehearsal through certain videos enables the student to build confidence in using the techniques during a real choking episode; one is then able to appear calm and composed during such emergencies. Having the knowledge and skill retention allows one to make the right turns swiftly, increasing the chances of a good outcome.
- Continuous Updates and Refreshers: There are countless sites on the internet that provide refresher training lessons and up to date skills assessment tests. One of the most important aspects of an effective resolution to the emergency situation is the consistency of the knowledge base.
Reference
- Mayo Clinic: Choking First Aid
- American Red Cross: Adult & Child Choking First Aid
- St John Ambulance: Adult Choking First Aid Advice
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are the common causes of choking in adults?
A: Common causes of choking in adults include eating too quickly, consuming large pieces of food, talking while eating, and having a foreign object lodged in the airway. Additionally, certain medical conditions can contribute to choking incidents.Q: What should I do if I witness someone who is choking?
A: If you see someone who is choking, first assess their ability to cough or speak. If they cannot, call the emergency number immediately and prepare to perform first aid techniques, such as back blows and chest thrusts, to relieve choking.Q: How can I relieve choking in an adult?
A: To relieve choking in an adult, perform abdominal thrusts or, if the person is too large, back blows and chest thrusts can be effective instead of abdominal thrusts. Use the heel of your hand to apply force just above the navel to clear the airway obstruction.Q: What are chest thrusts and when should they be used?
A: Chest thrusts involve using your hands to apply pressure to the chest of someone who is choking. They should be used when abdominal thrusts are not effective, especially if the person is pregnant or too large to handle safely.Q: What should I do if the person becomes unconscious while choking?
A: If the person becomes unconscious while choking, you should begin CPR immediately. Make sure to check the mouth for any visible foreign objects and attempt to clear the airway obstruction before continuing with compressions and rescue breaths.Q: Can I use back blows to help someone who is choking?
A: Yes, back blows can help relieve choking. Stand behind the person and use the heel of your hand to deliver up to five firm blows between the shoulder blades to try to clear the airway.Q: What is the difference between choking in adults and choking in infants?
A: Choking in infants often requires different techniques, such as back blows and chest thrusts specifically adapted for their smaller size. Adults typically require abdominal thrusts or chest thrusts to clear an airway obstruction effectively.Q: How can I prevent choking incidents from occurring?
A: To prevent choking incidents, eat slowly, chew food thoroughly, avoid talking while eating, and ensure that small objects are kept away from young children. Being aware of the risk of choking due to certain foods or objects can help reduce incidents.Q: What should I remember about performing first aid for choking?
If someone is choking, act quickly and stay calm. First, assess the situation to see if they can cough or speak. If they can't, start the Heimlich maneuver by standing behind them, placing your hands above their belly button, and delivering quick, inward and upward abdominal thrusts. For infants, use five back blows followed by five chest thrusts. If the object doesn’t dislodge and the person becomes unresponsive, call emergency services right away and begin CPR if you're trained to do so. Always prioritize their safety and your own while providing first aid.













 Login with Google
Login with Google Login with Facebook
Login with Facebook