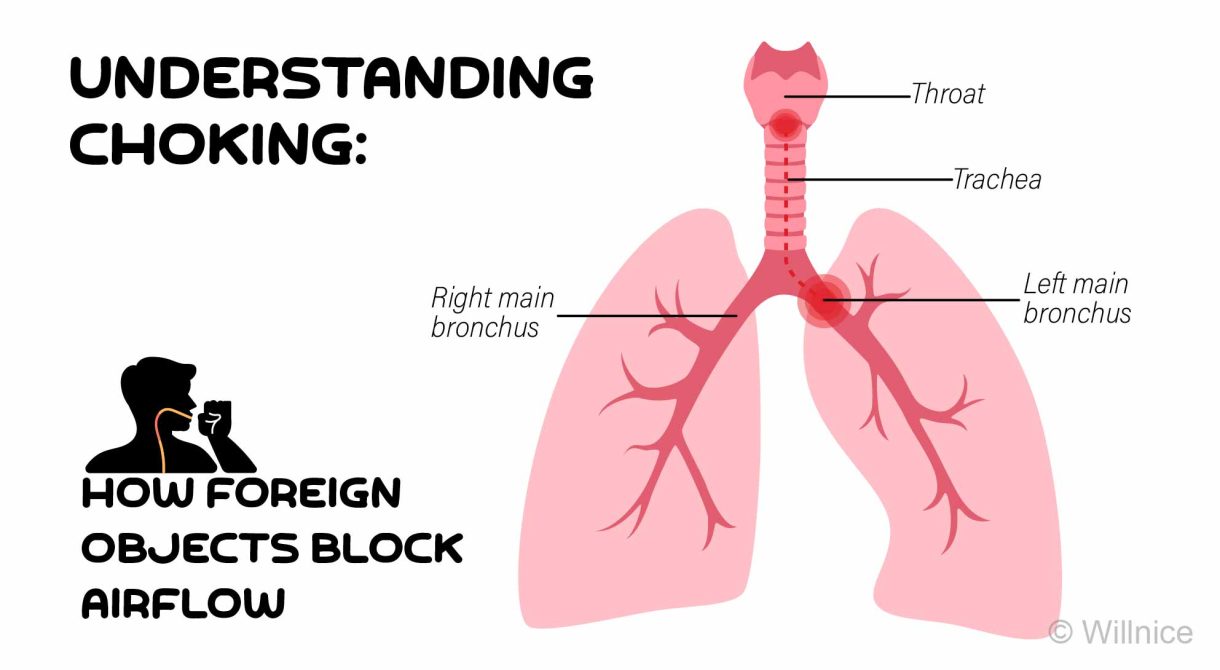
Understanding the signs of severe airway obstruction is crucial for effective choking intervention. Differentiating between mild and severe airway obstructions is key to applying the right first aid techniques promptly.
This guide not only helps you identify the signs of severe airway obstructions but also ensures you can take swift and correct life-saving actions without delay. Read further!
What is Severe Airway Obstruction?
Severe airway obstruction, also known as complete airway obstruction or severe choking, occurs when the airway is fully blocked, preventing any air from reaching the lungs.
This type of obstruction is a life-threatening emergency because it can quickly lead to unconsciousness, brain damage, and death due to oxygen deprivation if not promptly addressed. Immediate intervention is required to prevent severe consequences.
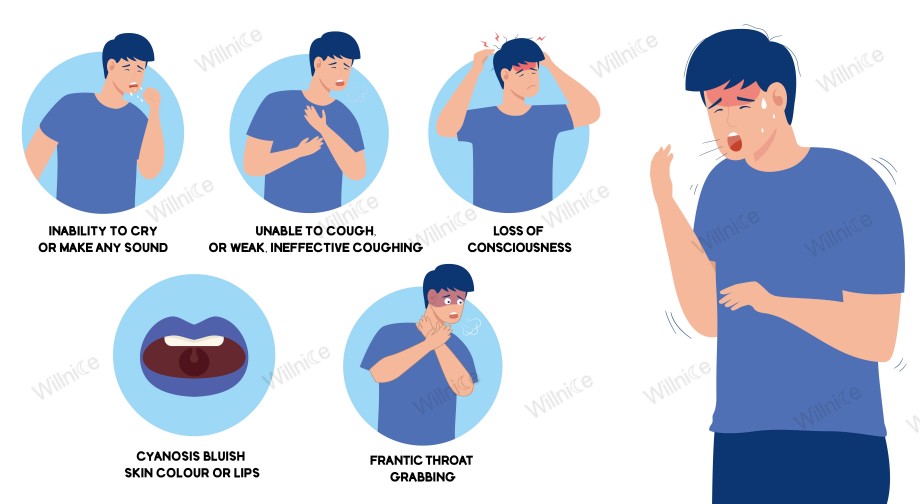
Signs and Symptoms of Severe Airway Obstruction
Review the signs and symptoms of severe airway obstruction listed below. If any are present, emergency first aid is necessary, and you must act immediately.
Extreme Breathing Difficulty or Unable to Breathe at all
The choking person may show extreme difficulty breathing or be completely unable to breathe, which are the most critical signs.
Extreme Breathing Difficulty
Extreme breathing difficulty, also known as shortness of breath or dyspnea, can occur due to airway obstruction or impaired respiratory function.
The choking person may struggle to inhale or exhale, with each breath requiring significant effort and often accompanied by weak, rapid, or noisy, gasping sounds.
The individual might also use accessory muscles around the rib cage or neck to help breathe, indicating a severe struggle to obtain enough oxygen.
Unable to Breathe at All
Inability to breathe refers to a complete cessation of breathing where the choking person cannot inhale or exhale at all, with no airflow in or out of the lungs.
This leads to a rapid depletion of oxygen in the body, which can quickly result in unconsciousness and brain damage. If not resolved promptly, it can cause death due to hypoxia.
Unable to Cough at All
Coughing relies on air forcefully expelling obstructions. However, with a severe airway obstruction, there is no air movement in or out of the lungs, eliminating the possibility of this reflex action.
As a result, the choking victim cannot cough effectively, or cough but no sound is coming out (silent cough) or is unable to cough at all.
Unable to Speak or Make Any Noise
In severe choking, because the airway is totally blocked, the choking person cannot speak, talk, cry, or make any noise, only producing silent mouth movements.
Clutching Throat With Hands
The choking victim may instinctively grasp at their throat with one or both hands, known as the universal sign for choking, and may appear extremely distressed or panicked while struggling to breathe.
Cyanosis or Purplish Complexion
Cyanosis refers to a bluish-purple discoloration of the skin, often visible on the lips, fingernails, and skin.
It occurs when a severe airway obstruction prevents sufficient oxygen from reaching the lungs, leading to a severe lack of oxygen in the bloodstream.
Loss of Consciousness
If the blockage is not cleared quickly, the person may lose consciousness due to severe oxygen deprivation, which can potentially lead to cardiac arrest and death. This situation necessitates immediate CPR.
High Level of Panic, Shock, Confusion, and Wide Eyes
The choking person may appear panicked, confused, or wide-eyed with a surprised facial expression. They may desperately wave their arms without making any sounds.
High-Pitched Squeaking Noises or No Sound
In cases of severe airway obstruction, the choking person trying to breathe or cough might produce high-pitched squeaking or wheezing sounds, or there may be no sound at all.
Save a Life: First Aid for Severe Airway Obstruction
In cases of severe airway obstruction, emergency first aid is required, and you must act right away.
For conscious individuals, it is recommended to perform the Heimlich maneuver (abdominal thrusts). For unresponsive individuals, perform CPR (chest compressions and rescue breaths) immediately.
Tips:
If you are alone and someone is choking, start giving first aid right away. Then call EMS/911 for help. You can also shout to get the attention of people nearby, but keep giving first aid while you wait for emergency services.
If there are others around, quickly ask someone to call EMS/911 and request an AED, while you continue to provide first aid to the choking victim.
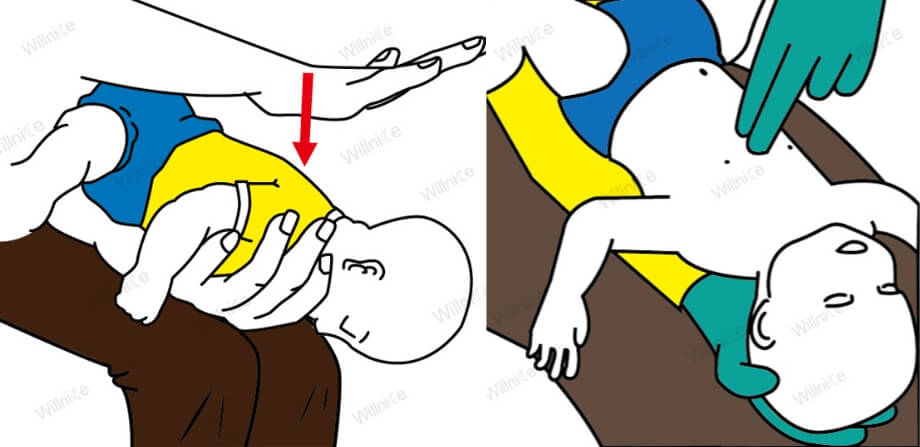
- Give back blows and chest thrusts to help remove the object.
- If the infant becomes unresponsive, begin CPR right away with chest compressions and rescue breaths.
- Use a mix of back blows and Heimlich maneuvers (abdominal thrusts).
- If the child becomes unresponsive, start CPR immediately.
- Apply a mix of back blows and Heimlich maneuvers (abdominal thrusts).
- If the person becomes unconscious, start CPR right away.
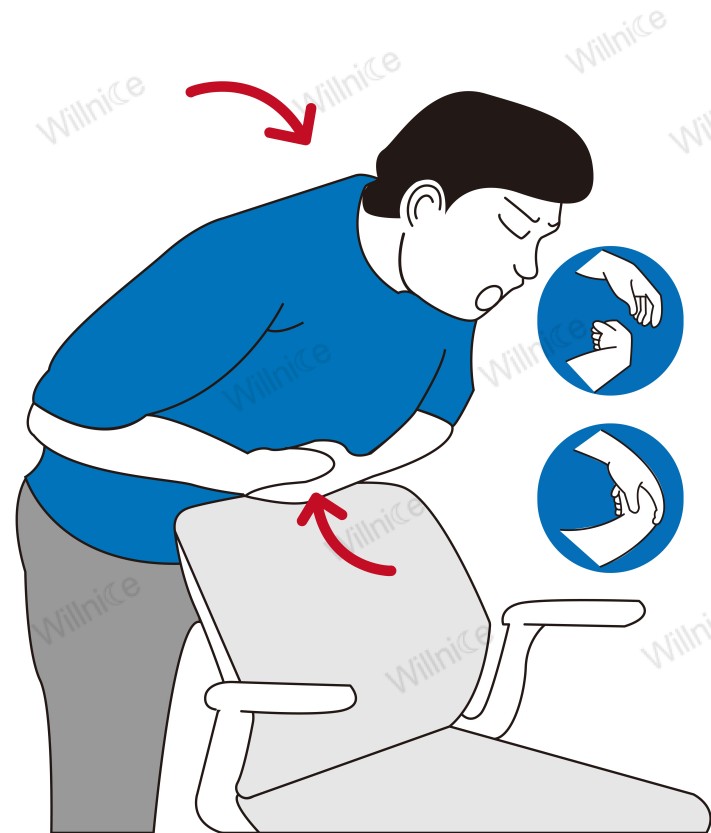
For Yourself
- If you’re alone and choking, first call 911 or your local emergency number.
- Then, perform the self-Heimlich maneuver by placing a fist just above your navel, grabbing it with your other hand, and thrusting inward and upward against a hard surface like the back of a chair.
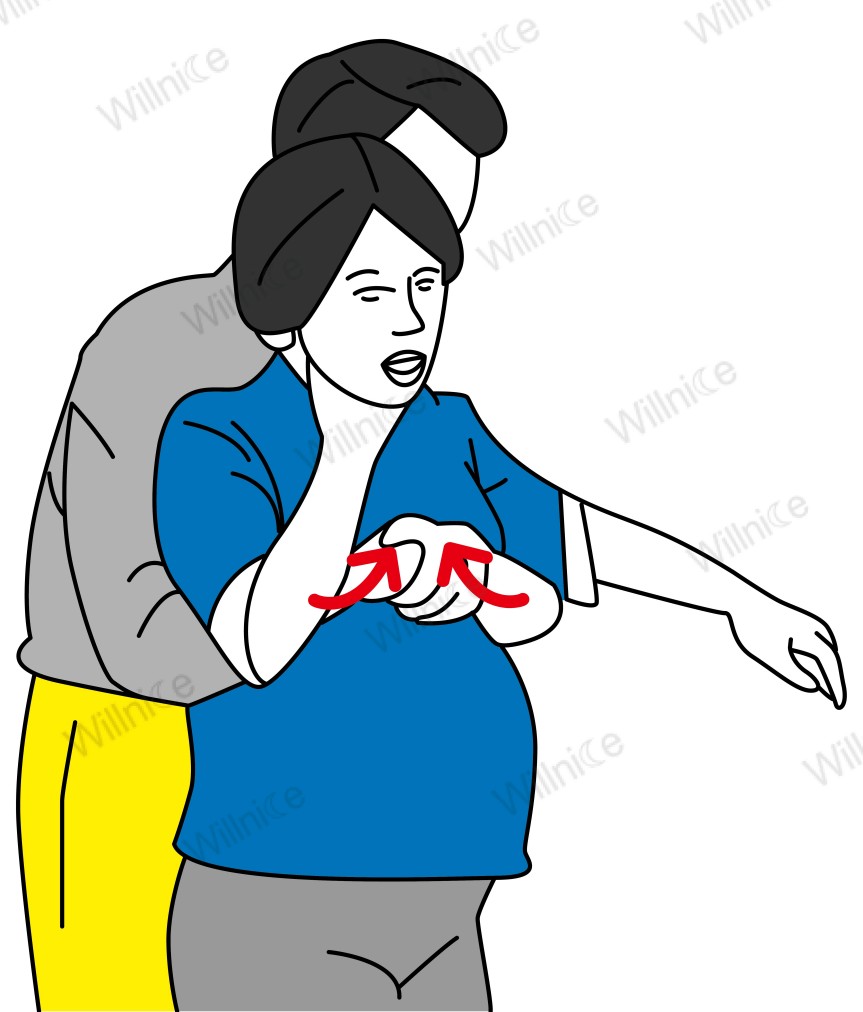
For Pregnant Woman Choking
- Avoid the standard Heimlich maneuver on pregnant women because it might harm the fetus.
- Instead, use chest thrusts as a safer alternative to clear the airway. Here’s how to perform the chest thrust on a pregnant woman.

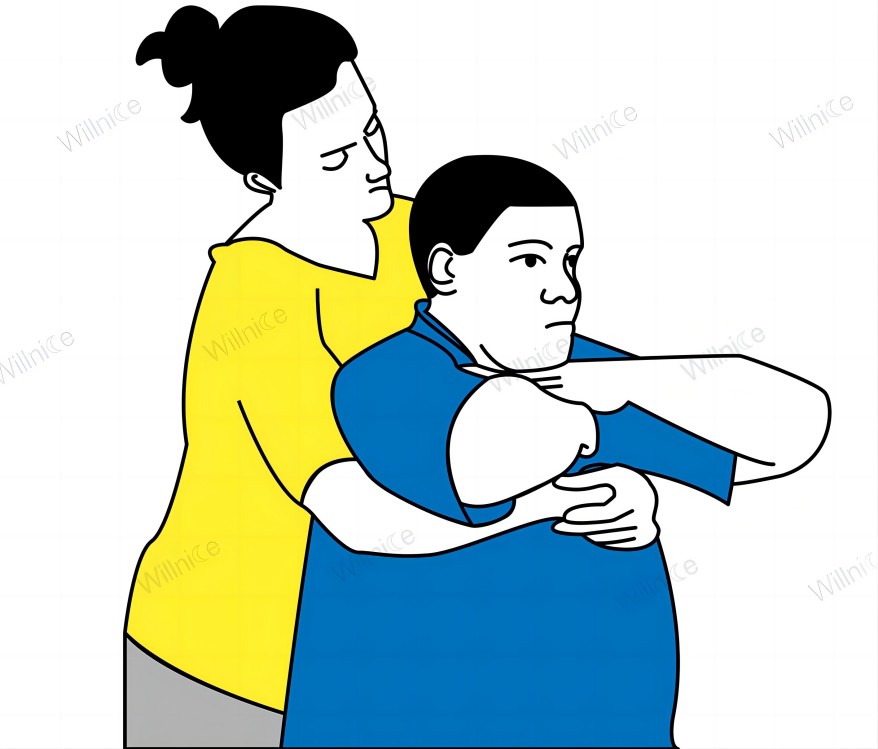
For Large Choking Victim
- If a choking victim is too large to perform the abdominal thrusts by wrapping your arms around their waist, opt for chest thrusts.
- Place your arms around the middle of their chest and give quick, firm thrusts to help dislodge the object.

FAQs
What are the types of choking?
Choking occurs when a foreign object lodges in the throat or windpipe, blocking the flow of air. It can generally be classified into two main types based on the severity of the airway obstruction: Partial airway obstructions (mild choking) and Complete airway obstructions (severe choking).
What is partial airway obstruction?
In this type of obstruction, the airway is not completely blocked, allowing the person to make some noise or cough. They can still breathe. The individual might be able to clear the blockage themselves by coughing forcefully. Symptoms may include coughing, gagging, watery eyes, and making noises while attempting to breathe.
Conclusion
Recognizing the signs of severe airway obstruction and taking prompt, correct first aid measures is crucial.
Severe airway obstruction can quickly lead to life-threatening conditions such as unconsciousness or cardiac arrest. So prompt identification and immediate action can save lives, greatly increasing the chances of survival and reducing the risk of long-term damage.








 Login with Google
Login with Google Login with Facebook
Login with Facebook