What Are the Signs and Symptoms of Someone Who Is Choking?
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of choking is essential to providing timely assistance. When a person is choking, their airway is blocked either partially or completely, which can lead to life-threatening situations if not addressed quickly. Below are the key indicators to look for:
Understanding the Physical Indicators of Choking
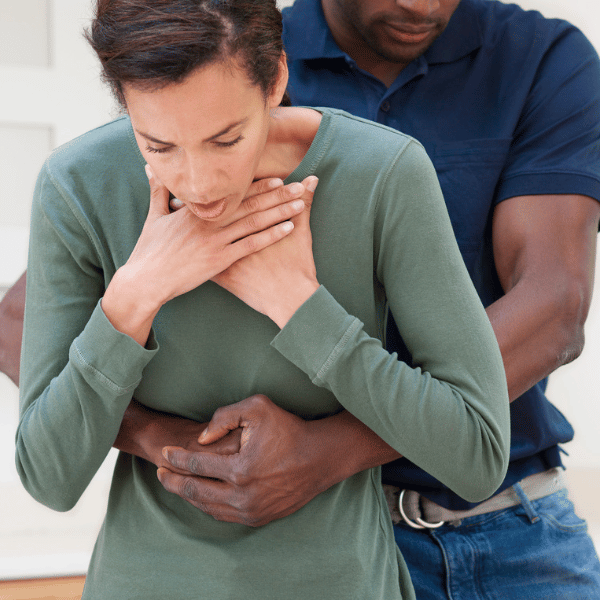
- Clutching the Throat - This is the universal sign for choking. The person may instinctively grab their throat with one or both hands.
- Difficulty Breathing or Noisy Breathing - The individual may struggle to breathe, producing wheezing or high-pitched sounds as air tries to pass through the obstruction.
- Inability to Speak or Cough—A complete blockage will prevent the person from speaking, coughing, or making vocal sounds.
- Blue or Pale Skin (Cyanosis) - Lack of oxygen may cause the skin, lips, or nails to take on a bluish or pale hue.
- Panicked or Distressed Look - A choking person often appears visibly distressed, panicked, or frightened.
- Loss of Consciousness - If the airway remains blocked for too long, the person may become unconscious due to a lack of oxygen.

What to Look For in Adults and Children?
Choking symptoms can often differ slightly between adults and children. Adults may exhibit the classic signs, such as clutching the throat or loud, forceful coughing if the airway is only partially blocked. Conversely, children may stop playing suddenly, become quiet, or exhibit unusual behavior. Infants may show signs like weak crying, noisy breathing, or a complete stoppage of sound.
How to Differentiate Between Coughing and Choking?
It’s crucial to distinguish between someone who is coughing and someone who is choking. A person coughing forcefully can still breathe and may eventually clear the obstruction on their own. Encourage them to keep coughing to expel the object. By contrast, choking occurs when there’s little or no sound due to the inability of air to pass through. An individual who is choking needs immediate intervention, such as abdominal thrusts, to clear the blockage.
Recognizing these signs and acting swiftly can save a life during a choking emergency. Always remain calm and prepared to help.
How to Help Someone Who Is Choking?
Step-by-Step Choking First Aid Instructions
- Assess the Situation
Ask, "Are you choking?" Look for signs such as clutching the throat, inability to speak, or difficulty breathing. If the person can cough or speak, encourage them to continue coughing to try to dislodge the object.
- Perform Back Blows
- Stand to the side and slightly behind the person. Support their chest with one hand and lean them forward so the object can come out of their mouth and not go deeper into their airway.
- With the heel of your dominant hand, deliver up to 5 firm back blows between the shoulder blades. Check after each back blow to see if the obstruction has been cleared.
- Perform Abdominal Thrusts (Heimlich Maneuver)
- Stand behind the person and wrap your arms around their waist.
- Place a fist with one hand just above the navel, with the thumb side facing in.
- Grasp your fist with the other hand and deliver quick, upward thrusts. Repeat this motion up to 5 times.
- Alternate Between Back Blows and Abdominal Thrusts
If the obstruction is still not cleared, alternate between 5 back blows and 5 abdominal thrusts until the object is expelled or the person becomes unresponsive.
When to Call for Help?
- If the Person Cannot Breathe or Becomes Unresponsive
Call emergency services immediately or have someone else make the call while you continue to perform first aid.
- Watch for Critical Signs
Professional medical assistance is urgently needed if the person shows signs of turning blue, losing consciousness, or the airway remains fully blocked despite first aid efforts.
If the Person Becomes Unresponsive
- Lower them gently to the ground.
- Begin CPR if trained to do so. Check the mouth between rescue breaths and chest compressions to see if the object can be removed. Only attempt to remove the object if it is visible and easily accessible.
Note for Infants and Children
Special care should be taken when assisting infants or small children. Instead of abdominal thrusts, infants younger than one year should deliver 5 back blows followed by 5 chest thrusts using two fingers.
Staying calm and following these steps can effectively assist someone choking, potentially saving their life.
What Is the Heimlich Maneuver and How Is It Performed?
The Heimlich maneuver, also known as abdominal thrusts, is a first-aid procedure for treating choking caused by an obstruction in the airway. It involves applying pressure just above the navel to expel the object blocking the airway. This method effectively saves lives and can be performed on adults, children, and infants with slight modifications.
Performing Abdominal Thrusts on a Choking Adult
- Assess the Situation: Confirm the person is choking by checking if they can cough, speak, or breathe. Ask, "Are you choking?"
- Position Yourself: Stand behind the person and wrap your arms around their waist. With one hand, place a fist just above the navel, thumb side inward.
- Apply Pressure: Grasp your fist and perform quick, upward thrusts with your other hand. Continue thrusts until the object is dislodged or the person can breathe again.
- Seek Medical Help: Even if the object is dislodged, it is important to seek medical attention to ensure no further complications.
Adapting the Heimlich for Children and Infants
For Children (Over One-Year-Old):
- Follow the same steps as an adult, but adjust the force of the thrusts to account for the child’s smaller size to avoid injury.
- Kneel to their level for better control and ensure your hands are positioned above the navel.
For Infants (Under One Year Old):
- Position the infant face-down along your forearm, supporting their head and neck. Deliver 5 firm back blows between the shoulder blades using the heel of your hand.
- If the object is not expelled, turn the infant face up, supporting their head, and perform 5 chest compressions using two fingers placed on the center of the chest just below the nipple line.
- Repeat the back blows and chest compressions until the object is cleared or medical help arrives.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Administering the Heimlich
- Applying Excessive Force: Using too much force, especially on children or frail adults, can cause internal injuries.
- Incorrect Hand Placement: Placing hands too high or too low can reduce the maneuver's effectiveness and may cause harm.
- Not Seeking Additional Help: Always call for emergency medical assistance, as the Heimlich maneuver may not fully clear the airway, or complications might occur afterward.
- Panicking: Staying calm is crucial for both the responder and the choking person. Panic can lead to errors in the procedure.
By correctly performing the Heimlich maneuver and adapting it for different age groups, you can act quickly and effectively in a choking emergency, potentially saving a life.
Why Is First Aid for Choking Important?
Choking is a life-threatening emergency that can happen to anyone at any time, making first aid knowledge essential. Each year, choking incidents account for thousands of preventable deaths worldwide. According to the National Safety Council, choking is the fourth leading cause of unintentional injury deaths in the United States, with food, small objects, and toys being common culprits. Timely intervention through proper first aid techniques dramatically increases survival rates and minimizes complications.
Statistics on Choking Incidents and Survival Rates
Statistics show quick and effective first-aid practices can save lives in choking emergencies. The American Red Cross estimates that over 4,000 choking-related deaths occur annually in the U.S. alone. However, survival rates improve significantly when bystanders intervene promptly with procedures like the Heimlich maneuver or back blows. Studies have shown that administering aid within the first few minutes of choking can reduce mortality by as much as 70%, emphasizing the importance of knowing what to do in such critical situations.
How First Aid Can Save Lives in Emergencies
First aid for choking involves dislodging an obstruction and preventing further harm. Techniques such as abdominal thrusts, chest compressions, and back blows are designed to expel the object while maintaining the person's oxygen levels to prevent brain damage. These skills empower bystanders to take quick action while waiting for emergency medical services to arrive, often making the critical difference between life and death.
The Role of the American Red Cross in Training
The American Red Cross is pivotal in educating the public about choking first aid. Through certified courses and accessible online resources, they provide hands-on training that equips individuals with confidence and the proper skills to handle choking emergencies effectively. By raising awareness and encouraging widespread participation in these programs, organizations like the American Red Cross ensure that more people are prepared to respond in critical moments, ultimately saving countless lives.
Understanding the importance of first aid for choking and taking steps to learn and practice these skills can prepare you to act decisively during emergencies, turning a potentially fatal situation into a survival story.
What Resources Are Available For Learning How To Chop First Aid?
Finding a First Aid Course Near You
One of the most effective ways to learn choking first aid is by enrolling in a certified first aid course. Many organizations, such as the American Red Cross and local community health centers, offer hands-on training that equips participants with practical skills to handle choking emergencies. Use online directories or search engines to locate nearby classes by entering terms like "first aid course near me.” These in-person courses often include expert instruction, demonstrations, and opportunities to practice techniques like the Heimlich maneuver, ensuring you gain confidence and competence.
Using a First Aid App for Quick Guidance
First aid apps are an excellent resource for immediate guidance during an emergency. Several organizations provide apps that outline steps to assist with choking incidents quickly and clearly. For example, the American Red Cross First Aid app includes step-by-step instructions, videos, and a checklist to help you act decisively. These apps are easy to download on your smartphone and useful for learning and real-time reference when faced with a choking emergency.
Accessing Online Resources from the American Red Cross
The American Red Cross offers online resources to help individuals learn choking first aid. Their website features detailed guides, video tutorials, and even interactive courses to walk you through the steps for aiding choking individuals, whether adults, children, or infants. These materials are accessible at any time, making it convenient to learn and review the procedures as needed. Additionally, certifications for online courses are often provided, allowing you to gain credentials from the comfort of your home.
By exploring these resources, you can ensure you’re well-prepared to respond effectively when choking poses a life-threatening emergency.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What should I do if someone is choking?
A: If someone is choking, it is essential to act quickly. First, assess whether the person can speak or cough. If they cannot speak and are in distress, you should give abdominal thrusts. Stand behind the person, place your arms around their waist, and perform five abdominal thrusts to try and dislodge the obstruction in their airway.
Q: How do I perform the abdominal thrust technique?
A: To perform the abdominal thrust technique, first, kneel behind the person who is choking. Wrap your arms around their waist and make a fist with one hand. Place the thumb side of your fist just above the person's navel. Grasp your fist with your other hand and give five quick, inward, and upward thrusts. This may help to dislodge the foreign object blocking the airway.
Q: What if the person becomes unresponsive while choking?
A: If the person becomes unresponsive and not breathing, it is crucial to call for emergency help immediately and begin CPR. Start by giving 30 chest compressions, followed by two rescue breaths. Continue this cycle until emergency personnel arrive or the person begins to show signs of life.
Q: Can I use back blows if someone is choking?
A: Yes, back blows can be an effective first-aid step. If the person is a choking adult or child, you can give five back blows between the shoulder blades using the heel of your hand. This technique can help dislodge the blockage from their airway. If the obstruction is not cleared, follow up with five abdominal thrusts.
Q: What is the difference between abdominal thrusts and chest thrusts?
A: Abdominal thrusts are performed by applying inward and upward pressure just above the navel to dislodge an obstruction in the airway. Chest thrusts, on the other hand, may be used for pregnant individuals or larger persons where abdominal thrusts may not be effective. Chest thrusts involve pressing down on the center of the chest with your hands, similar to CPR compressions.
Q: How can I tell if a person is choking?
A: Choking is when a person has a foreign object lodged in their windpipe, which prevents them from breathing properly. Signs that someone is choking include difficulty breathing, inability to speak, clutching their throat, and making high-pitched sounds. If they cannot cough or breathe, you should intervene immediately with first aid advice.
Q: What are the first aid steps to take when someone is choking?
A: The first aid steps to take when someone is choking include assessing the situation. If they can speak or cough, encourage them to continue coughing. If they cannot speak or are in distress, perform five back blows followed by five abdominal thrusts. If they become unresponsive, call for emergency services and begin CPR.
Q: Is it necessary to find a doctor after someone has choked?
A: Yes, it is advisable to find a doctor or seek medical attention after someone has choked, even if they appear to be okay afterward. There may be residual injury to the airway or internal structures that requires evaluation, especially if the person becomes unresponsive or has difficulty breathing later.
Q: What should I do if I am alone and choking?
A: If you are alone and choking, try to perform the abdominal thrust technique on yourself. You can do this by placing your hands above your navel and thrusting inward and upward. Alternatively, you can lean over a sturdy surface, such as a chair or table, to apply pressure to your abdomen and attempt to dislodge the obstruction.
References
- Red Cross: Adult & Child Choking: Symptoms and First Aid - This page from the Red Cross offers detailed instructions on performing abdominal thrusts for choking individuals.
- Red Cross: Responding to Emergencies - This document provides comprehensive information on first aid, including abdominal thrust techniques, as part of their emergency response training.
- Mayo Clinic: Choking: First aid - The Mayo Clinic outlines the steps for performing abdominal thrusts, also known as the Heimlich maneuver, as part of their first aid guidance.













 Login with Google
Login with Google Login with Facebook
Login with Facebook