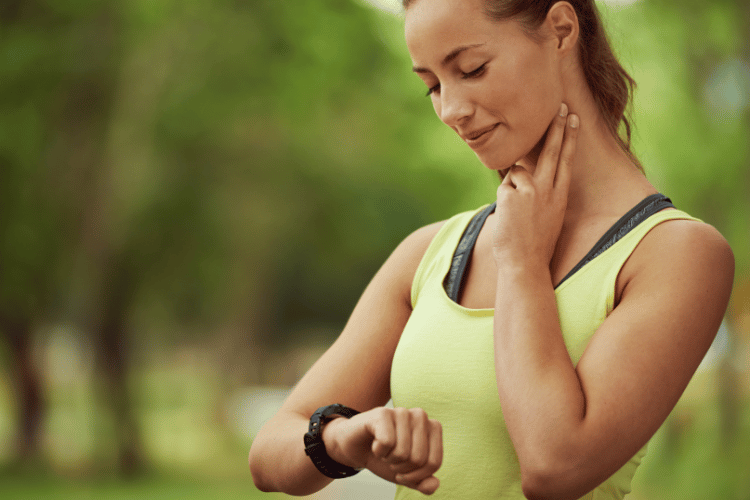

The human body relies on a complex network of vital signs to signal distress, and among the most critical is the carotid pulse. Located in the neck, this pulse point serves as a key indicator in life-threatening situations, particularly in cases of drowning. While most people associate drowning with dramatic gasping or flailing, the reality is far more insidious—silent, swift, and often unnoticed. In these emergencies, checking the carotid pulse can mean the difference between life and death.
For medical professionals, first responders, and even bystanders trained in CPR, understanding the role of the carotid pulse is essential. Unlike peripheral pulses (such as the radial pulse in the wrist), the carotid artery’s central location makes it a more reliable marker in low-blood-pressure scenarios, including near-drowning cases where circulation may be severely compromised.
Understanding the Carotid Pulse
The carotid pulse is a vital indicator of cardiovascular health, providing insight into the heart's and circulatory system's functioning. Found in the neck, this pulse is often used in medical settings to assess heart rate and blood flow. Understanding the carotid pulse involves exploring its anatomical basis, its role in health monitoring, and its significance in emergency and clinical scenarios.
What is the Carotid Pulse?
The carotid pulse refers to the rhythmic throbbing felt over the carotid arteries, which are located on either side of the neck. This pulse is caused by the ejection of blood from the heart into the arterial system during each heartbeat. It is a direct reflection of the heart's activity and is often used to measure heart rate, especially in situations where other pulse points are difficult to access.
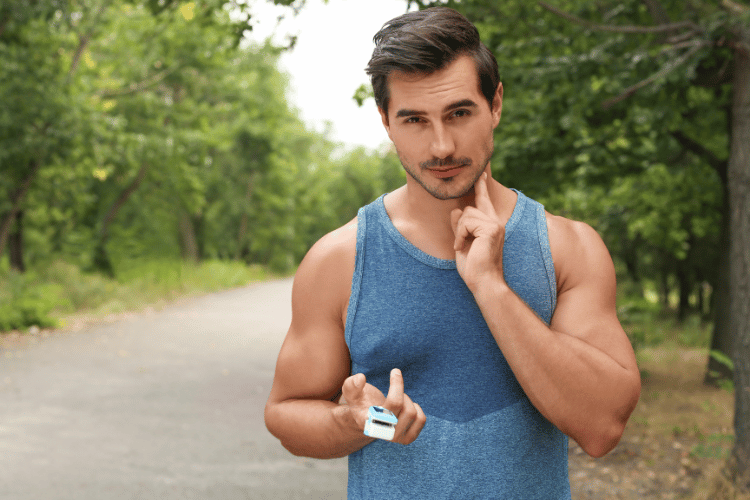

What is the Carotid Pulse
Anatomy of the Carotid Arteries
The carotid arteries are major blood vessels that supply oxygen-rich blood to the brain, neck, and face. Each side of the neck contains two carotid arteries: the internal carotid artery, which supplies blood to the brain, and the external carotid artery, which supplies blood to the face and scalp. These arteries are located close to the surface of the skin, making the carotid pulse easily palpable. The carotid sinus, a small dilated area at the base of the internal carotid artery, contains baroreceptors that help regulate blood pressure.
Importance of Checking the Carotid Pulse
Checking the carotid pulse is crucial in both medical and emergency settings. It is often used to quickly assess the presence of circulation in unresponsive individuals, such as during cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR). Additionally, the carotid pulse can provide valuable information about heart rate, rhythm, and overall cardiovascular health. However, care must be taken when palpating the carotid pulse, as excessive pressure can stimulate the carotid sinus and potentially lead to a drop in heart rate or blood pressure.
How to Take Your Pulse
Taking your pulse is a simple yet essential skill for monitoring your heart rate and overall cardiovascular health. The carotid pulse, located in the neck, is one of the most accessible and reliable pulse points. Learning how to properly check your carotid pulse properly involves understanding the correct technique, ensuring accuracy, and avoiding common errors that could lead to misleading results.
Step-by-Step Guide to Carotid Pulse Check
- Locate the Carotid Artery: Sit or lie down in a comfortable position. Use the index and middle fingers of one hand to gently press on the side of your neck, just below the jawline and beside the windpipe. Avoid using your thumb, as it has its own pulse that can interfere with accuracy.
- Apply Gentle Pressure: Press lightly until you feel a rhythmic throbbing. Excessive pressure can obstruct blood flow or stimulate the carotid sinus, which may cause dizziness or a drop in heart rate.
- Count the Beats: Once you locate the pulse, count the beats for 15 seconds and multiply by four to calculate your heart rate in beats per minute (BPM). For a more precise measurement, count for a full 60 seconds.
Tips for Accurate Palpation
- Stay Relaxed: Ensure you are calm and at rest before checking your pulse, as stress or physical activity can elevate your heart rate.
- Use Proper Finger Placement: Position your fingers correctly to avoid missing the pulse or pressing on the wrong area.
- Time It Right: Morning is often the best time to check your resting heart rate, as it provides a baseline for your cardiovascular health.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Using the Thumb: The thumb’s own pulse can lead to inaccurate readings.
- Pressing Too Hard: Excessive pressure can block the artery or trigger a reflex that lowers heart rate.
- Checking Both Sides Simultaneously: Palpating both carotid arteries at the same time can restrict blood flow to the brain, causing dizziness or fainting.
By following these steps and tips, you can effectively monitor your carotid pulse and gain valuable insights into your heart health.
Carotid Pulse Assessment Techniques
Assessing the carotid pulse is a critical skill in both clinical and emergency settings, providing valuable information about cardiovascular health and blood flow to the brain. Proper techniques for evaluating the carotid pulse include palpation and auscultation, each serving distinct purposes. Understanding these methods and knowing when to seek medical assistance ensures accurate assessment and timely intervention when needed.
Palpation Method
The palpation method is the most common technique for assessing the carotid pulse. To perform this:
- Positioning: Have the individual sit or lie down in a relaxed position. Use the pads of your index and middle fingers to locate the carotid artery on one side of the neck, just below the jawline and beside the windpipe.
- Gentle Pressure: Apply light pressure to feel the rhythmic pulsation. Avoid pressing too hard, as this can obstruct blood flow or stimulate the carotid sinus, potentially causing dizziness or a drop in heart rate.
- Count the Beats: Measure the pulse for 15 seconds and multiply by four to calculate beats per minute (BPM). For greater accuracy, count for a full 60 seconds.
Auscultation of the Carotid Arteries
Auscultation involves using a stethoscope to listen for abnormal sounds, such as bruits, which may indicate arterial narrowing or blockages. To perform auscultation:
- Place the Stethoscope: Position the stethoscope’s diaphragm over the carotid artery.
- Listen for Sounds: Ask the individual to hold their breath briefly to minimize background noise. Listen for any whooshing sounds, which may suggest turbulent blood flow.
When to Seek Medical Assistance?
Seek medical attention if you notice:
- Irregular Pulse: A pulse that is consistently irregular or abnormally fast or slow.
- Bruits: Abnormal sounds during auscultation, which may indicate carotid artery disease.
- Symptoms of Reduced Blood Flow: Dizziness, fainting, or weakness, which could signal insufficient blood supply to the brain.
By mastering these techniques and recognizing warning signs, you can effectively assess the carotid pulse and identify potential health concerns.
Carotid Pulse in Emergency Situations
In emergencies, the carotid pulse serves as a vital indicator of circulation and heart function. Its assessment can provide critical information about a person's cardiovascular status, especially in life-threatening scenarios. Recognizing symptoms that require immediate attention, taking prompt action, and ensuring proper follow-up are essential for effective emergency response and long-term care.
Recognizing Critical Symptoms
Identifying critical symptoms is the first step in managing emergencies involving the carotid pulse. Key signs to watch for include:
- Absence of a Pulse: This may indicate cardiac arrest or severe circulatory failure.
- Weak or Irregular Pulse: A faint or erratic pulse could signal shock, arrhythmias, or other cardiovascular issues.
- Accompanying Symptoms: Dizziness, loss of consciousness, chest pain, or difficulty breathing often point to serious underlying conditions requiring immediate intervention.
Immediate Actions for Emergency Response
When faced with an emergency involving the carotid pulse, take the following steps:
- Check for a Pulse: Use the index and middle fingers to palpate the carotid artery on one side of the neck. Avoid pressing both sides simultaneously to prevent restricting blood flow to the brain.
- Initiate CPR if Necessary: If no pulse is detected, begin cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) immediately and call for emergency medical assistance.
- Monitor Vital Signs: Continuously assess the pulse, breathing, and level of consciousness until professional help arrives.
Long-term Monitoring and Follow-up
After an emergency, long-term monitoring and follow-up care are crucial to prevent recurrence and manage underlying conditions. This may include:
- Medical Evaluation: A thorough examination to identify the cause of the emergency, such as heart disease or carotid artery blockages.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, and stress management.
- Regular Check-ups: Routine monitoring of cardiovascular health to detect and address potential issues early.
By understanding the role of the carotid pulse in emergencies and taking appropriate actions, you can help ensure timely and effective care in critical situations.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the significance of assessing the carotid pulse?
Assessing the carotid pulse is crucial in evaluating a person's heart rate and overall cardiovascular health. It indicates blood flow to the brain and can help determine if there are any issues with blood circulation, such as carotid artery stenosis, which may lead to serious health problems.
How can I find the pulse in the common carotid artery?
To find the common carotid artery pulse, use your index and middle fingers to gently press on one side of your neck, just below the jawline and beside the windpipe. Avoid using your thumb or pressing both sides simultaneously to ensure accuracy and safety.
What does it mean if the pulse may be felt on either side of the neck?
If the pulse may be felt on either side of the neck, it indicates that both carotid arteries are functioning and supplying blood to the head. However, if you notice significant differences in pulse strength or rate between the two sides, it could suggest vascular issues that require further evaluation.
How does the carotid pulsation relate to heart rate?
The carotid pulsation directly reflects the heart rate, as it is caused by the rhythmic contraction of the heart pushing oxygenated blood through the arteries. By measuring the pulse rate at the carotids, healthcare providers can assess the efficiency of the cardiovascular system and detect any arrhythmias or irregular pulse patterns.
What is the normal pulse rate in healthy individuals?
The normal pulse rate in healthy individuals typically ranges from 60 to 100 beats per minute. Factors such as physical activity, stress, and overall health can influence this rate. Monitoring the pulse can help identify conditions such as bradycardia or tachycardia.
Can palpating the carotid pulse be dangerous?
Palpating the carotid pulse is generally safe, but excessive pressure or incorrect technique can potentially cause discomfort or trigger a vagal response, leading to fainting. It's important to approach the assessment gently and know when to stop if the individual feels lightheaded.
What role does the carotid sinus play in pulse regulation?
The carotid sinus, located at the bifurcation of the common carotid artery, plays a vital role in regulating blood pressure and heart rate. It contains baroreceptors that detect changes in blood pressure and send signals to the brain to adjust heart rate and blood flow accordingly, ensuring adequate perfusion to the brain and body.
How can I check for a bounding pulse in the carotids?
A bounding pulse can be assessed by palpating the carotids and feeling for a strong, forceful pulse that may indicate increased blood volume or elevated blood pressure. This type of pulse may be caused by various conditions, including fever or hyperthyroidism, and requires further investigation if persistent.
What guidelines for cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) include the carotid pulse?
The guidelines for cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) recommend checking the carotid pulse to assess for pulselessness in an unconscious individual. If no pulse is detected, immediate CPR should be initiated to restore circulation and oxygenation, emphasizing the importance of timely intervention during cardiac arrest.
The Bottom Line
The carotid pulse is more than just an anatomical landmark—it’s a lifeline in drowning emergencies. Its central location and resilience under physiological stress make it indispensable for rapid triage. Whether you’re a lifeguard, EMT, or a bystander trained in first aid, mastering carotid pulse assessment ensures you’re prepared to act decisively when seconds count.
In critical situations, knowledge isn’t just power—it’s survival. Recognizing and responding to the carotid pulse could save a life, turning panic into purposeful action.














 Login with Google
Login with Google Login with Facebook
Login with Facebook