
Dehydration is a common yet often overlooked condition that can significantly impact your health and daily life. It occurs when your body loses more fluids than it takes in, leading to an imbalance that affects essential bodily functions. While mild dehydration can cause discomfort, severe cases can result in serious complications if not addressed promptly.
According to health experts, dehydration can affect anyone, but certain groups—such as children, older adults, and athletes—are at higher risk. Recognizing the signs and symptoms of dehydration is crucial for early intervention and effective treatment.
In this guide, we’ll explore what dehydration is, how to identify its symptoms, and the best ways to treat and prevent it. Whether you’re looking to recover from dehydration or avoid it altogether, this comprehensive guide will help you stay informed and hydrated.
Understanding Dehydration
Dehydration occurs when your body doesn’t have enough water to carry out its normal functions. This condition can make you feel unwell, leading to symptoms like dry mouth, fatigue, and dizziness. While mild dehydration can often be resolved by drinking fluids, severe cases may require immediate medical attention. Dehydration happens when your body loses more fluids than it takes in. This can occur due to excessive sweating from exercise or heat, vomiting, diarrhea, or inadequate fluid intake. Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes or kidney problems, can also increase the risk of dehydration. The primary causes of dehydration include fluid loss and insufficient hydration. Factors like hot weather, intense physical activity, or illnesses that cause vomiting and diarrhea are common triggers. Recognizing these causes and understanding the risk factors can help you take preventive measures, such as staying hydrated and avoiding prolonged exposure to heat. By addressing dehydration early and maintaining proper hydration habits, you can support your body’s essential functions and avoid complications.Signs of Dehydration
Dehydration can present with a variety of symptoms, depending on its severity. Recognizing these signs early can help you take action before the condition worsens.Common Symptoms
Some of the most common symptoms of dehydration are as follows:- Thirst: This is your body’s natural signal that it needs more fluids. Ignoring thirst can lead to worsening dehydration.
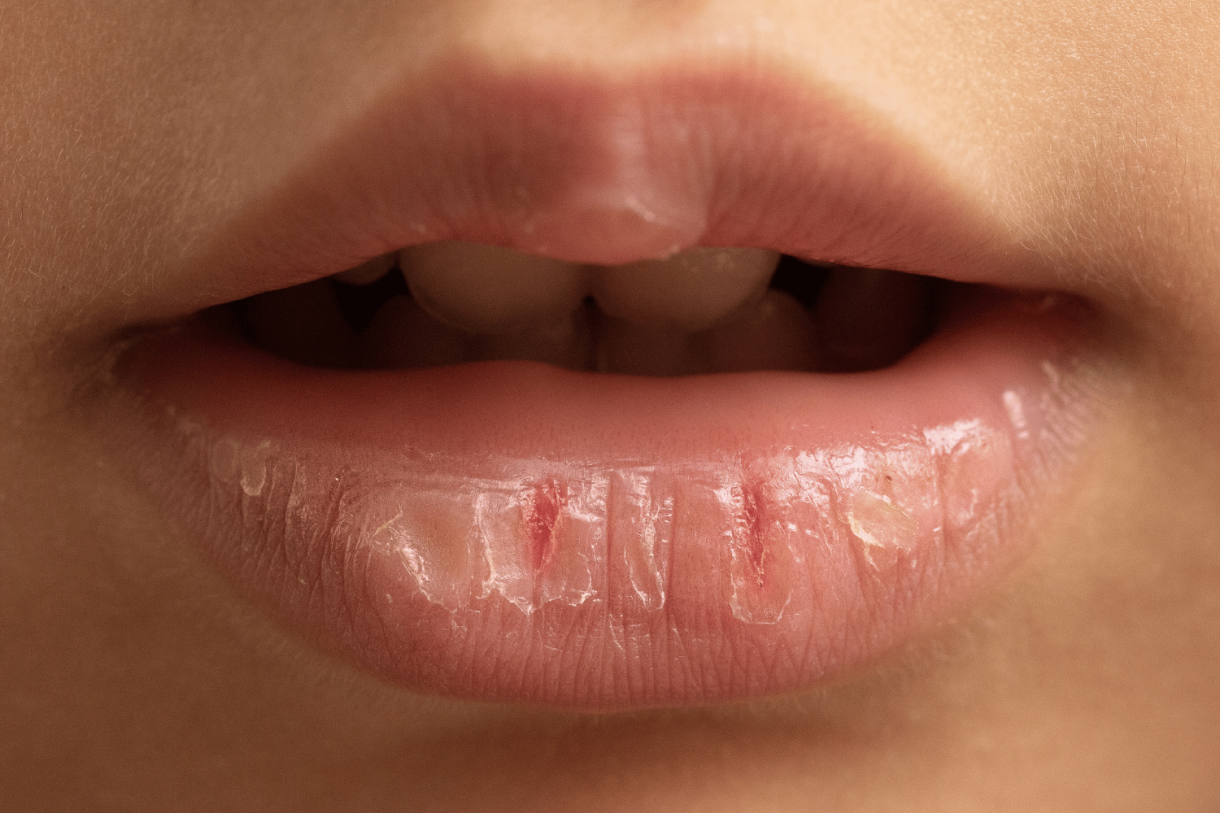
- Dry Mouth and Skin: A lack of moisture in the mouth and skin is an early indicator of dehydration. You may notice your lips becoming chapped or your skin feeling less elastic.
- Dark Urine: Urine that is darker than usual is a sign of concentrated waste due to low fluid levels. It’s a reliable indicator that your body needs more water.
- Fatigue: Feeling tired or sluggish is often linked to dehydration, as your body struggles to perform its normal functions without adequate fluids.
- Dizziness or Lightheadedness: A drop in blood pressure due to fluid loss can cause these symptoms, especially when standing up quickly.
Severe Symptoms
Severe symptoms caused by dehydration are listed below:- Rapid Heartbeat or Breathing: These signs indicate that your body is struggling to maintain normal function and may indicate severe dehydration.
- Sunken Eyes: A visible sign of severe dehydration, particularly in children and older adults.
- Confusion or Irritability: Dehydration can affect brain function, leading to mood changes, confusion, or difficulty concentrating.
- No Urination: A lack of urination for several hours is a red flag for severe dehydration and requires immediate attention.
- Shock: In extreme cases, dehydration can lead to shock, a life-threatening condition that requires urgent medical care.
Immediate Steps: What to Do for Dehydration
When dealing with dehydration, taking the proper steps promptly can make a significant difference in your recovery. Here’s a detailed guide to effectively address dehydration.Initial Actions
When to See a Doctor: If you experience severe symptoms such as confusion, rapid heartbeat, no urination for several hours, or signs of shock, seek medical attention immediately. These symptoms indicate severe dehydration that requires professional treatment. Self-Care Tips: For mild to moderate dehydration, start by increasing your fluid intake. Sip water slowly and frequently rather than drinking large amounts at once. Avoid caffeinated or alcoholic beverages, as they can worsen dehydration. Focus on consuming fluids that are easy on your stomach, such as water, clear broths, or oral rehydration solutions.Hydration
Importance of Fluids: Replenishing lost fluids is crucial to recovery. Dehydration causes your body to lose water and electrolytes, which are essential for normal functioning. Drink small sips of water throughout the day to avoid overwhelming your stomach. Rehydration Solutions: Oral rehydration solutions (ORS) are highly effective for replacing lost fluids and electrolytes. These solutions are available at most pharmacies and contain a balanced mix of salts and sugars. Alternatively, you can make a homemade rehydration solution by mixing 1/2 teaspoon of salt, six teaspoons of sugar, and 1 liter of clean water.Rest
Importance of Rest: Rest is essential for your body to recover from dehydration. Avoid strenuous activities and let your body conserve energy as it rehydrates and repairs itself. Gradual Return to Activity: Once you start feeling better, resume your normal activities gradually. Begin with light tasks and avoid intense physical exertion until you’re fully rehydrated and feeling strong. Listen to your body and adjust your activity levels accordingly. By following these steps, you can effectively manage dehydration and support your body’s recovery process.Dehydration Treatment
Treating dehydration effectively involves a combination of self-care, over-the-counter remedies, and, in severe cases, medical intervention. Here’s a guide to managing dehydration and restoring your body’s fluid balance.Over-the-Counter Solutions
Over-the-counter (OTC) solutions can be highly effective for mild to moderate dehydration. Electrolyte drinks or oral rehydration salts are specifically designed to restore fluid and electrolyte balance. These products are beneficial for dehydration caused by vomiting, diarrhea, or excessive sweating. They are widely available at pharmacies and are easy to use.Medical Treatment
For severe dehydration, medical intervention may be necessary. Intravenous (IV) fluids are often used to quickly restore hydration levels, especially for individuals who cannot keep fluids down due to vomiting or other complications. IV fluids deliver a precise balance of water, electrolytes, and nutrients directly into the bloodstream, ensuring rapid rehydration. This treatment is typically administered in a hospital or clinical setting.Home Remedies
For mild dehydration, home remedies can help replenish lost fluids. Drinking water, coconut water, or herbal teas can help restore hydration. Adding a pinch of salt and sugar to water creates a simple homemade rehydration solution that mimics the effects of commercial electrolyte drinks. These remedies are easy to prepare and can be used as a first step in managing dehydration. By combining these approaches, you can effectively treat dehydration and support your body’s recovery. If symptoms persist or worsen, it’s essential to seek medical attention promptly.How to Treat Dehydration at Home
Treating dehydration at home focuses on rehydration, dietary adjustments, and allowing your body the rest it needs to recover.Hydration Solutions
Hydration is the most important step in treating dehydration. Drink water frequently in small sips to avoid overwhelming your stomach. For added electrolytes, use oral rehydration solutions available at pharmacies or make a homemade version. A simple recipe includes mixing 1/2 teaspoon of salt, 6 teaspoons of sugar, and 1 liter of clean water. This solution helps replenish lost fluids and maintain electrolyte balance.Diet Adjustments
Incorporating water-rich foods into your diet can supplement fluid intake. Foods like cucumbers, watermelon, and oranges are excellent choices as they are hydrating and easy to digest. Avoid salty or sugary snacks, as they can worsen dehydration by drawing water out of your cells.Rest and Recovery
Rest is essential for your body to recover from dehydration. Avoid physical exertion and allow yourself plenty of time to rest. Gradually return to normal activities as you start to feel better, but don’t rush the process. Listening to your body and giving it the time it needs to heal will ensure a full recovery. By following these steps, you can effectively manage dehydration at home and support your body’s recovery. If symptoms persist or worsen, seek medical attention promptly.What to Eat and Drink After Dehydration
Choosing the right foods and drinks after dehydration can help your body recover faster and restore its balance.Initial Foods and Drinks
In the first stages of recovery, focus on rehydrating with water, clear broths, or oral rehydration solutions. These options help replenish lost fluids and electrolytes without overwhelming your stomach. Gradually introduce water-rich fruits and vegetables, such as watermelon, cucumber, and oranges, to support hydration and provide essential nutrients.Progressive Foods
As your condition improves, you can start adding more substantial but easy-to-digest foods to your diet. Plain rice, boiled potatoes, and oatmeal are excellent choices as they are gentle on the stomach and help restore energy. Introduce these foods gradually to ensure your body tolerates them well.Foods to Avoid
Avoid caffeinated, alcoholic, or sugary drinks, as they can worsen dehydration and hinder recovery. Additionally, steer clear of salty, fried, or heavily processed foods, as they can strain your digestive system and delay healing. By following these dietary guidelines, you can support your body’s recovery and regain strength after dehydration. Take it slow and listen to your body as you reintroduce foods and drinks into your routine.Preventing Dehydration
Preventing dehydration is all about maintaining proper hydration and recognizing early signs. Here’s how you can stay hydrated and avoid dehydration:Hydration Tips
Drinking water regularly throughout the day is essential, especially during hot weather or physical activity. Aim to sip water consistently rather than waiting until you feel thirsty. Using a reusable water bottle can help you track your intake and stay consistent with your hydration goals.Lifestyle Adjustments
Avoid excessive consumption of caffeine or alcohol, as these substances can dehydrate your body. Instead, focus on eating water-rich foods like fruits and vegetables, such as watermelon, cucumbers, and oranges, to supplement your fluid intake. These foods not only hydrate but also provide essential nutrients. By following these simple tips, you can effectively prevent dehydration and maintain your body’s fluid balance.Conclusion
Dehydration is a preventable condition that can have serious consequences if left untreated. By understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and taking proactive steps to stay hydrated, you can protect your health and well-being. Simple habits like drinking enough water, eating water-rich foods, and avoiding excessive caffeine or alcohol can make a big difference in maintaining proper hydration.
If you experience severe symptoms or struggle to rehydrate, don’t hesitate to seek medical attention. Staying informed and prepared is the key to managing dehydration effectively and ensuring your body stays healthy and balanced. Remember, hydration is the foundation of good health—so drink up and stay well!














 Login with Google
Login with Google Login with Facebook
Login with Facebook