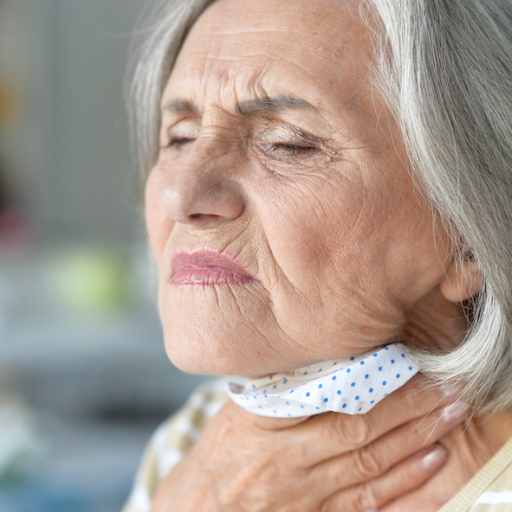

The rise of stock photos featuring old people choking is worth examining due to how multifaceted this phenomenon is. It may seem at first that these visual images are harmless, but they sit at the nexus of health consciousness, the frailty of old age, and how society views aging. The article intends to understand some of the deeper explanations that lead older adults to choke, focusing on geriatric-related changes and relevant morbidity, which increases the risk, where appropriate response techniques are needed. Through an authoritative and detailed analysis, we will show the readers the structure of these risks and how stock imagery may be a tool for increasing social awareness and influencing attitudes.

 This might be slightly morbid, but being in a choke situation where a person is grasping at his or her throat is a concept every professional in the healthcare business, in this case, the aged care industry, must understand. So, if you are in such a situation, do the following:
This might be slightly morbid, but being in a choke situation where a person is grasping at his or her throat is a concept every professional in the healthcare business, in this case, the aged care industry, must understand. So, if you are in such a situation, do the following:
 I would like to clarify the meaning of dysphagia before answering the questions related to it. Dysphagia appears to be a swallowing-related issue, but in a real sense, it is a lot more than that, as it affects the whole sequence of transferring food and liquids from the oral cavity to the stomach that is passing through the esophagus. This is the pertinent information that you need to know:
I would like to clarify the meaning of dysphagia before answering the questions related to it. Dysphagia appears to be a swallowing-related issue, but in a real sense, it is a lot more than that, as it affects the whole sequence of transferring food and liquids from the oral cavity to the stomach that is passing through the esophagus. This is the pertinent information that you need to know:
 As one who has been around, I know that the concept of old man choking stock photos has diverse functions with media and educational platforms. Such images help in exemplifying situations in health education curriculum materials, especially those dealing with the need to Understand the situation and Respond to a Choking Emergency. They are also often used in raising awareness about dysphagia or other swallowing problems in old age and thus increase understanding of potential risk factors for at risk people. Commercially these photos are useful in compiling presentation materials for the training of health care personnel so that they can easily identify with the case studies or emergency care that they are doing. Furthermore, in media advertising as well as in print ads, such images can be good in attracting people’s sights because they depict emergencies and the need of the hour in medicine, so the images created in the ads become very relevant to the promoted product or service. Making sure that these photos have ethical applications or are appropriately graphed is necessary to earn legitimacy for the intended communication goal without disrespecting the context.
As one who has been around, I know that the concept of old man choking stock photos has diverse functions with media and educational platforms. Such images help in exemplifying situations in health education curriculum materials, especially those dealing with the need to Understand the situation and Respond to a Choking Emergency. They are also often used in raising awareness about dysphagia or other swallowing problems in old age and thus increase understanding of potential risk factors for at risk people. Commercially these photos are useful in compiling presentation materials for the training of health care personnel so that they can easily identify with the case studies or emergency care that they are doing. Furthermore, in media advertising as well as in print ads, such images can be good in attracting people’s sights because they depict emergencies and the need of the hour in medicine, so the images created in the ads become very relevant to the promoted product or service. Making sure that these photos have ethical applications or are appropriately graphed is necessary to earn legitimacy for the intended communication goal without disrespecting the context.
 Apart from exercising and keeping up with nutrition, what else can senior men do to avoid the development of difficulties in swallowing, as you have learned from your extensive expertise in this field? Firstly, scheduling regular checkups is one way to address this problem because there may be additional factors at play, including disorders in nutrition. Also, seniors should be helped by relocation of the chew and food to be swallowed. Additionally, it is recommended that exercises be practiced to enhance the strength of the swallowing mechanism, possibly with a speech therapist's advice. Oral health, too, is another instance as many seniors’ poor dental hygiene aggravates dysphagia. Also, it avoids the risk of choking as well as facilitates the reduction of barriers during the process. Finally, such supportive measures will help frail men to optimize their swallowing functions. By bringing these recommended practices alongside, senior men can not only avoid future medical conditions but also relish their lifestyles as they like.
Apart from exercising and keeping up with nutrition, what else can senior men do to avoid the development of difficulties in swallowing, as you have learned from your extensive expertise in this field? Firstly, scheduling regular checkups is one way to address this problem because there may be additional factors at play, including disorders in nutrition. Also, seniors should be helped by relocation of the chew and food to be swallowed. Additionally, it is recommended that exercises be practiced to enhance the strength of the swallowing mechanism, possibly with a speech therapist's advice. Oral health, too, is another instance as many seniors’ poor dental hygiene aggravates dysphagia. Also, it avoids the risk of choking as well as facilitates the reduction of barriers during the process. Finally, such supportive measures will help frail men to optimize their swallowing functions. By bringing these recommended practices alongside, senior men can not only avoid future medical conditions but also relish their lifestyles as they like.
What Causes an Old Man to Choke

Common Symptoms of Dysphagia
Dysphagia, difficulty in swallowing, arises from imbalances in the complex movement activities of the oropharyngeal and esophageal phases of swallowing. A specialist in this field needs to know the classic signs, which are frequent coughs or choke episodes while eating, the feeling of food, liquids getting stuck in the throat or chest, bringing backward some foods that have not been digested, and recurrent and infectious pneumonia or other diseases in the respiratory system. In addition, the patients tend to drool, lose weight without intent, and have changes of voice and the quality of speech. It is pivotal to detect such signs early so as to reduce the chance of further complications developing and to facilitate the timely implementation of appropriate intervention measures.Identifying Swallowing Difficulties in the Elderly
A quick look at the literature suggests that a physician should anticipate problems with swallowing by closely watching for changes in appetite and health in the elderly. In this elderly population, I also look for factors such as difficulty in chewing, the need to avoid food, or perhaps long-lasting meals because of the sensation of thickening of the swallowing process. While patients ‘frequently have a history of stroke, parkinsonism, or Alzheimer's, I take this history into account as well. When it comes to evaluating the conditions, I find it easier to use diagnostic modalities, which in this case are videofluoroscopy or endoscopy, to determine the cause of the disorder. At the core of every single intervention process is a decision-making avenue that combines pure clinical observation and the patient’s perspectives to evolve individualized relievers that potentially suffice the safety and overall quality of life enhancement needs. The overall impact sought through this complete process is to ensure minimal risk of aspiration and its complications, ultimately enhancing elderly patients' health standards.How Swallowing Issues Lead to Choking
I also understand that swallowing as an action is composed of a multitude of actions, the interruption of any of which leads to a choking event. In other words, the act of swallowing can be thought of as a complex choreography that comprises multiple actions; if one of these actions is performed incorrectly, it can result in complications. There are a number of standard coordinates that need to be taken into account:- Coordination: Swallowing entails complex integration of the activities of the mouth, the throat, and the esophagus. When such integration is not maintained, the swallowed food might escape from the esophagus into the airway leading to choking.
- Muscle Strength: Many structures involved in swallowing come under the influence of senescence which makes it difficult for the elderly to optimally propel food through the esophagus. This reduced muscle strength can also result in incorrect propulsion of food where it is stretched or alternatively pushed into unwanted pathways.
- Sensory Function: The perception abilities of older adults, such as perception of foods in terms of taste and texture, to some extent gets reduced with age. This reduction may result in swallowing difficulty where people may not be able to perceive the urge to swallow or the timing for swallowing appropriately.
- Saliva Production: Proper physiological processes require sufficient saliva to lubricate food and facilitate its motion through the pharynx. Diminished saliva output which is usually age-related or medication related makes swallowing more difficult leading to sloppy ingestion of food.
How to Help a Choking Elderly Person?
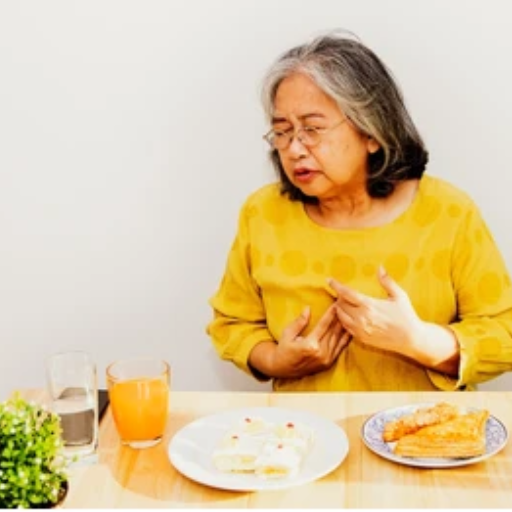 This might be slightly morbid, but being in a choke situation where a person is grasping at his or her throat is a concept every professional in the healthcare business, in this case, the aged care industry, must understand. So, if you are in such a situation, do the following:
This might be slightly morbid, but being in a choke situation where a person is grasping at his or her throat is a concept every professional in the healthcare business, in this case, the aged care industry, must understand. So, if you are in such a situation, do the following:
- Stay Calm and Assess the Situation: It is crucial to stay calm, and evaluate if the individual suffers from the inability to either cough or make any sounds. If they do not need to speak, motivate them to cough actively in order to expel the obstruction themselves. If however, they are unable to cough, then quick measures are required.
- Call for Emergency Help: Should the individual suffer from the above condition of being unable to speak, and breath for that matter, do not waste any more time and call for any professional help that you can get within your vicinity. This is extremely important because in scenarios like these time is key, and help should be at hand as soon as possible.
- Perform the Heimlich Maneuver:
- Position yourself directly with the back of the other person while embracing them around the waist.
- Use one hand in a fist and put it slightly above the person’s navel.
- Hug the fist by putting your other hand over it and make quick upward thrusts to remove the object which is blocking the person’s airway.
- If Unresponsive, Begin CPR:Should the Patient Not Respond, Employ CPR Techniques: If the patient losses consciousness, carefully place him/her on standby and proceed to give CPR, if trained. It involves mouth to mouth resuscitation and heart pumping to ensure that blood continues flowing and oxygen supplies the brain.
Emergency Steps to Take When Choking Occurs
Having worked in choking emergencies, I've managed to come up with a fixed response that allows for effective identification and quick diagnosis and treatment. The response by the people witnessing the choking incident has to be measured by how bad the situation is. One, for instance, is able to cough. I'd appreciate them coughing as hard as they can to try to dislodge whatever is causing the blockage. If they are able to speak but do not cough, or if they are not able to make any sound at all, I will not wait any longer. I picked up the phone and called for help, at the same time commencing the Heimlich maneuver. If the person has called for help first, then I move straight to help them by squeezing their abdomen while setting up my fist above their belly button. With my other hand around the fist, I start forcing the fist upwards rapidly. In case the person becomes unconscious, this is when I start resuscitation just so blood keeps flowing in the body and oxygen is also provided. The skills that I have reflect the need for such techniques as CPR and bring to the forefront the fact that a timely response is critical in emergencies.Understanding the Heimlich Maneuver for Seniors
I have come across individuals who are highly trained in emergency care, and one such technique that is useful in saving a choking geriatrician is the Heimlich maneuver. Please refer to me as, perhaps, an older or a simpler person. So, when it comes to older people who choke, the primary concern is to dislodge the object in the least intrusive and the quickest way possible from their trachea. I think that is how I see the situation and speak of it as a sequential procedure:- Assessment and Preparation: My first action is to look out for whether or not that individual is unable to speak or breathe. This helps me to gauge whether or not a timely action is warranted. If an individual is holding onto their throat, then it means they are looking for assistance.
- Positioning: In my strong frame, I move and place myself at that individual's back. It is important to have a good stance because one may expect to be moving around.
- Hand Placement: I take one of my hands, making it into a fist and placing it roughly an inch above the person’s outer right side of the belly button, which is the correct location since the pressure would not be too much for the ribs and organs.
- Thrusting Action: For the record of my second hand, I grasp my fist and to do the motions of the procedure I begin making rapid upward thrusts to the abdomen. Such kind of motion works on the diaphragm and increases pressure in the chest which increases the expulsion of that object in the airway.
- Monitoring Response: Every time I make my thrusts I always take time to note the response of the individual I am performing the procedure on. Sometimes, clearing the airway takes a couple of thumping attempts; therefore, I try to concentrate on low relief cough or the sound of breathing.
When to Call a Doctor in Choking Situations
I would like to explain that breaking the rules and calling a doctor are absolutely necessary during a choking event. Defining these parameters can help you gauge the seriousness of the situation and decide on the best possible course of action:- Inability to Cough, Speak, or Breathe: In case the person cannot cough which in turn means that they cannot talk or breathe it becomes imperative that a doctor is contacted without delay. In most instances these are the final signs which imply that the person is totally unable to breathe and therefore urgent medical attention is needed.
- Loss of Consciousness: For instance, it is worth noting that if the individual facing a choking incident fails to regain consciousness, then there is a compelling reason to reach out to emergency medical staff CNA Healthcare - motivic.com. Lack of oxygen denotes that the person is incapable to provide sufficient brain oxygen hence healthcare practitioners must assist.
- Persistent Difficulty After Intervention: If within the first few minutes of the incident where, a person bites an object, means or applies X force using their air passage system, the person is able to get rid of the object, then they may be a little disoriented. However, this should not stop others from assisting the person who is reportedly in distress. Choking may explain the lack of coordination and amelioration of haziness. Nonetheless, a doctor’s intervention is required even after the resolution.
- Recurring Choking Episodes: In case the swallowing or the rapid inhalation of food particles is a repeated occurrence then such an incident may suggest an underlying issue, problem or an illness. In such cases it is better to seek medical attention to avoid the chances of it happening again.
- Secondary Complications: In addition to this it is essential to flag any secondary issues that arise following an episode since these can be signs of an ailment or an injury that require further examination. If post the episode there is chest pain or a trouble in speaking then medical recommendation must be sought post the event.
Understanding Dysphagia: More Than Just Swallowing Issues
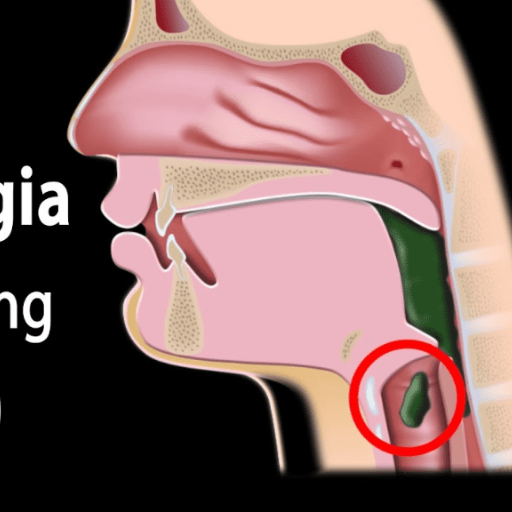 I would like to clarify the meaning of dysphagia before answering the questions related to it. Dysphagia appears to be a swallowing-related issue, but in a real sense, it is a lot more than that, as it affects the whole sequence of transferring food and liquids from the oral cavity to the stomach that is passing through the esophagus. This is the pertinent information that you need to know:
I would like to clarify the meaning of dysphagia before answering the questions related to it. Dysphagia appears to be a swallowing-related issue, but in a real sense, it is a lot more than that, as it affects the whole sequence of transferring food and liquids from the oral cavity to the stomach that is passing through the esophagus. This is the pertinent information that you need to know:
- Types of Dysphagia: The two Drepanos belong to the esophagus dysphagia or pharyngealises that masterpharyngeus dysphagiae manifestations, which provides an understanding where food may believe itself to be congested within any of the constrictions present along the tracts of neck and chest and secondly castor and phemopshageel as a clinical expression of the linguae pharynx.
- Causes: There are various types of Swallowing Difficulties due to a number of factors such as, but not limited to Structural Problem, Neurological Diseases, or Harmonic Discomforts.
- Symptoms: Watch out for signs that will assist in confirmation of the disorder such as chewing while providing some food, trouble in swallowing and breathing exercises, oral matter especially fire spilling out the mouth, extreme loss of weight, etc. These are signs and must be observed closely as they can mean a number of things including choking and burning.
- Risks: Feel your esophagus always sort of abusing fluids or stuff that hoods itself outside of the lungs.
- Diagnosis and Evaluation: Expecting the specialists to conduct a number of procedures such as a routine clinical note on a swallowing or vision or from an imaging abnormality pointing towards the diagnosis then performing a routine tonography.
- Treatment: Therapies can be assisted by swallowing specialists, and medicines can be prescribed to achieve muscle relaxation along the tract, allowing you to make swallowing much easier.
Diagnosing Dysphagia in Older Adults
In my professional opinion, detecting dysphagia in geriatric patients requires an individualized perspective, as its etiology and clinical manifestations are numerous and heterogeneous. First of all, the history of swallowing problems, their onset, and the symptoms should be established. A thorough physical assessment emphasizes the evaluation of oral and pharyngeal swallowing and the assessment of any structural abnormalities. Imaging techniques such as videofluoroscopic swallow study (VFSS) or fiberoptic endoscopic evaluation of swallowing (FEES) allow direct visualization of the act of swallowing and, therefore, help in the detection of such breakdown in function. At times,a speech-language pathology referral for a swallow function test is also required. Some blood tests and neurologic assessments could be done to exclude systemic or neuromuscular causes. It is important to highlight that prompt and precise diagnosis is fundamental in order to prepare an individualized plan that will avoid complications such as malnutrition, dehydration, and aspiration pneumonia and, more broadly speaking, will greatly improve the well-being of aged individuals.Long-term Treatments for Swallowing Difficulties
Coming from my experience in the field, I’d like to discuss the therapeutic options available for dysphagia from a first-person perspective. It is imperative to devise a multidisciplinary plan of management guided by the specific diagnosis of dysphagia. Collaborating routinely with trained speech-language pathologists for swallowing rehabilitation exercises is generally fundamental. This means that such specialists create individualized exercise regimes that involve the swallowing muscles so that eating and drinking can be done in a safer and more efficient manner. Changing dietary habits, for example, changing food’s texture and thickness, are also important factors in reducing the likelihood of choking as well as providing optimal nutrition. In some situations, medications might be available for the treatment of associated diseases such as gastroesophageal reflux or esophageal motility. But for more advanced dissolution of surgical options can be considered,d including, e.g., esophageal dilatation or myotomy for removal of membranes or circular constricting muscles of the yard. Monitoring and repeated examinations guarantee the compliance of treatment plans and anticipated requirements for safety of swallowing and people’s life sphere in common are improved.Exploring Old Man Choking Stock Photos and Their Usage
 As one who has been around, I know that the concept of old man choking stock photos has diverse functions with media and educational platforms. Such images help in exemplifying situations in health education curriculum materials, especially those dealing with the need to Understand the situation and Respond to a Choking Emergency. They are also often used in raising awareness about dysphagia or other swallowing problems in old age and thus increase understanding of potential risk factors for at risk people. Commercially these photos are useful in compiling presentation materials for the training of health care personnel so that they can easily identify with the case studies or emergency care that they are doing. Furthermore, in media advertising as well as in print ads, such images can be good in attracting people’s sights because they depict emergencies and the need of the hour in medicine, so the images created in the ads become very relevant to the promoted product or service. Making sure that these photos have ethical applications or are appropriately graphed is necessary to earn legitimacy for the intended communication goal without disrespecting the context.
As one who has been around, I know that the concept of old man choking stock photos has diverse functions with media and educational platforms. Such images help in exemplifying situations in health education curriculum materials, especially those dealing with the need to Understand the situation and Respond to a Choking Emergency. They are also often used in raising awareness about dysphagia or other swallowing problems in old age and thus increase understanding of potential risk factors for at risk people. Commercially these photos are useful in compiling presentation materials for the training of health care personnel so that they can easily identify with the case studies or emergency care that they are doing. Furthermore, in media advertising as well as in print ads, such images can be good in attracting people’s sights because they depict emergencies and the need of the hour in medicine, so the images created in the ads become very relevant to the promoted product or service. Making sure that these photos have ethical applications or are appropriately graphed is necessary to earn legitimacy for the intended communication goal without disrespecting the context.
Where to Find High-Res Pictures and Images
To gain industry expertise in sourcing images, I can help you understand where you can find high-resolution images. There are quite a number of stock photo websites that sell images of diverse subjects, including health and medical ones. One of the most reputable stock photos, Russell includes some websites such as copyright images, Getty images, and Adobe stock, which guarantee the variety and quality of images that meet professional expectations and the instinct to communicate visually. Other options include free websites like Unsplash and Pexels, which have photos that meet high-res standards, though there is lesser variety than paid-for websites. The most important thing is to understand the terms of use on these websites in order to have an understanding of whether the images can be used for that specific purpose, whether commercial, educational, or editorial functions. In these cases, these materials guarantee that you have the most suitable and relevant imagery to effectively promote the message they intend to promote while observing ethical considerations.Understanding Royalty-Free Photos for Stock Photos
I would like to explain to you the notion of royalty-free pictures. The term Royalty-free is associated with a licensing model that allows a user to pay a single fee and use the photo on multiple occasions without paying any fee for every time it is used. It’s a popular choice because it’s flexible. Here are some key parameters to understand:- License Duration: In the case of royalty-free images, the license usually doesn’t expire, allowing you to use the image forever as long as the conditions as stated are followed.
- Usage Flexibility: This model helps you to use the photos in multiple projects and in different areas like websites, advertisements, or educational materials without incurring extra costs. On the other hand, there may still be some restrictions with regard to use in mainstream advertising, so do check the particular license agreement.
- Non-exclusivity: A non-exclusive agreement is what generally facilitates royalty free licenses, implying that several clients can acquire and utilize the same image. This can however be an issue in case the project requires exclusivity as far as the license is concerned, a different type of license will be required.
- Modifications: An instance with exceptions is images that have been purchased under royalty-free conditions, which have a toning so that they can better fit the customer's needs, provided, of course, the image is not used in a manner that violates the licensing platform.
How Images Can Raise Awareness About Choking
grasping how they can be used to create awareness about a disorder such as choking is really very important, that is how pictures can be utilized. Of course, the visual content is fundamental in the following way:- Immediate Recognition:The brain processes photographs faster than it does written text which results in faster recognition of biopes. This comprehension is useful since it enhances the understanding of the risk, and actions required in a given situation during visualization.
- Emotional Engagement: The feeling of anxiety is heightened by witnessing certain photos, like someone who is choking. There’s no doubt that this effect amplifies the urgency of the request and raises people’s interest in a wide range of prevention and response techniques.
- Educational Clarity: Education is aided by images, such as in education materials whereby pictures undertake the meaning where words, again, would simply miss it. Where parts have to be explained visually, such as the Heimlich maneuver, distinctions can be made between oral and visual guides so as to ensure key points are not left out.
- Relatability: Choking in any context is commonly shown in photographs in a more informative way than an episode showing a person’s actual experience. More people across the globe are able to relate to such pictures and thus emphasizing the need for every person to be prepared.
- Cultural Sensitivity and Inclusivity: The inclusion of images of people from different cultures and all the images of people stressing on the fact that choking is a global problem, creates an awareness around the choking hazard and teaches people from all walks of life.
How to Prevent Swallowing Issues in Senior Men
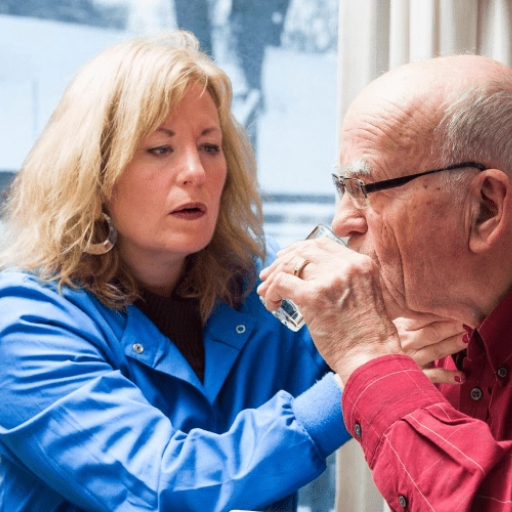 Apart from exercising and keeping up with nutrition, what else can senior men do to avoid the development of difficulties in swallowing, as you have learned from your extensive expertise in this field? Firstly, scheduling regular checkups is one way to address this problem because there may be additional factors at play, including disorders in nutrition. Also, seniors should be helped by relocation of the chew and food to be swallowed. Additionally, it is recommended that exercises be practiced to enhance the strength of the swallowing mechanism, possibly with a speech therapist's advice. Oral health, too, is another instance as many seniors’ poor dental hygiene aggravates dysphagia. Also, it avoids the risk of choking as well as facilitates the reduction of barriers during the process. Finally, such supportive measures will help frail men to optimize their swallowing functions. By bringing these recommended practices alongside, senior men can not only avoid future medical conditions but also relish their lifestyles as they like.
Apart from exercising and keeping up with nutrition, what else can senior men do to avoid the development of difficulties in swallowing, as you have learned from your extensive expertise in this field? Firstly, scheduling regular checkups is one way to address this problem because there may be additional factors at play, including disorders in nutrition. Also, seniors should be helped by relocation of the chew and food to be swallowed. Additionally, it is recommended that exercises be practiced to enhance the strength of the swallowing mechanism, possibly with a speech therapist's advice. Oral health, too, is another instance as many seniors’ poor dental hygiene aggravates dysphagia. Also, it avoids the risk of choking as well as facilitates the reduction of barriers during the process. Finally, such supportive measures will help frail men to optimize their swallowing functions. By bringing these recommended practices alongside, senior men can not only avoid future medical conditions but also relish their lifestyles as they like.
Dietary Adjustments to Ease Swallowing
I will recommend some possible dietary changes that would help ease swallowing challenges, particularly among senior men. To begin with, it is important to place a proper emphasis on texture modifications. It can be greatly beneficial to the patients to alter their diet to include soft and ripe fruits as well as well-cooked vegetables, tender meats, and other foods that can be easily mashed, as they all greatly lessen the problems associated with eating. Smooth textures will eliminate problems; therefore, pureed foods or cream soups and smoothies would also do wonders as well. The importance of fluid intake cannot be emphasized enough; therefore, safe and easy-to-swallow liquids and other semi-liquids should be preferred, and skinny fluids like water should be avoided if they pose a dry swallowing risk. In addition to food consistency, making small bite portions of the food by chopping it assists in minimizing the risk of choking as well. I also suggest checking the heat as some people prefer warmer or cooler items. In general, such specific dietary changes can help avoid risks and enhance eating satisfaction in people with swallowing difficulties.Exercises to Strengthen Swallowing Muscles
A trained industry professional such as myself would incorporate the practice of selected exercises designed to focus on swallowing muscle enhancement, thereby increasing efficiency and safety in the act. One of the most basic exercises is the Mendelsohn Maneuver, where a person lifts their Adam’s apple up for a couple of seconds with the aim of improving his/her swallowing movement coordination. An alternative exercise that appears to be effective to this end is the Shaker Exercise— this involves lying flat and turning the head towards one’s toes. This exercise is purportedly aimed at strengthening neck muscles, which may aid in ingesting food. The Effortful Swallow, which entails swallowing with greater force than normal is also believed to increase muscle power, which may be functional. Tongue Push-Ups— in which one pushes the tongue to the roof of the mouth— are, interestingly, also said to enhance the tongue, which is integral to having a proper swallowing technique. In order to ensure that these exercises are performed correctly and in a safe way, it is advisable to seek guidance from a speech/language pathologist as well as other health practitioners who usually specialize in the rehabilitation of dysphagia.Monitoring Swallowing Health Regularly
With industry experience, routine evaluation of swallowing function is essential in relation to the man’s age, as there might be a risk of severe complications in elderly men. This should include regular clinical follow-ups of the individuals by the so-called “swallowing professionals,” such as speech therapists, who may help in observing any changes or deterioration in the swallowing abilities. Periodic clinical swallow assessments may also give measurable results on the effectiveness and safety of swallowing. Furthermore, the integration of mealtime diaries of the person’s swallowing behaviors or comments on challenges faced during intake would facilitate the identification of trends and the need for changes in the care provided or the diet offered. It is useful to monitor swallowing health since patients and their family members are still able to assist in some cases before choking may actually happen which helps in enhancing swallowing capacity and quality of life.Reference
- Choking on Water: Why Do Elderly Adults Have Difficulty Swallowing - This article discusses reasons for dysphagia and choking in the elderly, including poor oral health, acid reflux, and cognitive issues.
- Nursing Home Residents and Choking Risk - This source covers causes of choking among nursing home residents, such as lack of training, poor supervision, and staffing issues.
- Avoiding Choking Hazards in the Elderly - This document explains why the elderly face greater choking risks, including dry mouth due to aging or medications.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are common choking hazards for babies and toddlers?
A: Common choking hazards for babies and toddlers include foods like whole grapes, hot dogs, popcorn, nuts, and hard candies. Non-food items such as small toys, coins, and buttons can also become a choking hazard. It's important to be aware of these items to prevent choking in young children.Q: How can I make foods safe for my baby or toddler during mealtime?
A: To make foods safe for your baby or toddler, cut foods into small pieces or thin strips. Avoid giving them large pieces that could lodge in their windpipe. For example, cut grapes lengthwise and slice hot dogs into thin strips. Always supervise your little one during mealtime.Q: What should I do if my child starts to gag or choke?
A: If your child starts to gag or choke, stay calm and try to assess if they can cough it out. If they cannot breathe or speak, call emergency services immediately and begin first aid, such as the Heimlich maneuver. Consider taking an infant CPR course to be prepared for choking emergencies.Q: How can baby-led weaning help in reducing the risk of choking?
A: Baby-led weaning can help reduce the risk of choking by allowing babies to explore and regulate their food intake. By offering developmentally appropriate finger foods, babies learn to chew and swallow effectively. Always ensure the foods are baby-safe and monitor your baby closely during meals.Q: At what age can children safely eat foods like nuts and popcorn?
A: Foods like nuts and popcorn should be avoided for children under four years old as they can easily become a choking hazard. It's important to wait until they are developmentally ready and able to eat these foods safely.Q: What precautions should be taken to prevent choking in babies?
A: To prevent choking in babies, always supervise them during meals, cut foods into small, manageable pieces, and avoid giving them hard, round, or sticky foods. Additionally, keep small objects out of reach and ensure toys are age-appropriate and considered safe for your child.Q: What role does the Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC) play in preventing choking hazards?
A: The Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC) helps prevent choking hazards by setting safety standards for toys and other products intended for babies and toddlers. They provide guidelines and recall products that are deemed unsafe to protect children from potential choking hazards.Q: How can I determine if a toy is safe for my young child?
A: To determine if a toy is safe for your young child, check for age recommendations on the packaging and ensure there are no small parts that could become a choking hazard. Additionally, consult CPSC guidelines and choose safe toys that are appropriate for your child's developmental stage.Q: Why is it important to be cautious with foods for babies and kids?
A: Being cautious with foods for babies and kids is crucial because they are still developing their chewing and swallowing skills. Certain foods can easily become a choking hazard, posing a serious risk. Preparing foods safely and educating caregivers on choking prevention can help ensure their safety.1851













 Login with Google
Login with Google Login with Facebook
Login with Facebook